Photographs of
|
|
|
|||||||||

|
Alcazar Segovia
The Alcázar of Segovia (literally, Segovia Castle) is a stone fortification, rising out on a rocky crag above the confluence of the rivers Eresma and Clamores near the Guadarrama mountains.
It is one of the most distinctive castle-palaces in Spain, shaped like the bow of a ship.
The Alcázar of Segovia, like many fortifications in Spain , started off as an Arab fort, which itself was built on a Roman fort but little of that structure remains. It has served as a royal palace, a state prison, a Royal Artillery College and a military academy since Moorish times. |
||||||||
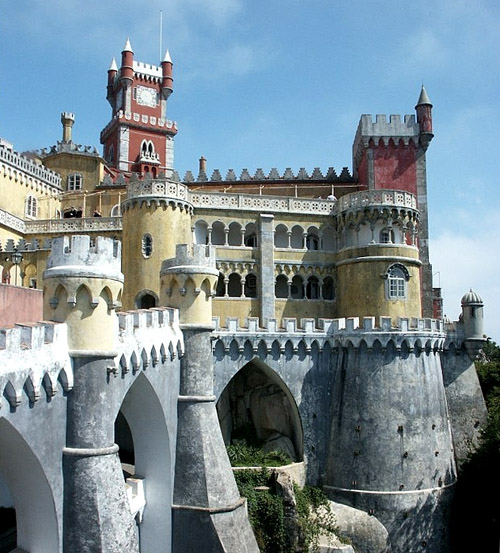 |
Pena Palace Sintra |
||||||||

|
The Peacock Room Castello di Sammezzano Reggello Tuscany |
||||||||
 |
Castello Barletta, Barletta-Andria-Trani Italy |
||||||||
 |
Matsumoto Castle, ("Crow Castle")
Matsumoto Castle is one of Japan's premier historic castles. The keep (tenshukaku), was completed in the late sixteenth century, It is listed as a National Treasure of Japan.
Matsumoto Castle is a flatland castle (hirajiro) built on a plain. Its defences would have included an extensive system of inter-connecting walls, moats, and gatehouses. |
||||||||
 |
Kolossi Castle west of Limassol |
||||||||
 |
|||||||||
 |
Schwerin Castle city of Schwerin Sited on an island in the city's main lake, the Schweriner See |
||||||||
 |
Hampton Court Palace Richmond upon Thames Greater London |
||||||||
 |
Dover Castle Dover, Kent, ENGLAND.
Dover Castle was founded in the 12th century and has been described as the "Key to ENGLAND" due to its defensive significance. It is the largest castle in ENGLAND.
During the reign of Henry II t the castle began to take recognisable shape. The inner and outer baileys and the great keep belong to this time. Maurice the Engineer was responsible for building the keep, one of the last rectangular keeps ever built.
Dover Castle is a Scheduled Monument and a Grade I listed building. The castle, its secret tunnels, and surrounding land are owned by English Heritage and the site is a major tourist attraction.
From the Cinque Ports foundation in 1050, Dover has always been a chief member. The Lord Warden of the Cinque Ports is officially head of the castle, in his conjoint position of Constable of Dover Castle, and the Deputy Constable has his residence in Constable's Gate. |
||||||||

|
Schloss Drachenburg (Drachenburg Castle) Königswinter on the Rhine near Bonn |
||||||||
|
|
The Gravensteen "castle of the count" Sint-Veerleplein Gent |
||||||||
 |
Castle of the Teutonic Order in Malbork, Marienburg (Mary's Castle)
This is the largest castle in the world by surface area, and the largest brick building in Europe. |
||||||||
|
|
Burg Eltz located above the Moselle River between Koblenz and Trier |
||||||||
|
|
|||||||||
 |
Ceiling Cardiff Castle Cardiff |
||||||||
 |
Trakai Island Castle Trakai on an island in Lake Galve
The castle is sometimes referred to as "Little Marienburg". |
||||||||

|
Olavinlinna (St. Olaf's Castle) Savonlinna
This is said to be the northernmost medieval stone fortress in Europe still standing |
||||||||
 |
Schwerin Castle city of Schwerin Sited on an island in the city's main lake, the Schweriner See |
||||||||
 |
Burg Hohenwerfen (Hohenwerfen Castle) above the town of Werfen, Salzach Valley
The castle is surrounded by the Berchtesgaden Alps. The fortification is a "sister" of Hohensalzburg Castle, both dating from the 11th century. A fortification was built here between 1075 and 1078 (during the Imperial Investiture Controversy) by Archbishop Gebhard of Salzburg as a strategic bulwark. He had three major castles extended to secure his archbishopric against the forces of King Henry IV. Gebhard was expelled in 1077 and could not return to Salzburg until 1086, only to die at Hohenwerfen two years later. In the following centuries Hohenwerfen served Salzburg's rulers, the prince-archbishops, as a military base, residence and hunting retreat. The fortress was extended in the 12th century and again in the 16th century during the German Peasants' War. Later it was used as a state prison and like many ecclesiastical prisons developed a particularly sinister reputation.
Hohenwerfen Castle served as the backdrop for the song "Do-Re-Mi" in the film The Sound of Music and as 'Schloss Adler' in the 1968 film Where Eagles Dare. Among the attractions offered by the fortress today are guided tours showing its weapons collection, a falconry museum and a fortress tavern. |
||||||||

|
Donjon de Ve Oise, Picardy,
The Donjon (keep) is part of the Château de Vez.
|
||||||||
|
|
Aljaferia Zaragoza
The Aljafería Palace is a fortified medieval Islamic palace in the Moorish taifa of Zaragoza of Al-Andalus |
||||||||
 |
Bouzov Castle, located between the village of Hvozdek and the town of Bouzov west of Litovel Moravia |
||||||||
 |
Alila Fort Bishangarh near Jaipur Rajasthan |
||||||||
 |
Bahla Fort situated at the foot of the Djebel Akhdar highlands |
||||||||
 |
Caerlaverock Castle on the southern coast of SCOTLAND 11 kilometres south of Dumfries on the edge of the Caerlaverock National Nature Reserve. |
||||||||
 |
Bratislavsky hrad (Bratislava Castle) Bratislava
|
||||||||
 |
Leeds Castle Kent
Leeds Castle is in Kent, ENGLAND, 5 miles (8 km) Southeast of Maidstone. A castle has been on the site since 1119. In the 13th century it came into the hands of King Edward I, for whom it became a favourite residence; in the 16th century, Henry VIII used it as a residence for his first wife, Catherine of Aragon.
The castle was a location for the 1949 film Kind Hearts and Coronets where it stood in for "Chalfont", the ancestral home of the d'Ascoyne family. The castle also appeared in Moonraker (1958) and Waltz of the Toreadors (1962). It was the set for the Doctor Who episode The Androids of Tara.
The castle today dates mostly from the 19th century and is built on islands in a lake formed by the River Len to the east of the village of Leeds. It has been open to the public since 1976 . |
||||||||
 |
Leeds Castle Kent
Leeds Castle is in Kent, ENGLAND, 5 miles (8 km) Southeast of Maidstone. A castle has been on the site since 1119. In the 13th century it came into the hands of King Edward I, for whom it became a favourite residence; in the 16th century, Henry VIII used it as a residence for his first wife, Catherine of Aragon.
The castle was a location for the 1949 film Kind Hearts and Coronets where it stood in for "Chalfont", the ancestral home of the d'Ascoyne family. The castle also appeared in Moonraker (1958) and Waltz of the Toreadors (1962). It was the set for the Doctor Who episode The Androids of Tara.
The castle today dates mostly from the 19th century and is built on islands in a lake formed by the River Len to the east of the village of Leeds. It has been open to the public since 1976 |
||||||||
 |
Castel Sant Angelo (The Mausoleum of Hadrian) Parco Adriano Rome |
||||||||
 |
The Château de Brissac Brissac-Quincé Maine-et-Loire |
||||||||
 |
Castel del Monte (Castle of the Mount), Andria, Apulia region
Castel del Monte is a 13th-century citadel and castle. It stands on a promontory, where it was constructed during the 1240s by the Emperor Frederick II, who had inherited the lands from his mother, Constance of Sicily.
It has neither a moat nor a drawbridge leading some to conclude that it was never intended as a defensive fortress; On the other hand, archaeological work has suggested that it originally had a curtain wall, so what we see today was just the keep of the original structure.
It is a World Heritage Site, and appears on the Italian version of the one-cent euro coin. |
||||||||
 |
Schloss Moritzburg (Castle Moritzburg) Schloßallee, 01468 Moritzburg, Saxony,
Moritzburg Castle is a Baroque palace in Moritzburg, in the German state of Saxony, about 13 kilometres (8.1 mi) Northwest of Dresden.
The castle is named after Duke Moritz of Saxony, who had a hunting lodge built here between 1542 and 1546. Schlösser |
||||||||
 |
Gammel Estrup (Gammel Estrup Manor) east of Randers City
Gammel Estrup Manor was built in 1490, but excavations have revealed evidence of earlier constructions also mentioned in texts under the name Essendrup dating back to 1340.
From 1930 the manor has served as a museum, showing the development of Danish nobility. |
||||||||
|
|
|||||||||
 |
Schloss Glücksburg (Lyksborg Slot or Glücksburg Castle) Glücksburg
Glücksburg Castle is one of the most important Renaissance castles in northern Europe.
It is the seat of the House of Schleswig-Holstein-Sonderburg-Glücksburg and was also used by the Danish kings.
Situated on the Flensburg Fjord the castle is now a museum owned by a foundation. |
||||||||
 |
Kasteel van Laarne (Laarne Castle) Laarne, East Flanders
Laarne Castle is a moated castle, established in the 11th or 12th century to guard the approaches to Ghent from the sea, it was comprehensively renovated in the 17th century.
Since 1953 the castle has belonged to the Koninklijke Vereniging der Historische Woonsteden en Tuinen van België ("The Royal Association of Historical Houses and Gardens in Belgium"), to whom it was given by the last private owner, the Comte de Ribaucourt. It is a protected national monument and is now used as a museum. |
||||||||
 |
Akashi Castle Akashi Hyogo Prefecture |
||||||||

|
The Alcázar of Segovia (Segovia Castle) Segovia |
||||||||
 |
The Aljafería Palace Zaragoza |
||||||||

|
Altena Castle Altena |
||||||||
 |
Amer Fort Amer Rajasthan |
||||||||

|
Kasteel Ammersoyen Kasteellaan Ammerzoden |
||||||||
 |
Arg-e-Bam (Bam Citadel) Bam Kerman Province |
||||||||

|
Azuchi Castle [reconstruction of the keep] on the shores of Lake Biwa Omi Province |
||||||||

|
The Castle of Bardi (or Landi) Upper Ceno Valley Parma Emilia-Romagna |
||||||||
 |
Fort de Bellegarde Le Perthus Pyrénées-Orientales |
||||||||

|
Bellver Castle Northwest of Palma Majorca Balearic Islands |
||||||||
 |
Château de Belœil Belœil Hainaut |
||||||||
 |
|||||||||

|
Château de Blandy-les-Tors Blandy-les-Tours, Seine-et-Marne,
The Château de Blandy-les-Tours was mentioned in a text in 1216. It belonged to Adam II de Chailly, Viscount of Melun. It consisted of a simple manor and chapel, the only construction made of stone. The site was previously a Merovingian necropolis.
In the 14th century, the castle was strongly modified with new fortifications and structures of defence. A moat was dug and a new gate-tower with a drawbridge was included in the enclosing wall. |
||||||||
 |
Bodiam Castle, East Sussex,
Bodiam Castle is a 14th-century moated castle. It was built in 1385 by Sir Edward Dalyngrigge, a former knight of Edward III, with the permission of Richard II, to defend the area against French invasion during the Hundred Years' War.
Bodiam Castle has a quadrangular plan. It has no keep, having its various chambers built around the outer defensive walls and inner courts. The corners and entrance are marked by towers, topped by crenellations.
It was the home of the Dalyngrigge family and the centre of the manor of Bodiam. The castle is protected as a Grade I listed building and Scheduled Monument. It has been owned by The National Trust since 1925, when it was donated by Lord Curzon on his death. It is open to the public. |
||||||||

|
Bodiam Castle, East Sussex,
Bodiam Castle is a 14th-century moated castle. It was built in 1385 by Sir Edward Dalyngrigge, a former knight of Edward III, with the permission of Richard II, to defend the area against French invasion during the Hundred Years' War.
Bodiam Castle has a quadrangular plan. It has no keep, having its various chambers built around the outer defensive walls and inner courts. The corners and entrance are marked by towers, topped by crenellations.
It was the home of the Dalyngrigge family and the centre of the manor of Bodiam. The castle is protected as a Grade I listed building and Scheduled Monument. It has been owned by The National Trust since 1925, when it was donated by Lord Curzon on his death. It is open to the public. |
||||||||
 |
Schloss Braunfels, |
||||||||
 |
Carondelet Castle |
||||||||
 |
Kasteel de Haar (Castle De Haar) near Haarzuilens Province of Utrecht |
||||||||
 |
Château de Chillon Veytaux, Montreux
The Château de Chillon (Chillon Castle) is an island castle located on the shore of Lake Geneva in the commune of Veytaux, at the eastern end of the lake, 3 km from Montreux
The first written record of the castle date to 1160. From the mid 12th century, the castle was home to the Counts of Savoy.
The Château de Chillon was made popular by Lord Byron, who wrote the poem The Prisoner Of Chillon; Byron also carved his name on a pillar of the dungeon.
The castle is also one of the settings in Henry James's novella Daisy Miller (1878). |
||||||||
 |
Château de Vufflens (Vufflens Castle) Vufflens-le-Château, Vaud,
A castle was built here in 1425 by Henri de Colombier on the site of a previous medieval castle. Of Henri Colombier's structure, the donjon, several towers, outbuildings, curtain wall and the gate-house survive.
In 1641 it was acquired by the de Senarclens family. .
Today the castle is a Swiss heritage site of national significance. It is currently privately owned and cannot be visited by the general public.
|
||||||||
 |
Bojnický Zámok (Bojnice Castle) Bojnice |
||||||||
 |
Vianden Castle Vianden
Vianden Castle (French: Château de Vianden, German: Burg Vianden Luxembourgish: Buerg Veianen), is located in Vianden, in the north of Luxembourg.
Vianden is one of the largest fortified castles west of the Rhine. Its origins date to the 10th century. The castle was built in the Romanesque style between the 11th and 14th centuries. Gothic aspects were added at the end of this period.
A Renaissance mansion was added in the 17th century. After the seventeenth century the castle was allowed to fall into ruin, and has recently been restored.
It is now open to visitors. |
||||||||
 |
Schloß Naudersberg (Naudersberg Castle) Nauders Tirol |
||||||||
 |
Château de Suscinio (or de Susinio) Sarzeau, Morbihan, Brittany,
Built in the late Middle Ages as the residence of the Dukes of Brittany.
The Château de Suscinio dates from the beginning of the 13th century. It was enlarged at the end of 14th century, when the heirs of the duchy were fighting to keep their possessions (Brittany was not annexed by France until 1514).
From 1471 to 1483, the castle was home to Jasper Tudor, Henry Tudor (later King Henry VII of ENGLAND), and the core of their group of exiled Lancastrians, numbering about 500 by 1483. Duke Francis II supported this group of exiles against Plantagenet demands for their surrender. |
||||||||
 |
Trakošcan Castle Varaždin County Northern CROATIA |
||||||||
 |
Hawa Mahal (Hawa Palace) Jaipur Rajasthan |
||||||||
 |
Schloss Hohenzollern (Hohenzollern Castle) 72379 Burg Hohenzollern, GERMANY
Hohenzollern Castle is the ancestral seat of the Hohenzollern family, who became German Emperors
A castle was first constructed here in the early 11th century. The present castle was constructed for King Frederick William IV of Prussia between 1846 and 1867. The design was based on English Gothic Revival architecture and the Châteaux of the Loire Valley.
In 1945 it became home to the former Crown Prince Wilhelm of GERMANY, son of the last Hohenzollern monarch, Kaiser Wilhelm II, who is buried there with his wife, Crown Princess Cecilie |
||||||||
 |
Burg Kriebstein (Kriebstein Castle) Kriebstein near Waldheim Saxony |
||||||||
 |
Parterre The Château de Villandry Villandry Indre-et-Loire |
||||||||
 |
The Château d'Ussé Rigny-Ussé Indre-et-Loire |
||||||||
 |
Falak-ol-Aflak Castle within the city of Khorramabad Lorestan Province |
||||||||
 |
Khiva City Walls Xorazm Province |
||||||||
|
|||||||||
 |
Burg Vischering (Vischering Castle) Lüdinghausen North Rhine-Westfalia |
||||||||
 |
Castle Stalker on a tidal islet on Loch Laich, an inlet off Loch Linnhe |
||||||||
 |
Spøttrup Borg Spøttrup |
||||||||
 |
Rocca Sanvitale (Sanvitale Castle) Fontanellato near Parma |
||||||||
 |
Mont Saint-Michel located one kilometre off the northwestern coast at the mouth of the Couesnon River near Avranches Normandy |
||||||||
 |
Traku salos pilis (Trakai Island Castle) Trakai (on an island in Lake Galve) |
||||||||
 |
Château de Sully-sur-Loire Sully-sur-Loire Loiret |
||||||||
 |
Torre de Belém (Belém Tower or the Tower of St Vincent) Santa Maria de Belém Lisbon |
||||||||
 |
Coca Castle Coca Segovia Castile-Leon |
||||||||
 |
Château de Castelnau-Bretenoux Prudhomat, Lot, Quercy
Construction began about 1100, under Hugues, baron of Castelnau, who built a wall around his manor. He was the ancestor of the powerful dynasty of Castelnau, who owned a rich and prosperous region and were vassals of the Counts of Toulouse. |
||||||||
 |
Spiral staircase The Royal Château de Chambord Chambord, Loir-et-Cher, FRANCE
The building, which was never completed, was constructed by King Francis I of France. The royal Château de Chambord is one of the most recognizable châteaux in the world because of its distinctive French Renaissance architecture which blends traditional French medieval forms with classical Renaissance structures.
Chambord was built to serve as a hunting lodge for Francis I, who maintained royal residences at the châteaux of Blois and Amboise. |
||||||||
 |
Château de Chenonceau Chenonceau, Indre-et-Loire
The estate of Chenonceau is first mentioned in writing in the 11th century. The current château was built in 1514–1522 on the foundations of an old mill and was later extended to span the river.
The bridge over the river was built (1556-1559) to designs by the French Renaissance architect Philibert de l'Orme, and the gallery on the bridge (1570–1576) to designs by Jean Bullant
The château has been classified as a Monument historique since 1840 by the French Ministry of Culture. It is one of the most famous Loire Valley châteaux. |
||||||||
 |
Château de Chenonceau Chenonceau, Indre-et-Loire
The estate of Chenonceau is first mentioned in writing in the 11th century. The current château was built in 1514–1522 on the foundations of an old mill and was later extended to span the river.
The bridge over the river was built (1556-1559) to designs by the French Renaissance architect Philibert de l'Orme, and the gallery on the bridge (1570–1576) to designs by Jean Bullant
The château has been classified as a Monument historique since 1840 by the French Ministry of Culture. It is one of the most famous Loire Valley châteaux. |
||||||||
![Castel dell'Ovo ["Egg castle"], Via Eldorado, 3, 80132 Napoli, Italy - www.castlesandmanorhouses.com Castel dell'Ovo ["Egg castle"], Via Eldorado, 3, 80132 Napoli, Italy - www.castlesandmanorhouses.com](photos/dell_ovo_01.jpg) |
Castel dell'Ovo ["Egg castle"], Via Eldorado, 3 80132 Naples, ITALY
Castel dell'Ovo is located on the former island of Megaride, now a peninsula, in the gulf of Naples. |
||||||||
 |
Château du Fayel Fayel Oise |
||||||||
 |
Château de Vincennes Avenue de Paris 94300 Vincennes, Val-de-Marne
The Château de Vincennes is a massive 14th and 17th century French royal castle now a suburb of the metropolis.
This donjon, 52 meters high, was the tallest medieval fortified structure of Europe. |
||||||||
 |
The Citadel of Rostov Yaroslavl Oblast |
||||||||
 |
Mamure kalesi (Mamure Castle) Anamur District Mersin Province |
||||||||
 |
Château de Tanlay Tanlay Yonne Burgundy |
||||||||
 |
The Château de Trécesson near the Paimpont forest Campénéac Morbihan Brittany |
||||||||
 |
Borgholms slott (Borgholm Castle) Borgholm
Borgholm Castle is the ruin of a fortress first built in the second half of the 12th century and rebuilt many times in later centuries. |
||||||||
 |
Château de Chenonceau Chenonceau, Indre-et-Loire
The estate of Chenonceau is first mentioned in writing in the 11th century. The current château was built in 1514–1522 on the foundations of an old mill and was later extended to span the river.
The bridge over the river was built (1556-1559) to designs by the French Renaissance architect Philibert de l'Orme, and the gallery on the bridge (1570–1576) to designs by Jean Bullant
The château has been classified as a Monument historique since 1840 by the French Ministry of Culture. It is one of the most famous Loire Valley châteaux. |
||||||||
 |
Kasteel Ammersoyen (Ammerzoden Castle) Maasdriel Gelderland |
||||||||
 |
Château de Vaux-le-Vicomte Maincy near Melun Seine-et-Marne |
||||||||
 |
Hrad Ceský Šternberk (Ceský Šternberk Castle) Ceský Šternberk Central Bohemian Region |
||||||||
 |
|||||||||
 |
Château de La Motte-Tilly 10400 La Motte-Tilly Aube
|
||||||||
 |
Schloss Braunfels (Braunfels caste) Lahn-Dill-Kreis Gießen, Hesse |
||||||||
 |
Ribat Castle Sousse Sousse |
||||||||
 |
Kasteel de Borrekens (Borrkens Castle, known also as Vorselaar Castle) Vorselaar Antwerp |
||||||||
|
|
|||||||||
 |
Castello DI Padernello (Padernello Castle) Padernello (near San Giacomo) Brescia |
||||||||
 |
Corvin Castle, also known as Corvins' Castle, Hunyad Castle or Hunedoara Castle [Castelul Huniazilor or Castelul Corvinilor (Romanian)] [Vajdahunyad vára (Hungarian)] Hunedoara Transylvania
|
||||||||
 |
Bozcaada Castle formerly known as Tenedos Bozcaada Bozcaada district Çanakkale province
Bozcaada Castle is one of the best preserved castles of Turkey |
||||||||
 |
Schloss Lichtenstein (Lichtenstein Castle) near Honau Swabian Alb Baden-Württemberg |
||||||||
 |
Schloss Schönbühel (Schoenbuhel Castle) Schönbühel-Aggsbach below Melk on the right bank of the Danube |
||||||||
![Castelo de São Jorge (Castle of São Jorge [Saint George]) Lisbon, Portugal - www.castlesandmanorhouses.com Castelo de São Jorge (Castle of São Jorge [Saint George]) Lisbon, Portugal - www.castlesandmanorhouses.com](photos/sao_jorge_01.jpg) |
Castelo de São Jorge (Castle of São Jorge [Saint George]) Lisbon
Castle of Saint George is a Moorish castle occupying a commanding hilltop overlooking the historic centre Lisbon. |
||||||||
 |
Boyabat castle Boyabat Boyabat district Sinop Province Black Sea region |
||||||||
 |
Bobolice Castle Bobolice Myszków County Silesian Voivodeship
Bobolice Castle is a royal castle built in the middle of the 14th century in the Polish Jura |
||||||||
![Trencín Castle, [Trenciansky hrad (Slovak) trencséni vá, (Hungarian)], Trencín, western Slovakia. - www.castlesandmanorhouses.com Trencín Castle, [Trenciansky hrad (Slovak) trencséni vá, (Hungarian)], Trencín, western Slovakia. - www.castlesandmanorhouses.com](photos/trenciansky_01.jpg) |
Trencín Castle [Trenciansky hrad (Slovak) trencséni vá, (Hungarian)] Trencín western SLOVAKIA |
||||||||
 |
Hrad Karlštejn (Karlštejn Castle) Karlštejn 172, 267 18 Karlštejn Central Bohemia |
||||||||
 |
Peacock Room Castello DI Sammezzano Reggello Tuscany |
||||||||
 |
Château Frontenac 1 Rue Des Carrières Québec QC G1R 4P5
Château Frontenac is a grand hotel operated as Fairmont Le Château Frontenac. It was designated a National Historic Site of Canada in 1980. |
||||||||
 |
Burg Satzvey (Satzvey Castle) An der Burg 3, 53894 Mechernich Nordrhein-Westfalen |
||||||||
 |
Medieval walled cité of Provins Provins Seine-et-Marne Île-de-France
Provins, a town of medieval fairs, became a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2001 |
||||||||
 |
Castello Mafredonico (Chiaramonte Castle) Mussomeli province of Caltanissetta Sicily |
||||||||
 |
Schloss Oberhofen (Oberhofen Castle) Oberhofen Canton of Bern |
||||||||
 |
Culzean Castle Maybole KA19 8LE Carrick Ayrshire
Culzean Castle is the former home of the Marquess of Ailsa, the chief of Clan Kennedy, but is now owned by the National Trust for Scotland. |
||||||||
![The Punakha Dzong or Pungtang Dechen Photrang Dzong [the palace of bliss], Punakha, Bhutan. - www.castlesandmanorhouses.com The Punakha Dzong or Pungtang Dechen Photrang Dzong [the palace of bliss], Punakha, Bhutan. - www.castlesandmanorhouses.com](photos/punakha.jpg) |
The Punakha Dzong or Pungtang Dechen Photrang Dzong [the palace of bliss] Punakha Bhutan |
||||||||
 |
Burg Stein (Stein Castle) Stein 1, 08118 Hartenstein Hartenstein Saxony |
||||||||
 |
Château de Farcheville commune of Bouville Essonne |
||||||||
 |
Ceiling Castello DI Sammezzano Reggello Tuscany |
||||||||
 |
Reinhardstein Castle [Château de Reinhardstein (French)] [Burg Reinhardstein (German)] Ovifat Waimes (Weismes) province of Liège |
||||||||
 |
Le château de Vêves (Vêves Castle) outside the village of Celles province of Namur
The Castle of Vêves is classified as Major Heritage of Wallonia. |
||||||||
 |
Schloss Bürresheim, (Bürresheim Castle) 56727 Mayen Rhineland-Palatinate |
||||||||
 |
Schloss Bürresheim, (Bürresheim Castle) 56727 Mayen Rhineland-Palatinate |
||||||||
 |
Gyeongbokgung (Gyeongbokgung Palace or Gyeongbok Palace) Jongno-gu Seoul
Gyeongbokgung was a royal palace |
||||||||
 |
Wasserschloß Glatt Schloß 1, 72172 Sulz am Neckar Rottweil Baden-Württemberg
|
||||||||
 |
Burg Kreuzenstein (Kreuzenstein castle) 2100 Leobendorf bei Korneuburg near Leobendorf |
||||||||
 |
Burg Pfalzgrafenstein (Pfalzgrafenstein Castle) Falkenau island, in the Rhine river near Kaub
Pfalzgrafenstein is a toll castle on the Falkenau island, otherwise known as Pfalz Island. |
||||||||
 |
Schloss Braunfels (Braunfels castle) Belzgasse 1, 35619 Braunfels Lahn-Dill-Kreis Hesse |
||||||||
 |
|||||||||
 |
Mont Saint-Michel 50170 Le Mont-Saint-Michel Normandy
Mont Saint-Michel is an island commune approximately one kilometre off France's northwestern coast, at the mouth of the Couesnon River near Avranches. |
||||||||
 |
Coca Castle Coca Segovia Castile-Leon |
||||||||
 |
Aughnanure Castle, County Galway, Ireland
Aughnanure is one of over 200 tower houses in County Galway, constructed mainly by Gaelic and Anglo-Norman land owning families. The tower lies close to the shores of Lough Corrib
|
||||||||
 |
Dunguaire Castle, County Galway, Ireland
Dunguaire Castle is a 16th-century tower house on the southeastern shore of Galway Bay, near Kinvarra.
The name derives from the Dun of King Guaire, the legendary king of Connacht.
The castle's 75-foot tower and its defensive wall have been restored, and the grounds are open to tourists during the summer. |
||||||||
 |
Dunster Castle, Dunster, Somerset, ENGLAND
Dunster Castle is a former motte and bailey castle, now a country house. The castle lies on the top of a steep hill called the Tor, and has been fortified since the late Anglo-Saxon period. After the Norman conquest William de Mohun constructed a timber castle on the site as part of the pacification of Somerset. A stone shell keep was built on the motte by the start of the 12th century. At the end of the 14th century the de Mohuns sold the castle to the Luttrell family, who continued to occupy the property until the late 20th century.
In the 1860s and 1870s, the architect Anthony Salvin was employed to remodel the castle to fit Victorian tastes; this work extensively changed the appearance of Dunster to make it appear more Gothic and Picturesque.
Following the death of Alexander Luttrell in 1944, the castle and surrounding lands were sold off to a property firm. The Luttrells bought back the castle in 1954, but in 1976 Colonel Walter Luttrell gave Dunster Castle and most of its contents to the National Trust, which operates it as a tourist attraction. It is a Grade I listed building and scheduled monument. |
||||||||
 |
Chor Minor Khodja Nurobobod St, Bukhara |
||||||||
 |
Saladin Citadel Cairo,
The Saladin Citadel is a medieval Islamic fortification, on Mokattam hill near the center of Cairo. |
||||||||
 |
The Palacio Real (Royal Palace)
The Palacio Real de Madrid is the official residence of the Spanish Royal Family in Madrid, but is only used for state ceremonies.
A foreign ambassador arrives at the Royal Palace to deliver his diplomatic credentials to the King |
||||||||
 |
Fortress of Guaita
Guaita is one of three peaks which overlooks the city of San Marino, the capital of San Marino.
The Guaita fortress is the oldest of the three towers constructed on Monte Titano. It was built in the 11th century. |
||||||||
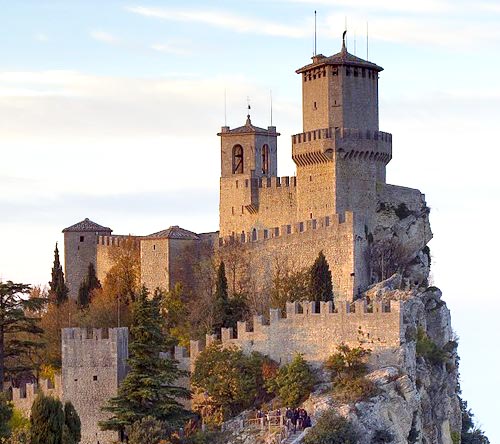 |
Fortress of Guaita
Guaita is one of three peaks which overlooks the city of San Marino, the capital of San Marino.
The Guaita fortress is the oldest of the three towers constructed on Monte Titano. It was built in the 11th century |
||||||||
 |
Derawar Fort Cholistan Desert
Derawar Fort is a large square fortress near Bahawalpur.
The forty bastions of Derawar are visible for many miles around in Cholistan Desert. The walls have a circumference of 1500 metres and stand up to thirty metres high.
The first fort on the site was built by Hindu Rajput, Rai Jajja Bhati of Jaisalmer. It remained in the hands of the royal family of Jaisalmer until captured by the Nawabs of Bahawalpur in 1733. In 1747, the fort was lost but, Nawab Mubarak Khan took the stronghold back in 1804. |
||||||||
 |
Rohtas Fort Punjab
Rohtas Fort is a historical garrison fort located near the city of Jhelum in Punjab.
It was built by the Afghan king Sher Shah Suri in 16th century to subdue the rebellious tribes of the northern Punjab region, .
This fort is about 4 km in circumference and is UNESCO World Heritage Site |
||||||||
 |
Fortress of Guaita
Guaita is one of three peaks which overlooks the city of San Marino, the capital of San Marino.
The Guaita fortress is the oldest of the three towers constructed on Monte Titano. It was built in the 11th century |
||||||||
 |
Oravský Hrad, located above the Orava river in the village of Oravský Podzámok, SLOVAKIA.
In Eglish it is called Orava Castle, in German Arwaburg and in Hungarian: Árva vára)
Orava Castle stands on the site of an old wooden fortification, built after the Mongol invasion of Hungary of 1241.The later design was in Romanesque and Gothic style. Later still it was reconstructed as a Renaissance and Neo-Gothic structure,.
Many scenes of the 1922 film Nosferatu were filmed here. After a period of dilapidation the castle became a national monument after World War II,. |
||||||||
 |
Predjama Castle, Predjama, Inner Carniola, Slovenia
It is a Renaissance castle built within a cave mouth |
||||||||
 |
Trakoscan Varaždin County
Trakošcan dates back to the 13th century.
|
||||||||
 |
Nehaj Fortress Senj
The Nehaj Fortress is located on a hill called Nehaj. |
||||||||
 |
Swallow's Nest Crimean peninsula southern UKRAINE
The Swallow's Nest is a decorative castle located between Yalta and Alupka.
It was built between 1911 and 1912 in Gaspra, on top of the Aurora Cliff, to a Neo-Gothic design by the Russian architect Leonid Sherwood.
The castle overlooks the Cape of Ai-Todor on the Black Sea coast and is located near the remains of the Roman castrum of Charax.
The Swallow's Nest is one of the most popular visitor attractions in the Crimea, and has become a well known symbol of the Crimea's southern coastline. |
||||||||
 |
Vaduz Castle (German Schloß Vaduz) Vaduz
Vaduz Castle is the palace and official residence of the Prince of Liechtenstein.
The castle gave its name to the town of Vaduz, the capital of Liechtenstein, which it overlooks from an adjacent hilltop. |
||||||||
 |
Vaduz Castle (German Schloß Vaduz) Vaduz
Vaduz Castle is the palace and official residence of the Prince of Liechtenstein.
This is the rear view. |
||||||||
 |
East Gate, Ancient City of Fenghuang |
||||||||
 |
Swallow's Nest Crimean peninsula southern UKRAINE
The Swallow's Nest is a decorative castle located between Yalta and Alupka.
It was built between 1911 and 1912 in Gaspra, on top of the Aurora Cliff, to a Neo-Gothic design by the Russian architect Leonid Sherwood.
The castle overlooks the Cape of Ai-Todor on the Black Sea coast and is located near the remains of the Roman castrum of Charax.
The Swallow's Nest is one of the most popular visitor attractions in the Crimea, and has become a well known symbol of the Crimea's southern coastline. |
||||||||
 |
Spišský Castle Spiš, SLOVAKIA
The ruins of Spiš Castle form one of the largest castle sites in Central Europe.
It was included in the UNESCO list of World Heritage Sites in 1993 |
||||||||
 |
Schloss Hohenzollern (Hohenzollern Castle) 72379 Burg Hohenzollern, GERMANY
Hohenzollern Castle is the ancestral seat of the Hohenzollern family, who became German Emperors
A castle was first constructed here in the early 11th century. The present castle was constructed for King Frederick William IV of Prussia between 1846 and 1867. The design was based on English Gothic Revival architecture and the Châteaux of the Loire Valley.
In 1945 it became home to the former Crown Prince Wilhelm of GERMANY, son of the last Hohenzollern monarch, Kaiser Wilhelm II, who is buried there with his wife, Crown Princess Cecilie |
||||||||
|
|
|||||||||
 |
Castle Rising, Castle Rising, Norfolk, ENGLAND.
Castle Rising is a ruined medieval fortification built soon after 1138 by William d'Aubigny II, who had risen through the ranks of the Anglo-Norman nobility to become the Earl of Arundel.
It was inherited by William's descendants before passing into the hands of the de Montalt family in 1243. The Montalts later sold the castle to Queen Isabella, who lived there after her fall from power in 1330. Isabella extended the castle buildings and enjoyed a regal lifestyle, entertaining her son, Edward III on several occasions. After her death, it was granted to Edward, the Black Prince, to form part of the Duchy of Cornwall. It was later aqcired by the Howard family.
English Heritage took over control of the castle in 1983 and continued to operate it as a tourist attraction. The castle is protected by UK law as an ancient monument and a grade I listed building. It remains in the custody of English Heritage, but since 1998 has been managed by its owner, Baron Howard of Rising. |
||||||||
 |
Château de Peyrelade Rivière-sur-Tarn, Aveyron
A castle existed here at least as far back as the 12th century. It was the scene of incessant battles and sieges until 1633 when it was dismantled on the orders of Cardinal Richelieu. Thanks to its position controlling the entrance to the Gorges du Tarn, it was one of the most important castles in the Rouergue province
The name is derived from the occitan "Pèira Lada", meaning wide rock
Objects found on the site suggest it was inhabited in prehistoric times.
|
||||||||
 |
Schloss Augustusburg, Parkplatz, Max-Ernst-Allee, 50321 Brühl, GERMANY
The Augustusburg and Falkenlust palaces constitute an historical building complex in Brühl, North Rhine-Westphalia, GERMANY, which have been listed as a UNESCO cultural World Heritage Site since 1984.
The palaces were built at the beginning of the 18th century by the Archbishop-Elector of Cologne, Clemens August of Bavaria of the Wittelsbach family. |
||||||||
 |
Citadel of Salah Ed-Din. Saône or Saladin Castle, Al-Haffah, Latakia Governorate
the site has been fortified since at least the mid 10th century. In 975 the Byzantine Emperor John I Tzimiskes captured the site and it remained under Byzantine control until around 1108.
Early in the 12th century crusaders assumed control of the site and it became part of the newly formed Principality of Antioch. The Crusaders undertook an extensive building programme, giving the castle much of its current appearance.
In 1188 it fell to the forces of Saladin after a three-day siege.
In 2006, the castles of Qal'at Salah El-Din and Krak Des Chevaliers were together recognised as a World Heritage Site by UNESCO. |
||||||||
 |
Schloss Bottmingen Schlossgasse, 4103 Bottmingen, Basel-Land, SWITZERLAND
It is a Swiss heritage site of national significance
|
||||||||
 |
Vianden Castle Vianden
Vianden Castle (French: Château de Vianden, German: Burg Vianden Luxembourgish: Buerg Veianen), is located in Vianden, in the north of Luxembourg.
Vianden is one of the largest fortified castles west of the Rhine. Its origins date to the 10th century. The castle was built in the Romanesque style between the 11th and 14th centuries. Gothic aspects were added at the end of this period.
A Renaissance mansion was added in the 17th century. After the seventeenth century the castle was allowed to fall into ruin, and has recently been restored.
It is now open to visitors. |
||||||||
 |
Château de Gaillo Gaillon, Haute-Normandie
The Château de Gaillon is a renaissance castle, begun in 1502 on ancient foundations. |
||||||||
 |
Château de Virieu, 38730 Virieu, Isère
Le château de Virieu was built in stone around 1010,
It is classified as a French monument historique in 1990. |
||||||||
 |
Château de Sercy Sercy, Saône-et-Loire, Bourgogne
The Château de Sercy is a XII century castle modified in the XVI century.
It is classed as a French monument historique. |
||||||||
 |
Schloss Moritzburg (Castle Moritzburg), Schloßallee, 01468 Moritzburg, Saxony, GERMANY
Moritzburg Castle is a Baroque palace in Moritzburg, in the German state of Saxony, about 13 kilometres (8.1 MI) Northwest of Dresden.
The castle is named after Duke Moritz of Saxony, who had a hunting lodge built here between 1542 and 1546. |
||||||||
 |
Schloss Altdöbern, Altdöbern, Brandebourg, GERMANY |
||||||||
 |
Schloss Bottmingen Schlossgasse, 4103 Bottmingen, Basel-Land, SWITZERLAND
It is a Swiss heritage site of national significance |
||||||||
 |
Schloss Burgsteinfurt, Steinfurt, Münster,
North Rhine-Westphalia, GERMANY |
||||||||
 |
Château de Val, Les Fontilles 15270 Lanobre, Cantal
The Château is located on the shore of the Lake Bort-les-Orgues
It is classé as a Monument historique |
||||||||
 |
Helfstyn Castle Lipník nad Becvou, Prerov, Olomouc, CZECH REPUBLIC
The ruins of the castle are perched on a knoll above the narrowest part of the Moravian Gate and above the left bank of the river Becva.
The complex is 187 meters long and up to 152 meters wide. It is one of the largest castles in terms of area in the Czech Republic. |
||||||||
 |
Moszna Castle Moszna, POLAND
The castle is one of the best known monuments in the western part of Upper Silesia. |
||||||||
 |
Superior garden shed, |
||||||||
 |
Hever Castle, Hever, Edenbridge, Kent TN8 7NG, ENGLAND.
Hever Castle began as a country house, built in the 13th century. From 1462 to 1539 it was the seat of the Bullen (later Boleyn family.
Anne Boleyn, the second queen consort of King Henry VIII , spent her early youth there, after her father, Thomas Boleyn had inherited it in 1505.
It later came into the possession of King Henry's fourth wife, Anne of Cleves.
The castle is now a major tourist attraction. |
||||||||
 |
Kasteel van Ooidonk (Ooidonck Castle) Ooidonkdreef 9, 9800 Deinze, BELGIUM
The castle is the residence of the Earl t'Kint de Roodenbeke.
A fortress was first built on the site of the present castle in 1230, intended to defend the city of Ghent and to fortify the river Leie. |
||||||||
 |
Burg zu Burghausen, Burghausen Castle, Upper Bavaria, GERMANY
Burghausen Castle is the longest castle complex in Europe. The gothic castle comprises the main castle with the inner courtyard and five outer courtyards. |
||||||||
 |
Schwerin Castle, Lennéstraße 1, 19053, Schwerin, GERMANY
Schwerin Castle is situated on an island in the city's main lake, the Schweriner See.
For centuries the palace was the home of the dukes and grand dukes of Mecklenburg and later Mecklenburg-Schwerin.
It currently serves as the seat of the Mecklenburg-Vorpommern Landtag (state parliament) . It is regarded as one of the most important works of romantic Historicism in Europe and designated to become a World Heritage Site.
|
||||||||
 |
Above average sandcastle |
||||||||
 |
Château de Val Les Fontilles, 15270 Lanobre, Cantal
The Château is located on the shore of the Lake Bort-les-Orgues
It is classé as a Monument historique |
||||||||
 |
Arg-é Bam (Bam Citadel), Bam, Kerman Province, southeastern Iran
The Arg-e Bam was the largest adobe building in the world. It was a lrge fortress/city in whose heart the citadel was located, but because of the impressive look of the citadel, which forms the highest point, the entire fortress is referred to as the Bam Citadel.
It is listed by UNESCO as part of the World Heritage Site
The origin of this massive citadel on the Silk Road can be traced beyondthe Achaemenid period (6th to 4th centuries BC). The heyday of the citadel was from the 7th to 11th centuries, when it lay at the crossroads of important trade routes and known for the production of silk and cotton garments.
On December 26, 2003, the Citadel was almost completely destroyed by an earthquake, along with much of the rest of Bam. It is currently being rebuilt. |
||||||||
 |
Totnes Castle, Castle Street, Totnes, Devon TQ9 5NU, ENGLAND
The castle occupies a commanding position atop a large hill above the town, and guards the approach to three valleys, including that of the River Dart.
The surviving stone keep and curtain wall date from around the 14th century. Totnes Castle is one of the best preserved examples of a Norman motte and bailey castle in ENGLAND |
||||||||
 |
Himeji Castle, a hilltop Japanese castle complex in Himeji, in Hyogo Prefecture, Japan.
The castle is regarded as the finest surviving example of prototypical Japanese castle architecture, comprising a network of 83 buildings with advanced defensive systems from the feudal period.
Himeji Castle is also known as Hakuro-jo ("White Egret Castle") or Shirasagi-jo ("White Heron Castle") because of its white exterior and supposed resemblance to a bird taking flight.
The Castle dates to 1333, when Akamatsu Norimura built a fort on top of Himeyama hill.
Himeji Castle is the largest and most visited castle in Japan, and it was registered in 1993 as one of the first UNESCO World Heritage Sites in the country. The area within the middle moat of the castle complex is a designated Special Historic Site and five structures of the castle are also designated Japanese National Treasures. |
||||||||
 |
Himeji Castle, a hilltop Japanese castle complex located in Himeji, in Hyogo Prefecture, Japan.
The castle is regarded as the finest surviving example of prototypical Japanese castle architecture, comprising a network of 83 buildings with advanced defensive systems from the feudal period.
Himeji Castle is also known as Hakuro-jo ("White Egret Castle") or Shirasagi-jo ("White Heron Castle") because of its white exterior and supposed resemblance to a bird taking flight.
The Castle dates to 1333, when Akamatsu Norimura built a fort on top of Himeyama hill.
Himeji Castle is the largest and most visited castle in Japan, and it was registered in 1993 as one of the first UNESCO World Heritage Sites in the country. The area within the middle moat of the castle complex is a designated Special Historic Site and five structures of the castle are also designated Japanese National Treasures. |
||||||||
 |
Library at the Château de Fontainebleau
The Château (or Palace) of Fontainebleau is located 55 kilometres from the centre of Paris,
Fontainebleau is one of the largest French royal châteaux. The building is arranged around a series of courtyards. set around the remainder of the Forest of Fontainebleau, a former royal hunting park.. |
||||||||
 |
Château du Plessis-Bourré, Écuillé, Maine-et-Loire department
The Château du Plessis-Bourré is a château in the Loire Valley, built in less than 5 years from 1468 to 1472 by Finance Minister Jean Bourré, principal advisor to King Louis XI.
The château has not been modified externally since its construction and still has a fully working drawbridge
It was classified as a Monument historique in 1931.
The Château du Plessis-Bourré has been the location setting for numerous films. |
||||||||
 |
The Chindia Tower (Romanian: Turnul Chindiei) is a tower in the Curtea Domneasca monuments ensemble in Târgoviste, ROMANIA
The tower was begun in the fifteenth century during the second reign of Prince Vlad III the Impaler over Wallachia, taking its final form during the 19th century. It has a spectacular batter (or talus).
During its history it has been used as a guard point, a fire spotter and for storing and protecting the state treasury.
The tower now houses an exhibition of documents, weapons and objects which belonged to Vlad the Impaler. |
||||||||
 |
The Veste Coburg, or Coburg fortress, is situated on a hill above the city of Coburg, Bavaria, GERMANY
Veste Coburg (also called the "Franconian Crown")is one of GERMANY's largest castles. It dominates the town of Coburg on Bavaria's border with Thuringia.
The Veste Coburg was the historical seat of the independent duchy of Coburg in Franconia, now part of the German state of Bavaria.
Martin Luther lived in the Veste for a number of months during the Diet of Augsburg in 1530.
In the twentieth century, the castle was the residence of Charles Edward, Duke of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha, a grandson of Queen Victoria, who was also (until 1919) the 2nd Duke of Albany in the United Kingdom. |
||||||||
 |
The Alcázar of Segovia (Segovia Castle) is located in the old city of Segovia, SPAIN.
Rising out on a rocky crag above the confluence of the rivers Eresma and Clamores near the Guadarrama mountains, it is one of the most distinctive castle-palaces in SPAIN
Alcázar (from Arbic for "The Castle") was originally built as a fortress but has served as a royal palace, a state prison, a Royal Artillery College and a military academy. |
||||||||
 |
Torrechiara Castle, Langhirano, province of Parma, ITALY
Torrechiara was built by Pier Maria II Rossi, Count of San Secondo, between 1448 and 1460.
The building was a defensive structure, but also a mansion for the count's lover, Bianca Pellegrini, for which a famous hall, the Camera d'Oro ("Golden Chamber") was built with decorations by Benedetto Bembo.
Scenes of the 1985 film Ladyhawke were shot at the castle. |
||||||||
 |
The University of Timbuktu, located in the city of Timbuktu, Mali, West Africa
The University of Timbuktu was established in the 12th century. Teaching included geography, mathematics, the sciences, and medicine.
During the 12th century, the university had an enrollment of around 25,000 students from Africa as well as parts of the Mediterranean within a city of around 100,000 persons.
The castle like construction is useful when, periodically, religious fanatics attempt to destroy University facilities, artefacts and manuscrits, most recently in 2013. |
||||||||
 |
Tarasp Castle Lower Engadin, Graubünden, SWITZERLAND
Chastè da Tarasp (Tarasp Castle or in German, Schloss Tarasp) sits on a hill top near Tarasp.
Located in the Romansh speaking area of Switerland, it is a Swiss heritage site of national significance.
|
||||||||
 |
Smolenický zámok (Smolenice Castle) lies on the eastern slope of the LittleCarpathians, near the town of Smolenice, SLOVAKIA. |
||||||||
 |
Schloss Hohenschwangau (Hohenschwangau Castle), Hohenschwangau, near the town of Füssen, part of the county of Ostallgäu in southwestern Bavaria, GERMANY.
It is located very close to the border with Austria.GERMANY
Hohenschwangau Castle (the name means High Swan County Castle) is a 19th-century palace in southern GERMANY.
It was built by his father, King Maximilian II of Bavaria and was the childhood residence of the future King Ludwig II of Bavaria |
||||||||
 |
Château-Gaillard, above the commune of Les Andelys overlooking the River Seine, in the Eure département of historical Normandy, now Upper Normandy
Château Gaillard is a ruined medieval castle
Construction began in 1196 under the auspices of Richard the Lionheart, King of ENGLAND and Duke of Normandy. The castle was built in just two years, at the same time the town of Petit Andely
. Château Gaillard has a complex and advanced design - possibly designed by Richard himself. It uses principles of concentric fortification It was also one of the earliest European castles to use machicolations - an idea that Richard might well have brought back from the Holy Land. The castle consists of three enclosures separated by dry moats, with a keep in the inner enclosure.
Château Gaillard was captured in 1204 by the French king, Philip II, after a lengthy siege. In the mid-14th century, the castle became the residence of the exiled David II of Scotland.
The castle changed hands several times in the Hundred Years' War, but in 1449 the French captured Château Gaillard from the English for the last time, and from then on it remained in French ownership.
Henry IV of France ordered the demolition of Château Gaillard in 1599; The castle ruins are listed as a monument historique by the French Ministry of Culture. |
||||||||
 |
Pernstejn Castle Nedvedice, South Moravian Region, CZECH REPUBLIC
Pernštejn Castle (Czech: hrad Pernštejn) is located on a rock above the village of Nedvedice and the rivers Svratka and Nedvedicka, some 40 km northwest of Brno.
Pernštejn came to be known as the marble castle because of the marble-like stone used to frame the doors and windows. |
||||||||
 |
Oravský Hrad located above the Orava river in the village of Oravský Podzámok
In Eglish it is called Orava Castle, in German Arwaburg and in Hungarian: Árva vára)
Orava Castle stands on the site of an old wooden fortification, built after the Mongol invasion of Hungary of 1241.The later design was in Romanesque and Gothic style. Later still it was reconstructed as a Renaissance and Neo-Gothic structure,.
Many scenes of the 1922 film Nosferatu were filmed here. After a period of dilapidation the castle became a national monument after World War II,. |
||||||||
 |
|||||||||
 |
Montacute House Montacute, Somerset
Montacute House is a late Elizabethan country house typical of English architecture in transition from the medieval Gothic to the Renaissance Classical.
It is one of the finest houses to survive almost unchanged from the Elizabethan era, and has been designated by English Heritage as a Grade I listed building, and Scheduled Ancient Monument.
The house was built in about 1598 by Sir Edward Phelips, Master of the Rolls and the prosecutor during the trial of the Gunpowder Plotters.
Lord Curzon lived at the house with his mistress, the novelist Elinor Glyn. It was acquired by the National Trust in 1927 |
||||||||
 |
Le Château de Val |
||||||||
 |
San Vittore alle Chiuse Genga, Marche
San Vittore alle Chiuse is not a castle but a Roman Catholic abbey and church.
The edifice is known from the year 1011, and is example of Byzantine-influenced architecture in Italy. |
||||||||
 |
Althorp Gallery Althorp Northamptonshire
Althorp is a country estate of about 14,000 acres (60 square km) and a Grade I listed stately home in. It is about 5 miles (8.0 km) north-west of the county town of Northampton.
It is the official residence of The Earl and Countess Spencer. It was the home of Diana, Princess of Wales before her marriage to Charles, Prince of Wales.
(It's the current Earl Spencer sitting reading the book) |
||||||||
 |
The Château de Vendeuvre Vendeuvre, near to Lisieux in Normandy
Classed as a Historic Monument, Vendeuvre is a prototypical aristocratic Norman country house.
It was opened to the public in 1983. |
||||||||
 |
Schloss Nymphenburg Munich, Bavaria
The Nymphenburg Palace ("Nymph's Castle"), is a Baroque palace once the main summer residence of the House of Wittelsbach (rulers of Bavaria) |
||||||||
 |
Château Fort de Gisors Haute-Normandie
King William II of ENGLAND ordered Robert of Bellême to build the first castle at Gisors. Henry I of ENGLAND was responsible for the octagonal stone keep surmounting the motte. Henry's work at Gisors was part of a programme of royal castle building in Normandy during his reign to secure the region against the aspirations of the French crown.
The castle is also known for its links with the Templars. Put into their charge by the French king between 1158 and 1160, it became the final prison of the Grand Master of the Order, Jacques de Molay, in 1314. |
||||||||
 |
Château de Champlâtreux Epinay-Champlâtreux, Val-d’Oise, Île-de-France
Le château de Champlâtreux was built between 1751 et 1757 by the architect Jean-Michel Chevotet.
It is classified as a Monument Historique |
||||||||
 |
Château de la Motte Husson Martigne Sur Mayenne 53470 |
||||||||
 |
La cour d’honneur, l’hôtel des Invalides 7th arrondissement, Paris
Les Invalide , officially L'Hôtel national des Invalides (The National Town-House of the Invalids), is a complex of buildings containing museums and monuments, relating to the military history of France, as well as a hospital and a retirement home for war veterans (the building's original purpose).
The complex houses the Musée de l'Armée, the military museum of the Army of France, the Musée des Plans-Reliefs, and the Musée d'Histoire Contemporaine, as well as the burial site for some of France's war heroes. |
||||||||
 |
Kasteel van Wijnendale Wijnendale, Torhout, West Flanders
The present castle is largely a 19th-century reconstruction, but a part of the north wing is still 15th century.
One wing is inhabited by the present owners. Another wing is a museum, open to the public. |
||||||||
 |
Qaitbay Citadel Alexandria
The Citadel of Qaitbay (or the Fort of Qaitbay) is a 15th-century defensive fortress located on the Mediterranean sea coast at Alexandria, on the eastern side of the northern tip of Pharos Island at the mouth of the Eastern Harbour.
It is built on the site of the famous Lighthouse of Alexandria - probably from stones from the ruined lighthouse.
It was built in 1477 AD by Sultan Al-Ashraf Sayf al-Din Qa'it Bay, from whom it takes its name. |
||||||||
 |
Château Fort de Guédelon Treigny, Yonne, Burgundy
Château Fort de Guédelon (Guédelon Castle) is a medieval construction project. The object of which is to build a castle using only the techniques and materials used in the Middle Ages.
Building materials, including wood and stone, are obtained locally. Jacques Moulin, the chief architect for the project, designed the castle according to the architectural model developed during the 12th and 13th centuries by Philip II of France.
Construction started in 1997 under Michel Guyot, owner of Saint-Fargeau castle. The site was chosen in the light of the availability of a stone quarry, in a large forest, with a pond close by.
The project has created 55 jobs and is now a tourist destination, with more than 300 000 visits each year
When completed in the 2020s, it should be an authentic recreation of a 13th-century medieval castle. . |
||||||||
 |
Castello di Gradara (Gradara Castle), Gradara, Marche, ITALY.
Gradara Castle is protected by two walls, the outermost of which extends for almost 800 meters. |
||||||||
 |
Château-Gaillard, above the commune of Les Andelys overlooking the River Seine, in the Eure département of historical Normandy, now Upper Normandy
Château Gaillard is a ruined medieval castle
Construction began in 1196 under the auspices of Richard the Lionheart, King of ENGLAND and Duke of Normandy. The castle was built in just two years, at the same time the town of Petit Andely
. Château Gaillard has a complex and advanced design - possibly designed by Richard himself. It uses principles of concentric fortification It was also one of the earliest European castles to use machicolations - an idea that Richard might well have brought back from the Holy Land. The castle consists of three enclosures separated by dry moats, with a keep in the inner enclosure. |
||||||||
 |
Fagaras Castle Fagaras, Brazov County
In 1696, following penetration of the Austrian army in Transylvania, Fagaras Castle (or Fagaras Fortress) became Crown property of the Habsburgs. |
||||||||
 |
The Château de Chantilly Chantilly
The site comprises two attached buildings : the Petit Château built around 1560 for Anne de Montmorency, and the Grand Château, which was destroyed during the French Revolution and rebuilt in the 1870s.
Owned by the Institut de France, the château houses the Musée Condé, a public art galleriy. |
||||||||
 |
Entrance Hall in Osterley House, Hounslow, London
Osterley House (or Osterley Park) is a mansion set in a large park. When the house was built it was surrounded by rural countryside.
It was one of a group of large houses close to London which served as country retreats for wealthy families, but which were not true country houses, as they lacked large agricultural estates. |
||||||||
 |
Interior, Donjon de Vez Oise, Picardy
The Donjon (keep) is part of the Château de Vez.
|
||||||||
 |
Donjon de Vez Oise, Picardy
The Donjon (keep) is part of the Château de Vez. |
||||||||
 |
Château fort de la Hunaudaye Plédéliac, Côtes-d'Armor, Brittany
Castle Hunaudaye is a thirteenth century castle. It is classified as a Monument historique since February 1922. |
||||||||
 |
Château du Lude, Le Lude, Sarthe department, Pays-de-la-Loire
The Château du Lude is one of the many great châteaux of the Loire Valley and stands at the crossroads of Anjou, Maine and Touraine.
Le Lude is a stronghold transformed into an elegant house during the Renaissance and the 18th century. It has been inhabited by the same family for the last 260 years.
The Château gardens have evolved throughout the centuries, with an English style landscape, a rose garden, topiaries, a labyrinth and a botanical walk. |
||||||||
 |
The Château de Pierrefonds Pierrefonds, Oise département, Picardy
The Château is on the southeast edge of the Forest of Compiègne, north east of Paris, between Villers-Cotterêts and Compiègne.
The Château de Pierrefonds still features most of the characteristics of defensive military architecture from the Middle Ages, though it underwent major restoration in the 19th century. |
||||||||
 |
Château de La Roche Saint-Priest-la-Roche, Loire département
The castle stands on an island in the lake formed by the Villerest dam . It was built on a rocky platform overlooking the Loire river from a height of 30 metres. During the 1930s, the construction project for the Villerest dam by EDF condemned the château to disappear below the water. It was bought for a symbolic one franc by the commune. It is now situated on an island. |
||||||||
 |
Château de La Roch Saint-Priest-la-Roche, Loire département
The castle stands on an island in the lake formed by the Villerest dam . It was built on a rocky platform overlooking the Loire river from a height of 30 metres. During the 1930s, the construction project for the Villerest dam by EDF condemned the château to disappear below the water. It was bought for a symbolic one franc by the commune. It is now situated on an island. |
||||||||
 |
Château de La Roche Saint-Priest-la-Roche, Loire département
The castle stands on an island in the lake formed by the Villerest dam . It was built on a rocky platform overlooking the Loire river from a height of 30 metres. During the 1930s, the construction project for the Villerest dam by EDF condemned the château to disappear below the water. It was bought for a symbolic one franc by the commune. It is now situated on an island. |
||||||||
 |
Château de Chillon Veytaux, Montreux, SWITZERLAND
The Château de Chillon (Chillon Castle) is an island castle located on the shore of Lake Geneva in the commune of Veytaux, at the eastern end of the lake, 3 km from Montreux
The first written record of the castle date to 1160. From the mid 12th century, the castle was home to the Counts of Savoy.
The Château de Chillon was made popular by Lord Byron, who wrote the poem The Prisoner Of Chillon; Byron also carved his name on a pillar of the dungeon.
The castle is also one of the settings in Henry James's novella Daisy Miller (1878). |
||||||||
 |
Château d'Anjony Tournemire, Cantal département, Auvergne
The Château d'Anjony is known in Occitan as the Chastèl d'En Jòni, (the Castle of Lord Jòni). It is built of reddish basal
] It is located in a strategic position on the Tournemire promontory and dominates the rich landscape of the Doire valley with its four tall towers.
The castle and its estate are classified as a monument historique by the French Ministry of Culture. |
||||||||
 |
Château d'Ainay-le-Vieil Ainay-le-Vieil, Cher
Built in the 14th century, this moated castle has been listed as a Monument historique since 1968 by the French Ministry of Culture. |
||||||||
 |
Château d'Ainay-le-Vieil Ainay-le-Vieil, Cher
Built in the 14th century, this moated castle has been listed as a Monument historique since 1968 by the French Ministry of Culture. |
||||||||
 |
Castello Piccolomini (Celano Castle), Celano, provincia dell'Aquila, Marsica, ITALY
The square castle, with round towers at the corners, was erected in its present form on the top of the San Vittorino Hill.
Its construction was commissioned by Count Pietro Berardi around the year 1392, and was finished around 1451.
Today, the castle hosts the Museum of Sacred Art of the Marsica. |
||||||||
 |
Castello Piccolomini (Celano Castle), Celano, provincia dell'Aquila, Marsica, ITALY
The square castle, with round towers at the corners, was erected in its present form on the top of the San Vittorino Hill.
Its construction was commissioned by Count Pietro Berardi around the year 1392, and was finished around 1451.
Today, the castle hosts the Museum of Sacred Art of the Marsica. |
||||||||
 |
Castle of Bussy Rabutin
The Château de Bussy-Rabutin, also known as Château de Bussy-le-Grand, developed from a 12th-century castle,
The castle was founded by Renaudin de Bussy. It was rebuilt in the 14th century, and the Renaissance galleries were added in the 1520s. It was altered during the reigns of Henri II (1547–1559) and Louis XIII (1610–1643). |
||||||||
 |
Warkworth Castle, Warkworth, Northumberland, ENGLAND
It is an example of a Norman Motte and bailey castle.
Both town and castle occupy a loop of the River Coquet, less than a mile from ENGLAND's north-east coast.
Traditionally the castle's construction has been ascribed to Prince Henry of Scotland in the mid-12th century, but it may have been built by King Henry II of ENGLAND when he took control of ENGLAND's northern counties. |
||||||||
 |
Warkworth Castle, Warkworth, Northumberland, ENGLAND
It is an example of a Norman Motte and bailey castle.
Both town and castle occupy a loop of the River Coquet, less than a mile from ENGLAND's north-east coast.
Traditionally the castle's construction has been ascribed to Prince Henry of Scotland in the mid-12th century, but it may have been built by King Henry II of ENGLAND when he took control of ENGLAND's northern counties. |
||||||||
 |
Ortenberg Schloss, Ortenau, Baden-Wurttemberg, GERMANY |
||||||||
 |
|||||||||
 |
The castle of Bourtzi Nafplio, Argolis, Peloponnese
The castle of Bourtzi is located in the middle of the harbour of Nafplio. Venetians completed its fortification in 1473 to protect the city from pirates and invaders from the sea. It fell to Ottoman Turks along with the rest of Greece.
The Greeks regained it from the Turks on June 18, 1822, from where they assisted in the siege of Nafplio. Until 1865 it served as a fortress. It was then transformed into residence of the executioners of convicts from the castle of Palamidi. From 1930 to 1970, it served as a hotel. Since then, it is mainly a tourist attraction. |
||||||||
 |
The castle of Bourtzi Nafplio, Argolis, Peloponnese
The castle of Bourtzi is located in the middle of the harbour of Nafplio. Venetians completed its fortification in 1473 to protect the city from pirates and invaders from the sea. It fell to Ottoman Turks along with the rest of Greece.
The Greeks regained it from the Turks on June 18, 1822, from where they assisted in the siege of Nafplio. Until 1865 it served as a fortress. It was then transformed into residence of the executioners of convicts from the castle of Palamidi. From 1930 to 1970, it served as a hotel. Since then, it is mainly a tourist attraction. |
||||||||
 |
Burg Altena (Altena Castle), Altena, Märkischer Kreis, North Rhine-Westphalia, GERMANY
Altena Castle is a Medieval hill castle in the town of Altena in western GERMANY. It was erected by the early Counts of Berg - in the early 12th century. Eventually, the House of Berg abandoned Altena and moved their residence to Hamm.
In 1912, Richard Schirrmann established the world's first youth hostel within the castle, which is still in use today (the Jugendherberge Burg Altena). |
||||||||
 |
Wasserschloss Klaffenbach, Wasserschloßweg 6, 09123 Chemnitz, GERMANY |
||||||||
|
|
|||||||||
 |
Castel Roncolo, territory of Ritten, near the city of Bolzano in South Tyrol, ITALY.
The castle is known as Runkelstein Castle in English and Schloss Runkelstein in German.
It is a medieval fortification on a rocky spur. In 1237 Alderich, Prince-Bishop of Trent gave the brothers Friedrich and Beral, Lords of Wange,n permission to construct a castle on the rock then called Runchenstayn. |
||||||||
 |
Schloss Greyerz / Château de Gruyères) Rue du Château 8, 1663 Gruyères, Fribourg, SWITZERLAND
The Castle is one of the most famous in Switzerland. |
||||||||
 |
Castel Beseno, Beseno, Trentino-Alto Adige, ITALY
Castel Beseno - Schloss Pysein in German language, Beseno Castle in English - is the largest fortified structure of Trentino-Alto Adige. |
||||||||
 |
Castello Mafredonico, Mussomeli (Mussumeli in Sicilian), Caltanissetta, Sicily, ITALY.
The Chiaramonte Castle Castello Mafredonico, was built in 1370 in Norman-Gothic style. It stands on a high crag at 778 metres, 2 km outside the town.
It has halls, dungeons and torture cells, and a chapel with a alabaster depicting the Madonna dell Catena (1516). |
||||||||
 |
Schloss Hohenzollern (Hohenzollern Castle) 72379 Burg Hohenzollern, GERMANY
Hohenzollern Castle is the ancestral seat of the Hohenzollern family, who became German Emperors
A castle was first constructed here in the early 11th century. The present castle was constructed for King Frederick William IV of Prussia between 1846 and 1867. The design was based on English Gothic Revival architecture and the Châteaux of the Loire Valley.
In 1945 it became home to the former Crown Prince Wilhelm of GERMANY, son of the last Hohenzollern monarch, Kaiser Wilhelm II, who is buried there with his wife, Crown Princess Cecilie |
||||||||
 |
Burg Hochosterwitz, near Sankt Georgen am Längsee, east of the town of Sankt Veit an der Glan in the state of Carinthia, AUSTRIA
Hochosterwitz Castle is considered to be one of Austria's most impressive medieval castles.
There are 14 defensive gates, each equipped with different methods of guarding the path. Local legend maintains that the castle has never been conquered and that none of the attacks managed to get beyond the fourth gate. |
||||||||
 |
Blickling Hall, Blickling, Norfolk, ENGLAND,
In the 15th century, Blickling Hall was in the possession of Sir John Fastolf, who made a fortune in the Hundred Years' War, and whose coat of arms is still on display here.
Later, the Hall came into the possession of the Boleyn family. It was home to Sir Thomas Boleyn, Earl of Wiltshire, the father of Anne Boleyn.
Blickling Hall has been in the care of the National Trust since 1940.
|
||||||||
 |
City Walls, Arg-é Bam (Bam Citadel), Bam, Kerman Province, southeastern
The Arg-e Bam was the largest adobe building in the world. It was a lrge fortress/city in whose heart the citadel was located, but because of the impressive look of the citadel, which forms the highest point, the entire fortress is referred to as the Bam Citadel.
It is listed by UNESCO as part of the World Heritage Site
The origin of this massive citadel on the Silk Road can be traced beyondthe Achaemenid period (6th to 4th centuries BC). The heyday of the citadel was from the 7th to 11th centuries, when it lay at the crossroads of important trade routes and known for the production of silk and cotton garments.
On December 26, 2003, the Citadel was almost completely destroyed by an earthquake, along with much of the rest of Bam. It is currently being rebuilt. |
||||||||
 |
Interior, Arg-é Bam (Bam Citadel), Bam, Kerman Province, southeastern IRAN
The Arg-e Bam was the largest adobe building in the world. It was a lrge fortress/city in whose heart the citadel was located, but because of the impressive look of the citadel, which forms the highest point, the entire fortress is referred to as the Bam Citadel.
It is listed by UNESCO as part of the World Heritage Site
The origin of this massive citadel on the Silk Road can be traced beyondthe Achaemenid period (6th to 4th centuries BC). The heyday of the citadel was from the 7th to 11th centuries, when it lay at the crossroads of important trade routes and known for the production of silk and cotton garments.
On December 26, 2003, the Citadel was almost completely destroyed by an earthquake, along with much of the rest of Bam. It is currently being rebuilt. |
||||||||
 |
Alhambra Palace, Granada, Andalusia, SPAIN
The Alhambra (Calat Alhambra) is a palace and fortress complex, originally constructed as a small fortress in 889 and rebuilt in the mid 11th century by the Moorish king Mohammed ben Al-Ahmar of the Kingdom of Granada.
It was converted into a royal palace in 1333 by Yusuf I, Sultan of Granada. The Alhambra's Islamic palaces were built for the last Muslim emirs in Spain and its court of the Nasrid dynasty. After the Reconquista by the Reyes Católicos ("Catholic Monarchs") in 1492, some portions were used by Christian rulers. The Palace of Charles V, built by Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor in 1527, was inserted in the Alhambra within the Nasrid fortifications.
It is now one of Spain's major tourist attractions, exhibiting the country's most significant and well known Islamic architecture, together with 16th-century and later Christian buildings and gardens.
The Alhambra is a UNESCO World Heritage Site |
||||||||
 |
Alhambra Palace, Granada, Andalusia, SPAIN
The Alhambra (Calat Alhambra) is a palace and fortress complex, originally constructed as a small fortress in 889 and rebuilt in the mid 11th century by the Moorish king Mohammed ben Al-Ahmar of the Kingdom of Granada.
It was converted into a royal palace in 1333 by Yusuf I, Sultan of Granada. The Alhambra's Islamic palaces were built for the last Muslim emirs in Spain and its court of the Nasrid dynasty. After the Reconquista by the Reyes Católicos ("Catholic Monarchs") in 1492, some portions were used by Christian rulers. The Palace of Charles V, built by Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor in 1527, was inserted in the Alhambra within the Nasrid fortifications.
It is now one of Spain's major tourist attractions, exhibiting the country's most significant and well known Islamic architecture, together with 16th-century and later Christian buildings and gardens.
The Alhambra is a UNESCO World Heritage Site |
||||||||

|
Matsumoto Castle, ("Crow Castle")
Matsumoto Castle is one of Japan's premier historic castles. The keep (tenshukaku), was completed in the late sixteenth century, It is listed as a National Treasure of Japan.
Matsumoto Castle is a flatland castle (hirajiro) built on a plain. Its defences would have included an extensive system of inter-connecting walls, moats, and gatehouses. |
||||||||
 |
Château de Beynac Beynac-et-Cazenac, Dordogne
The castle is one of the best-preserved and best known in the Dordogne, perched on top of a limestone cliff, dominating the town and the north bank of the Dordogne River
The castle was built in the 12th century by the barons of Beynac (one of the four baronies of Périgord) to control the valley of the Dordogne River.
The sheer cliff face was sufficient to discourage any assault from that side, so the defences were concentrated on the plateau on the other side. They included double crenellated walls, double moats,and a double barbican. |
||||||||
 |
Château de Beynac Beynac-et-Cazenac, Dordogne
The castle is one of the best-preserved and best known in the Dordogne, perched on top of a limestone cliff, dominating the town and the north bank of the Dordogne River
The castle was built in the 12th century by the barons of Beynac (one of the four baronies of Périgord) to control the valley of the Dordogne River.
The sheer cliff face was sufficient to discourage any assault from that side, so the defences were concentrated on the plateau on the other side. They included double crenellated walls, double moats,and a double barbican. |
||||||||
 |
Interior, Palácio de Monserrate (Monserrate Palace), Parque de Monserrate, 2710-405 Sintra, PORTUGAL
The Monserrate Palace is an exotic palatial villa near Sintra, Portugal, the traditional summer resort of the Portuguese court. It was built in 1858 for Sir Francis Cook, an English baronet who was created Visconde de Monserrate by King Luís. |
||||||||
 |
The Arab Cieling Cardiff Castle Cardiff, WALES
Cardiff Castle is a combination of medieval castle and Victorian Gothic revival mansion located in the city centre.
The original motte and bailey castle was built in the late 11th century by Norman invaders on top of a 3rd-century Roman fort. |
||||||||
 |
Schloss Moritzburg (Castle Moritzburg), Schloßallee, 01468 Moritzburg, Saxony, GERMANY
Moritzburg Castle is a Baroque palace in Moritzburg, in the German state of Saxony, about 13 kilometres (8.1 mi) northwest of Dresden.
The castle is named after Duke Moritz of Saxony, who had a hunting lodge built here between 1542 and 1546. |
||||||||
 |
The Great Hall, Hatfield House, Great North Rd, Hatfield, Hertfordshire AL9 5NQ, ENGLAND
Hatfield House is a country house set in a large park, to the east of Hatfield, Hertfordshire, ENGLAND. It is a prime example of Jacobean architecture
The present Jacobean house was built in 1611 by Robert Cecil, First Earl of Salisbury and Chief Minister to King James I and has been the home of the Cecil family ever since.
Hatfield House is currently the home of Robert Gascoyne-Cecil, 7th Marquess of Salisbury.
The house is open to the public
|
||||||||
 |
Vianden Castle Vianden
Vianden Castle (French: Château de Vianden, German: Burg Vianden Luxembourgish: Buerg Veianen), is located in Vianden, in the north of Luxembourg.
Vianden is one of the largest fortified castles west of the Rhine. Its origins date to the 10th century. The castle was built in the Romanesque style between the 11th and 14th centuries. Gothic aspects were added at the end of this period.
A Renaissance mansion was added in the 17th century. After the seventeenth century the castle was allowed to fall into ruin, and has recently been restored.
It is now open to visitors. |
||||||||
 |
Schloss Körtlinghausen Körtlinghausen 4, 59602 Rüthen |
||||||||
 |
La Conciergerie 2 Boulevard du Palais, 75001 Paris
La Conciergerie is a former royal palace and prison located by the seine on the west of the Île de la Cité. It is part of the larger complex known as the Palais de Justice, which is still used for judicial purposes. |
||||||||
 |
Trakošcan Castle Varaždin County Northern CROATIA |
||||||||
 |
Trakai Island, Teutonic castle on Lake Galve
The construction of the castle was begun in the 14th century and completed around 1409.
Trakai was one of the main centres of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and the castle held great strategic importance. |
||||||||
 |
Château de Vigny Vigny Val-d'Oise Île-de-France |
||||||||

|
Château de Beynac Castle in Beynac-et-Cazenac |
||||||||
 |
Schloss Mespelbrunn (Mespelbrunn Castle) Mespelbrunn |
||||||||

|
Sazova Mahallesi Eskisehir |
||||||||
 |
Castle Howard North Yorkshire |
||||||||

|
Kitchens Fontevraud Abbaye, Fontevraud-l'Abbaye near Chinon Anjou |
||||||||
 |
Schwerin Castle city of Schwerin Sited on an island in the city's main lake, the Schweriner See |
||||||||
 |
Bedzin Castle Zamkowa Bedzin |
||||||||
 |
Edinburgh Castle, Castle Rock, Edinburgh, SCOTLAND
Edinburgh Castle is a historic fortress diminating the skyline of the city of Edinburgh. There has been a royal castle on the rock since at least the reign of David I in the 12th century.
As one of the most important strongholds in the Kingdom of Scotland, Edinburgh Castle was involved in many historical conflicts from the Wars of Scottish Independence in the 14th century to the Jacobite Rising of 1745.
The castle houses the Scottish regalia, known as the Honours of Scotland and is the site of the Scottish National War Memorial and the National War Museum of Scotland. The British Army is still responsible for some parts of the castle.
The castle is in the care of Historic Scotland and is Scotland's most-visited paid tourist attraction. As the backdrop to the Edinburgh Military Tattoo during the annual Edinburgh International Festival the castle has become a recognisable symbol of Edinburgh and of Scotland. |
||||||||
 |
Paphos Castle, Paphos, East Coast
Paphos Castle is located on the edge of Paphos harbour. It was originally built as a Byzantine fort to protect the harbour. It was then rebuilt by the Lusignans in the thirteenth century after being destroyed in the earthquake of 1222.
In 1570 it was dismantled by the Venetians. After capturing the island, the Ottomans restored and strengthened it.
It was declared a listed building in 1935 and represents one of the most distinctive landmarks of the city of Paphos.] |
||||||||

|
Trakai Island Castle Lake Galve |
||||||||
 |
Château de Josselin Josselin Morbihan Brittany |
||||||||
 |
Arg-é Bam (Bam Citadel), Bam, Kerman Province, southeastern IRAN
The Arg-e Bam was the largest adobe building in the world. It was a lrge fortress/city in whose heart the citadel was located, but because of the impressive look of the citadel, which forms the highest point, the entire fortress is referred to as the Bam Citadel.
It is listed by UNESCO as part of the World Heritage Site
The origin of this massive citadel on the Silk Road can be traced beyondthe Achaemenid period (6th to 4th centuries BC). The heyday of the citadel was from the 7th to 11th centuries, when it lay at the crossroads of important trade routes and known for the production of silk and cotton garments.
On December 26, 2003, the Citadel was almost completely destroyed by an earthquake, along with much of the rest of Bam. It is currently being rebuilt. |
||||||||
 |
Veliki Tabor in the region of Zagorje near Desinic, 8 km (5.0 miles) west of Pregrada
Veliki Tabor is a fortress and museum in northwest Croatia, dating from the 12th century.
The castle's present appearance dates from the 16th century |
||||||||
 |
Chepstow Castle 1 Bridge St, Chepstow, Monmouthshire NP16 5EY, WALES
Chepstow Castle, located on top of cliffs overlooking the River Wye, is the oldest surviving post-Roman stone fortification in Britain. It was the southernmost of a chain of castles built along the English–Welsh border in the Welsh Marches.
Its construction was begun under the Norman Lord William fitzOsbern, soon afterwards made Earl of Hereford,
The castle ruins are a Grade I lhistorical monument |
||||||||
 |
Château de Lassay Lassay-les-Châteaux, Mayenne
The original castrum or castellum here, built in the early years of the twelfth century, was probably a motte and bailey castle.
The present Château de Lassay was classified as a monument historique in 1862 and is still a private residence. |
||||||||
 |
Castello Valentino, Turin, ITALY
Castello del Valentino (Castle of Valentino) is located in Valentino Park. It was one of the Residences of the Royal House of Savoy included in the list of UNESCO World Heritage Sites in 1997.
Today it is the seat of the Architecture Faculty of the Polytechnic University of Turin. |
||||||||
 |
The Palace of Mysore (orAmba Vilas Palace) Mysore, Karnataka
The palace is the official residence of the Wodeyars, the former royal family of Mysore, which ruled the princely state of Mysore from 1399 to 1947.
The palace also houses two durbar halls (ceremonial meeting hall of the royal court).
Mysore Palace is now one of the most famous tourist attractions in India, |
||||||||
 |
Gyeongbokgung Seoul
Gyeongbokgung, also known as Gyeongbokgung Palace or Gyeongbok Palace, is a royal palace.
Constructed in 1395, the palace was later burned, and abandoned for almost three centuries. It was reconstructed in 1867, as the main and largest palace of the Five Grand Palaces built by the Joseon Dynasty.
The name means "Palace" [Gung] "Greatly Blessed by Heaven" [Gyeongbok].
In the early 20th century, much of the palace was destroyedby Imperial Japan. Since then, the walled palace complex has been gradually restored to its original form. |
||||||||
 |
The Catherine Palace, Sadovaya ulitsa, 7, Pushkin RUSSIA, 196601
The Catherine Palace is a Rococo palace located in the town of Tsarskoye Selo, 25 km southeast of St. Petersburg, Russia.
It was the summer residence of the Russian tsars. |
||||||||
 |
Schloss Linderhof (Linderhof Palace), Bavaria, GERMANY.
Linderhof Palace is located near Ettal Abbey.in Southwest Bavaria.
It is the smallest of the three palaces built by King Ludwig II of Bavaria, and the only one he lived to see completed. |
||||||||
|
|
|||||||||
 |
Changdeokgung Jongno-gu, Seoul
Changdeokgung means "Prospering Virtue Palace". The palace is also known as Changdeokgung Palace and Changdeok Palace
It is set within a large park and is one of the "Five Grand Palaces" built by the kings of the Joseon Dynasty (1392–1897). It is located east of Gyeongbok Palace, Changdeokgung, along with Changgyeonggung, is also referred to as the "East Palace"
Changdeokgung was the favored palace of many Joseon princes and retained many elements dating from the Three Kingdoms of Korea period not incorporated in the more contemporary Gyeongbokgung.
Like the other Five Grand Palaces in Seoul, it was heavily damaged during the Japanese occupation of Korea (1910-1945). |
||||||||
 |
The Pena National Palace, São Pedro de Penaferrim, municipality of Sintra
The Pena National Palace, in Portuguese the Palácio Nacional da Pena, is a Romanticist palace on the top of a hill above the town of Sintra. On a clear day it can be easily seen from Lisbon
It is a national monument andnotable expression of 19th-century Romanticism. The palace is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and one of the Seven Wonders of Portugal.
It is also used for state occasions by the President of the Portuguese Republic and by other government officials. |
||||||||
 |
Tofte Manor from sunken garden
Tofte Manor Souldrop Road, Sharnbrook, Bedfordshire MK44 1HH |
||||||||
 |
Château de Maisons (now Château de Maisons-Laffitte), Maisons-Laffitte, northwestern Paris, department of Yvelines, Île-de-France
Le château de Maisons-Laffitte was designed by François Mansart from 1630 to 1651. It is a prime example of French baroque architecture and a reference point in the history of French architecture. |
||||||||
 |
The Palais des Tuileries Paris
This illustration shows the Palais des Tuileries in the 17th century
The Tuileries Palace was a royal palace in Paris which stood on the right bank of the River Seine. It was the usual Parisian residence of most French monarchs, from Henry IV to Napoleon III. Iit was destroyed in the upheaval of the Paris Commune in 1871.
Built in 1564, it was gradually extended until it closed off the western end of the Louvre courtyard and displayed a façade of 266 metres. Since the destruction of the Tuileries, the Louvre courtyard has remained open and the site is now the location of the eastern end of the Tuileries Garden, forming an elevated terrace between the Place du Carrousel and the gardens proper. |
||||||||
 |
The Royal Palace of La Granja de San Ildefonso San Ildefonso, near Segovia
The Royal Palace of La Granja de San Ildefonso in known in Spanish as the Palacio Real de La Granja de San Ildefonso. It is an 18th-century palace, the summer residence of the Kings of Spain from the reign of Philip V.
The palace was built in a restrained baroque style, surrounded by extensive gardens in the French manner, with sculptural fountains.
It is now open to the public as a museum. |
||||||||
 |
Belvédère supérieur Vienna,
The Belvedere is a historic building complex consisting of two Baroque palaces (the Upper and Lower Belvedere), the Orangery, and the Palace Stables. It houses the Belvedere museum.
The buildings are set in a Baroque park landscape. The grounds are set on a gentle gradient and include decorative tiered fountains and cascades, Baroque sculptures, and majestic wrought iron gates. The Baroque palace complex was built as a summer residence for Prince Eugene of Savoy.
The Belvedere was built during a period of extensive construction in Vienna, the imperial capital and home to the ruling Habsburg dynasty. This period of prosperity followed Prince Eugene of Savoy's successful conclusion of a series of wars against the Ottoman Empire. |
||||||||
 |
Hever Castle Hever, Kent, near Edenbridge
Hever Castle began as a country house, built in the 13th century.
From 1462 to 1539 it was the seat of the 'Bullen', family later known as the Boleyn family. Anne Boleyn, the second queen consort of King Henry VIII of ENGLAND, spent her early youth there, after her father, Thomas Boleyn had inherited it in 1505.
It later came into the possession of King Henry VIII's fourth wife, Anne of Cleves.
The castle is now a tourist attraction. |
||||||||
 |
Château de Durtal Durtal, Maine-et-Loire
The château was classé as a monument historique en 1900. |
||||||||
 |
Stordalen Castle
Side View |
||||||||
 |
Château de Monbazillac Dordogne, Aquitane |
||||||||
 |
Pernštejn Castle, above the village of Nedvedice, northwest of Brno, in the South Moravian Region, CZECH REPUBLIC.
Pernštejn (Czech: hrad Pernštejn) came to be known as the marble castle because of the marble-like stone used to frame the doors and windows.
The castle was founded by the Lords of Medlov probably between 1270–1285. Its history is closely connected to the Lords of Pernštejn (Pernštejnové) and their descendants. It has kept its intact appearance in the Gothic and Renaissance form as it was finished in the first half of the 16th century by the Pernštejns, then the richest and most powerful lordly family of the Czech kingdom.
It has the most extraordinary entrance tower.
Pernštejn is one of the best preserved castles in Czech Republic. |
||||||||
 |
Alcazar, Seville, SPAIN
The Alcázar of Seville is known in Spanish as the "Reales Alcázares de Sevilla" litterally the Royal Alcazars of Seville,
It is a royal palace, originally a Moorish fort. It is the oldest royal palace still in use in Europe, and it was registered in 1987 by UNESCO as a World Heritage Site.
The Almohades were the first to build a palace, which was called Al-Muwarak, on the site of the modern day Alcázar. The palace is one of the best remaining examples of mudéjar architecture. Subsequent monarchs made their own additions to the Alcázar.
The upper levels of the Alcázar are still used by the royal family as the official Seville residence and are administered by the Patrimonio Nacional. |
||||||||
 |
|||||||||
 |
Castle of Bourtzi Harbour of Nafplio
The Venetians completed its fortification here in 1473 to protect the city from pirates and invaders from the sea.
The Greeks regained it from the Turks on June 18, 1822, from where they assisted in the siege of Nafplio.
Until 1865 it served as a fortress. It was then transformed into residence of the executioners of convicts from the castle of Palamidi.
From 1930 to 1970, it served as a hotel. Since then it has been a tourist attraction.. |
||||||||
 |
Château de Pau Pau, Pyrénées-Atlantiques
The Château de Pau is a castle in the centre of Pau, the capital of Pyrénées-Atlantiques and Béarn. The château is located in the centre of Pau and dominates that quarter of the city
King Henry IV of France and Navarre was born here on December 13, 1553. The castle has a small garden that was tended by Marie Antoinette when she spent much of the summer in the city. The castle was used by Napoleon as a holiday home during his period of power.
The castle is classified as a Monument historique since 1840 by the French Ministry of Culture. The castle contains a collection of tapestries. |
||||||||
 |
Amarah Palace Najran, Aba Al Saud Historical Area,
Amarah or Emara Palace is a daub castle located in the central ancient city in Najran. It is a good example of the traditional architecture of the region.
The castle was built from daub (mud & straw) with its foundations built of stones. It is composed of 65 rooms and housed the local governor and his deputy and personal companions (khawis). The building takes the shape of a classic castle with high rectangular walls and round guard towers at the four corners. Inside (shown in the photo) is a well which dates back to pre-Islamic age. |
||||||||
 |
Château de la Balue La Balue, 35560 Bazouges-la-Pérouse
The 17th century château stands between Saint-Malo and Mont-Saint-Michel, in a landscape of rolling hills and forests, and not far from the Atlantic coastline. It is a French historical monument known for its beautiful gardens and for the many literary celebrities who have stayed there. |
||||||||
 |
Kumbhalgarh Fort Rajsamand District, Rajasthan state
Kumbhalgarh is a Mewar fortress and World Heritage Site included in Hill Forts of Rajasthan. Built during the course of the 15th century by Rana Kumbha and enlarged through the 19th century.
Occupied until the late 19th century, the fort is now open to the public and is spectacularly lit for a few minutes each evening.
(According to an uncle of the present Mararana of Udaipur, it was designed to allow four hoursemen to ride abreast around the walls (The steps are more recent)) |
||||||||
 |
The Palace of the Grand Master of the Knights of Rhodes, on the island of Rhodes in GREECE.
The Palace is one of the few examples of Gothic architecture in Greece. It was previously a citadel of the Knights Hospitaller and functioned as a palace, headquarters and fortress.
The present palace was built in the early 14th century by the Knights of Rhodes, who controlled Rhodes and other Greek islands from 1309 to 1522, to house the Grand Master of the Order.
After the island was captured by the Ottoman Empire, the palace continued to be used as a command center and fortress. |
||||||||
 |
Side view Château Villette Condécourt
Château Villette is a manor house hotel located 40 minutes away from Paris. It has numerous outbuildings including a chapel and adjacent reception room, horse stable and greenhouse.
More than 185 acres (0.75 km2) of garden were designed by Le Nôtre and spread out behind the château in the central axis with two rectangular lakes filled with birds and fish,
In the film Da Vinci Code, it iwas the home of Sir Leigh Teabing. |
||||||||
 |
Burghausen Upper Bavaria
Burghausen Castle in Burghausen, Upper Bavaria, is the longest castle complex in Europe (1,043 m).
The gothic castle comprises the main castle with the inner courtyard and five outer courtyards. The outermost point of the main castle is the Palas with the ducal private rooms. Today it houses the castle museum, including late Gothic paintings of the Bavarian State Picture Collection. On the town side of the main castle next to the donjon are the gothic inner Chapel of St. Elizabeth (1255) and the Dürnitz (knights' hall) with its two vaulted halls. Opposite the Dürnitz are the wings of the Duchess' residence. |
||||||||
 |
Palais de l'Isle Annecy
The Palais de l'Isle is a castle in the Thiou canal, built in 1132. It was the primary residence of the Lord of Annecy as early as the 12th century, and later became the Count of Geneva's administrative headquarters.
Later it became a courthouse, a mint, and finally a jail from the Middle Ages until 1865, and then again during World War II.
The Palais de l'Ile was classified as a Historical Monument in 1900, and today houses a local history museum. |
||||||||
 |
Château de Champs Champs-sur-Marne, Seine-et-Marne, Île-de-France
The Château de Champs was built in its present form in 1699 for the treasurer Charles Renouard de la Touaneby by Pierre Bullet, architecte du roi.
Around 1750, a beautiful rococo salon chinois (Chinese salon) was added to the château with wall paintings by noted artist Christophe Huet.
Louis César entertained many of famous writers here, including Diderot, Voltaire, d'Alembert and François-Augustin de Paradis de Moncrif. |
||||||||
 |
Wasserschloss Haus Bodelschwingh Mengede, Dortmund
Wasserschloss Haus Bodelschwingh (Bodelschwingh Castle) is a moated castle, built in the 13th century by the family of Bodelschwingh (it is now owned by the family Knyphausen)
Bodelschwinghstraße castle is located near to the water tower house Dellwig and the moated castle Haus Rodenberg the largest and most important water castle in Dortmund.
Near the castle there developed a settlement which kept its independence until 1928. Today, the district of Bodelschwingh belongs to the municipality of Mengede.
The castle is registered as a historic landmark in the list of monuments of the city of Dortmund. |
||||||||
 |
Château du Lude Le Lude, Sarthe department, Pays-de-la-Loire
The Château du Lude is one of the many great châteaux of the Loire Valley and stands at the crossroads of Anjou, Maine and Touraine.
Le Lude is an old stronghold transformed into an elegant house during the Renaissance and the 18th century. It has been inhabited by the same family for the last 260 years.
The Château gardens have evolved throughout the centuries, with an English style landscape, a rose garden, topiaries, a labyrinth and a botanical walk. |
||||||||
 |
The Château de Biron Biron, Dordogne
The Château de Biron is a large castle in the valley of the Lède. This photograph shows just one small tower.
It was the castle from which the Gontaut-Biron took their name. It was their seat from the twelfth century. Biron was seized by Simon IV de Montfort in 1212 from forces sypathetic to the Cathars.
The Plantagenets held it at times during the 14th and 15th centuries. Biron was erected as a duché-pairie in 1598, for Charles de Gontaut, created duc de Biron.
The present château bears additions over the centuries: notably a twelfth-century keep and sixteenth-century living quarters and vaulted kitchens.
Since 1928, it has been listed as a monument historique by the French Ministry of Culture. The local commune purchased the Château de Biron in 1978, with a view to restoring it as a tourist attraction. |
||||||||
 |
Castillos de Monzón y Loarre Loarre, Huesca. SPAIN.
The Loarre castle complex was built largely during the 11th and 12th centuries, when its position on the frontier between Christian and Muslim lands gave it strategic importance.
The first of the two major building programs began ca. 1020, when Sancho el Mayor (r. 1063–94) reconquered the surrounding lands from the Muslims. At least three towers, two of which survive, the Homage tower (Torre del Homenaje) and the "Tower of the Queen" (Torre de la Reina), are attributed to this campaign.
The Homage tower was built in an isolated position in front of the fortifications, to which it was connected by a wooden bridge. The Torre de la Reinahas both Lombard and Mozarabic architectural forms. |
||||||||
 |
Arteaga Tower, Biscay, Basque Country
The Arteaga Tower is a medieval castle rebuilt in the 19th Century for the French empress Eugénie de Montijo Napoleon III and Eugenia de Montijo had it rebuilt when their son was proclaimed an honorary citizen of Biscay. |
||||||||
 |
Ardverikie Castle Kinlochlaggan, Newtonmore, PH20 1BX
Ardverikie House, built in the Scottish baronial style in 1870, is a private hous in the Highlands. It sits on a promontory overlooking King Fergus's Island with its ancient ruins. Its three mile private drive winds past the largest inland beach in the country and round the loch.
The house played host to Queen Victoria and Prince Albert for a month before they bought Balmoral.
It features in BBC's series Monarch of the Glenn. |
||||||||
 |
Castel del Monte (Castle of the Mount) Andria, Apulia region
Castel del Monte is a 13th-century citadel and castle standing on a promontory. It was constructed during the 1240s by the Emperor Frederick II, who had inherited the lands from his mother, Constance of Sicily.
It has neither a moat nor a drawbridge leading some to conclude that it was never intended as a defensive fortress; On the other hand, archaeological work has suggested that it originally had a curtain wall, so what we see today might be just the keep of the original structure.
The Castel del MonteIt is a World Heritage Site, and appears on the Italian version of the one-cent euro coin. |
||||||||
 |
Alcazar Segovia
The Alcázar of Segovia (literally, Segovia Castle) is a stone fortification, rising out on a rocky crag above the confluence of the rivers Eresma and Clamores near the Guadarrama mountains. It is one of the most distinctive castle-palaces in Spain, shaped like the bow of a ship.
The Alcázar of Segovia, like many fortifications in Spain , started off as an Arab fort, which itself was built on a Roman fort but little of that structure remains.
It has served as a royal palace, a state prison, a Royal Artillery College and a military academy since Moorish times. |
||||||||
 |
Château de Vincennes Avenue de Paris, 94300 Vincennes, Val-de-Marne,
The Château de Vincennes is a massive 14th and 17th century French royal castle now in a a suburb of the metropolis.
This donjon, 52 meters high, was the tallest medieval fortified structure of Europe. |
||||||||
 |
Château de Lassay Lassay-les-Châteaux, Mayenne
The original castrum or castellum here, built in the early years of the twelfth century, was probably a motte and bailey castle.
The present Château de Lassay was classified as a monument historique in 1862 and is still a private residence. |
||||||||
 |
Château de Champlâtreux Epinay-Champlâtreux, Val-d’Oise, Île-de-France
The Château de Champlâtreux was built between 1751 and 1757 by the architect Jean-Michel Chevotet.
It is classified as a Monument Historique |
||||||||
 |
Alcazar Segovia
The Alcázar of Segovia (literally, Segovia Castle) is a stone fortification, rising out on a rocky crag above the confluence of the rivers Eresma and Clamores near the Guadarrama mountains.
It is one of the most distinctive castle-palaces in Spain, shaped like the bow of a ship.
The Alcázar of Segovia, like many fortifications in Spain , started off as an Arab fort, which itself was built on a Roman fort but little of that structure remains. It has served as a royal palace, a state prison, a Royal Artillery College and a military academy since Moorish times. |
||||||||
 |
Château de Val Les Fontilles, 15270 Lanobre, Cantal
The Château is located on the shore of the Lake Bort-les-Orgues
It is classé as a Monument historique |
||||||||
 |
Château de la Servayrie, Mouret, Marcillac-Vallon, Rodez, Aveyron, Midi-Pyrénées, FRANCE. |
||||||||
 |
Minaret of Great Mosque Samarra,
The Great Mosque of Samarra was a 9th-century mosque commissioned in 848 and completed in 851 by the Abbasid caliph Al-Mutawakkil.
The Great Mosque of Samarra was at one time the largest mosque in the world; its minaret, the Malwiya Tower, is a vast spiralling cone 52 meters high and 33 meters wide with a spiral ramp.
The mosque was destroyed in 1278 CE after the Hulagu Khan invasion of Iraq. Today, only the outer wall and its minaret remain. |
||||||||
 |
Paro Taktsang located in the cliffside of the upper Paro valley, Bhutan
Paro Taktsang is an alternative name for what is properly known as the Taktsang Palphug Monastery, known in English as the Tiger's Nest). It is a prominent Himalayan Buddhist sacred site and temple complex. A temple complex was first built in 1692, around the Taktsang Senge Samdup cave where Padmasambhava, a noted Guru, is said to have meditated in the 8th century.
Padmasambhava is credited with introducing Buddhism to Bhutan and is the tutelary deity of the country. |
||||||||
 |
Château de Combourg Ille-et-Vilaine, Brittany
Privately owned, the Château de Combourg stands on a small hill next to Lac Tranquille in the town of Comburg. The original castle here was built around 1025 by Archbishop Guinguené, who gave it to his illegitimate brother Riwallon.
Alterations were made between the 15th and 19th centuries.
The castle now consists of four large, powerful rectangular buildings of dressed granite, with crenellations, machicolations, and roofs, enclosing a rectangular courtyard. In each corner is a round tower, also with crenellations and machicolations, and with conical roofs. |
||||||||
 |
|||||||||
 |
Grand Gallery Strawberry Hill House Twickenham, London
Strawberry Hill House, often referred to simply as Strawberry Hill, is the Gothic Revival villa built by Horace Walpole from 1749. It as so influential that is the exemplar of a style known as "Strawberry Hill Gothic". It prefigured the nineteenth-century Gothic revival.
Walpole rebuilt the existing house in stages in 1749, 1760, 1772 and 1776. He progressively added gothic features such as towers and battlements outside and elaborate decoration inside to create "gloomth" to suit his collection of antiquarian objects.
After a £9 million, two-year-long restoration, Strawberry Hill House reopened to the public in 2010 |
||||||||
 |
Château de Vufflens (Vufflens Castle), Vufflens-le-Château, Vaud
A castle was built here in 1425 by Henri de Colombier on the site of a previous medieval castle. Of Henri Colombier's structure, the donjon, several towers, outbuildings, curtain wall and the gate-house survive.
In 1641 it was acquired by the de Senarclens family. .
Today the castle is a Swiss heritage site of national significance. It is currently privately owned and cannot be visited by the general public.
|
||||||||
 |
Musée National Château de Pau Pau, Pyrénées-Atlantiques
The Château de Pau is a castle in the centre of Pau, the capital of Pyrénées-Atlantiques and Béarn. The château is located in the centre of Pau and dominates that quarter of the city
King Henry IV of France and Navarre was born here on December 13, 1553. The castle has a small garden that was tended by Marie Antoinette when she spent much of the summer in the city. The castle was used by Napoleon as a holiday home during his period of power.
The castle is classified as a Monument historique since 1840 by the French Ministry of Culture. The castle now contains a collection of tapestries. |
||||||||
 |
Tarasp Castle Lower Engadin, Graubünden
Chastè da Tarasp (Tarasp Castle or in German, Schloss Tarasp) sits on a hill top near Tarasp.
Located in the Romansh speaking area of Switerland, it is a Swiss heritage site of national significance. |
||||||||
 |
Château de Najac Najac, Aveyron département
The the royal fortress of Najac was built in 1253 on the orders of Alphonse de Poitiers, brother of Saint Louis, on the site of a square tower built in 1100 by Bertrand of St Gilles, son of Raymond IV, Count of Toulouse before the area was annexed by France.
The castle is built at the summit of a hill formed by a loop of the river.
The castle holds a world record for its 6.80 metre high archères (arrow loops), designed to allow use by three archers at the same time. A secret corridor, hidden within the walls, links the Romanesque tower to the chapel of the keep.
Najac has been near major events including, the Albigensian Crusade, the Hundred Years' War, the imprisonment of the Knights Templar, the peasants' revolts, and the French Revolution.
The castle has been listed as a monument historique by the French Ministry of Culture since 1925. |
||||||||
 |
Fyvie Castle Fyvie, near Turriff, Aberdeenshire
The earliest parts of Fyvie Castle date from the 13th century - some sources claim it was built in 1211 by William the Lion. Fyvie was the site of an open-air court held by Robert the Bruce. Charles I lived there as a child.
Inside, the castle stronghold features a great wheel stair, a display of original arms and armour, and a collection of portraits.
The Scottish industrialist Alexander Leith (later Baron Leith of Fyvie) bought the castle in 1885. It was sold to the National Trust for Scotland by his descendants in 1984. |
||||||||
 |
Château de Suscinio (or de Susinio) Sarzeau, Morbihan, Brittany
Built in the late Middle Ages as the residence of the Dukes of Brittany.
The Château de Suscinio dates from the beginning of the 13th century. It was enlarged at the end of 14th century, when the heirs of the duchy were fighting to keep their possessions (Brittany was not annexed by France until 1514).
From 1471 to 1483, the castle was home to Jasper Tudor, Henry Tudor (later King Henry VII of ENGLAND), and the core of their group of exiled Lancastrians, numbering about 500 by 1483. Duke Francis II supported this group of exiles against Plantagenet demands for their surrender. |
||||||||
 |
Schloss Greyerz / Château de Gruyères) Rue du Château 8, 1663 Gruyères, Fribourg
The Castle is one of the most famous in Switzerland. |
||||||||
|
|
|||||||||
 |
Château de Durtal, Durtal, Maine-et-Loire
Thie photograph shows one tower.
The château was classé as a monument historique en 1900. |
||||||||
 |
Montal Castle Saint-Jean-Lespinasse, Lot, Midi-Pyrénées
The Château de Montal, situated in the vallée de la Bave, is a Renaissance château with two wings flanking the courtyard. It has three round and one square tower.
It was classified as historical monument in 1909. |
||||||||
 |
Château de Suscinio (or de Susinio) Sarzeau, Morbihan, Brittany
Built in the late Middle Ages as the residence of the Dukes of Brittany.
The Château de Suscinio dates from the beginning of the 13th century. It was enlarged at the end of 14th century, when the heirs of the duchy were fighting to keep their possessions (Brittany was not annexed by France until 1514).
From 1471 to 1483, the castle was home to Jasper Tudor, Henry Tudor (later King Henry VII of ENGLAND), and the core of their group of exiled Lancastrians, numbering about 500, by 1483. Duke Francis II supported this group of exiles against Plantagenet demands for their surrender. |
||||||||
 |
Château de Chenonceau Chenonceau, Indre-et-Loire
The estate of Chenonceau is first mentioned in writing in the 11th century. The current château was built in 1514–1522 on the foundations of an old mill and was later extended to span the river.
The bridge over the river was built (1556-1559) to designs by the French Renaissance architect Philibert de l'Orme, and the gallery on the bridge (1570–1576) to designs by Jean Bullant
The château has been classified as a Monument historique since 1840 by the French Ministry of Culture. It is one of the most famous Loire Valley châteaux. |
||||||||
 |
Château d'Harcourt Harcourt, Eure
The Château d'Harcourt is the cradle of the Harcourt family. The first stone castle here was built by Robert II d'Harcourt, a crusader companion of Richard Lionheart.
Harcourts appear later among the most important barons of Normandy. Jean II d'Harcourt was a Maréchal de France.
The castle is one of the best preserved castles in the country and contains the oldest arboretum in France. |
||||||||
 |
Bodiam Castle East Sussex
Bodiam Castle is a 14th-century moated castle. It was built in 1385 by Sir Edward Dalyngrigge, a former knight of Edward III, with the permission of Richard II, to defend the area against French invasion during the Hundred Years' War.
Bodiam Castle has a quadrangular plan. It has no keep, having its various chambers built around the outer defensive walls and inner courts. The corners and entrance are marked by crenellated towers.
It was the home of the Dalyngrigge family and the centre of the manor of Bodiam. The castle is protected as a Grade I listed building and Scheduled Monument. It has been owned by The National Trust since 1925, having been donated by Lord Curzon on his death. It is open to the public. |
||||||||
 |
Samdrubtse Dzong or Shigatse Dzong Shigatse
Samdrubtse Dzong was probably built in the 15th century. It looked like a smaller version of the Potala. It had had turret-like fortifications at the ends and a central Red Palace.
It used to be the seat of the kings of Ü-Tsang and the capital of the province of Ü-Tsang or Tsang
The castle was totally dismantled at the instigation of the Chinese in 1961. Between 2005 and 2007, the building was reconstructed in concrete, and wainscotted with natural stones. |
||||||||
 |
Buckingham Palace, Westminster, London
Buckingham Palace is the official London residence and principal workplace of the monarch of the United Kingdom.. The palace is often at the centre of state occasions and royal hospitality. It is also a focus at times of national rejoicing.
Originally known as Buckingham House, the building which forms the core of today's palace was a large townhouse built for the Duke of Buckingham in 1703.
It was acquired by King George III in 1761 as a private residence for Queen Charlotte and was then known as "The Queen's House". |
||||||||
 |
Pernstejn Castle Nedvedice, South Moravian Region
Pernštejn Castle (Czech: hrad Pernštejn) is located on a rock above the village of Nedvedice and the rivers Svratka and Nedvedicka, some 40 km northwest of Brno.
Pernštejn came to be known as the marble castle because of the marble-like stone used to frame the doors and windows. |
||||||||
 |
Château de Val Les Fontilles, 15270 Lanobre, Cantal
The Château is located on the shore of the Lake Bort-les-Orgues.
It is classé as a Monument historique. |
||||||||
 |
Château de Boulogne sur Mer Boulogne-sur-Mer, Pas-de-Calais
The castle was built in the 13th century by Philippe Hurepel (1180-1234), count of Boulogne and son of Philip II of France. It houses the Boulogne museum. |
||||||||
 |
Château de Sceaux Sceaux, Hauts-de-Seine
The Château de Sceaux is a grand country house not far from Paris. Located in a park laid out by André Le Nôtre, it houses the Musée de l’Île-de-France, a museum of local history.
The former château was built for Jean-Baptiste Colbert, Louis XIV's minister of finance, who purchased the domaine in 1670.
The present château, designed to evoke the style of Louis XIII, dates from the Second Empire. Some of Colbert's outbuildings remain, as does the basis of the garden layout.
|
||||||||
 |
Château de la Madeleine Chevreuse, département of Yvelines, Île de France
The construction of the Château de la Madeleine began between 1020 and 1090, under Guy I, Lord of Chevreuse. From this period, only the keep remains. Originally, the keep was surrounded by a wooden palisade, replaced by stone curtain walls during the 12th century.
A century later, probably under Anseau de Chevreuse, the castle was modified, notably with the construction of the machicolations. The gatehouse was protected by a moat.
The castle changed hands in 1356. Ingerger le Grand, Lord of Chevreuse and Amboise, was taken prisoner by ENGLAND during the Hundred Years' War. He was obliged to sell his domain to pay his ransom; the castle was bought by the future Pierre de Chevreuse.
The existing fortifications were improved under the reigns of Charles V and Charles VI; who financed the outworks with royal taxes. Modifications were completed under Louis XI (1461 – 1483). The village was also fortified: a crenelated rampart, 3.5 m high (11.5 feet) with turrets, was built. The defence was completed by a 15 m large ditch (50 feet). |
||||||||
 |
Conisbrough Castle Conisbrough, South Yorkshire
Conisbrough Castle is a 12th-century castle, whose remains are dominated by the 97-foot (29.5m) high circular keep, supported by six buttresses. It is shown here as it would have looked before falling into ruin.
The site, strategically placed in one of few historic crossings of the River Don, has been home to a fortification since at least 600 AD. It belonged to one of the seven English kings, prior to the unification of ENGLAND.
In the mid-1990s, the keep was restored, The building is one of South Yorkshire's primary tourist attractions. It is managed by English Heritage. |
||||||||
 |
Château de Najac Najac, Aveyron département
The the royal fortress of Najac was built in 1253 on the orders of Alphonse de Poitiers, brother of Saint Louis, on the site of a square tower built in 1100 by Bertrand of St Gilles, son of Raymond IV, Count of Toulouse before the area was annexed by France.
The castle is built at the summit of a hill formed by a loop of the river.
The castle holds a world record for its 6.80 metre high archères (arrow loops), designed to allow use by three archers at the same time. A secret corridor, hidden within the walls, links the Romanesque tower to the chapel of the keep.
Najac has been near major events including, the Albigensian Crusade, the Hundred Years' War, the imprisonment of the Knights Templar, the peasants' revolts, and the French Revolution.
The castle has been listed as a monument historique by the French Ministry of Culture since 1925. |
||||||||
 |
Novgorod Kremlin Walls Novgorod Oblast
Novgorod Kremlin (also Detinets) stands on the left bank of the Volkhov River in Veliky Novgorod. The compound was originally the site of a pagan burial ground upon which the first bishop of Novgorod built the Cathedral of Holy Wisdom around 989.
The current fortress was built between 1484 and 1490 by Muscovite builders following Grand Prince Ivan III's conquest of the city in 1478; a third of it was paid for by the Novgorodian archbishop Gennady.
It is eliptical, 545 meters long and 240 meter wide with nine surviving towers (three other towers have not survived). The walls are 1,487 meters in circumference.
UNESCO recognised Novgorod as a World Heritage Site in 1992 |
||||||||
 |
Trerice Kestle Mill, near Newquay, Cornwall, ENGLAND
Trerice is an Elizabethan manor house, The building features a main south-east facing range of 'E'-plan abutting a south-west range containing two earlier phases.
Phase I consisted of a tower house with low north-west block. This was extended early in the 16th century, probably by 'Jack of Tilbury', to include a 2-storey range to the south-east of the earlier tower, together now forming the bulky south wing.
Sir John IV Arundell, High Sheriff of Cornwall added the main range of the E-plan circa 1570-1573. At the period it was fashionable build house with an E shaped plan (E for Queen Elizabeth)
The house, along with its surrounding garden, is a National Trust property. |
||||||||
 |
Château Solvay, also called the Château de La Hulpe La Hulpe, Walloon Brabant, BELGIUM.
The château was built by the Marquis de Béthune in the French style in 1842. In the late 19th century, the house and estate were acquired by Ernest Solvay, and have since been known as the Domaine Solvay.
Today the property is owned by the regional government of Wallonia, and is classified as an "Exceptional Heritage Site in Wallonia." The grounds are open to the public. |
||||||||
 |
Schloss Hohenzollern (Hohenzollern Castle) 72379 Burg Hohenzollern, Hechingen, Baden-Wurtemberg, GERMANY
Hohenzollern Castle is the ancestral seat of the Hohenzollern family, who became German Emperors
A castle was first constructed here in the early 11th century. The present castle was constructed for King Frederick William IV of Prussia between 1846 and 1867. The design was based on English Gothic Revival architecture and the Châteaux of the Loire Valley.
In 1945 it became home to the former Crown Prince Wilhelm of GERMANY, son of the last Hohenzollern monarch, Kaiser Wilhelm II, who is buried there with his wife, Crown Princess Cecilie. |
||||||||
 |
Dunster Castle Dunster, Somerset, ENGLAND.
Dunster Castle is a former motte and bailey castle, now a country house, sited on top of a Tor. The site has been fortified since the late Anglo-Saxon period.
A stone shell keep was built on the motte by the start of the 12th century, and the castle survived a siege during the early years of the Anarchy. At the end of the 14th century the de Mohuns sold the castle to the Luttrell family, who continued to occupy the property until the late 20th century.
The castle was expanded several times by the Luttrell family during the 17th and 18th centuries; they built a large manor house within the Lower Ward of the castle in 1617.
The medieval castle walls were mostly destroyed following the siege of Dunster Castle at the end of the English Civil War, when Parliament ordered the defences to be slighted to prevent their further use.
In the 1860s and 1870s the castle was remodelled to Victorian tastes.
In 1976 Colonel Walter Luttrell gave Dunster Castle and most of its contents to the National Trust, which now operates it as a tourist attraction. It is a Grade I listed building and scheduled monument. |
||||||||
 |
Schloss Irmelshause Irmelshausen, Höchheim, Rhön-Grabfeld, Bavaria, GERMANY.
Irmelshausen lies on the old border between East and West GERMANY. It is one of the most appealing castles in Franconia, first mentioned in the year 800 when Emhild, the Abbess of Milz and a relative of Charlemagne, gave the associated village to the Counts of Henneberg.
The castle escaped attack and destruction in both the Peasants' War of 1525 and the Thirty Years' War of 1618-48 when almost all the surrounding castles were taken and sacked. Parts of the castle were previously taller but during a remodeling in 1854 the half-timbered sections were lowered to the present height. |
||||||||
 |
Gwalior Qila (Gwalior Fort) Gwalior, Madhya Pradesh
Gwalior Fort is an 8th-century hill in central India. The fort consists of a defensive structure and two main palaces, Gurjari Mahal and Man Mandir. |
||||||||
 |
Le château de Lavoûte-Polignac Lavoûte-sur-Loire, Haute-Loire, FRANCE
It is one of the châteaux of the Loire.
It was for centuries one of the favourite rences of the Polignac family. Like most other French château it was siezed by the state in 1793 (the Polignac family having escaped to Vienna) and sold off as a "national good".
In the nineteenth century the Polignac family bought it back, and Melchior, Comte de Polignac, had the south aisle repaired (the other two wings having fallen too far into ruin). |
||||||||
 |
The Potala Palace Lhasa
The Potala Palace was the chief residence of the Dalai Lama until the 14th Dalai Lama fled to India during the 1959 Tibetan uprising.
It is now a museum and UNESCO World Heritage Site. |
||||||||
 |
Dar Al Hajar Wadi Dhahr Valley
Dar al-Hajar, also known as the Imam's Rock Palace is perched on top of a rock pinnacle, some 15 km away from the capita city of Sana.
It is typical of Yemeni architecture, seeming to grow out of the rocks on which it is constructed, and with characteristic Yemeni painting of its windows and building edges.
The palace was built in the 1930s by Imam Yahya as his summer residence (Most of the apparently ancient castles in this part of the world are less than a century old)
The palace has been restored for visitors, and turned into a museum. |
||||||||
 |
lo Palais dei Papas (in Occitan) / The Palais des Papes / Papal Palace Avignon, southern FRANCE.
The Papal Palace is one of the largest and most important medieval Gothic buildings in Europe.
Fortress and palace, it was the seat of Western Christianity during the 14th century. Six papal conclaves were held in the Palais.
The Palais is actually made up of two buildings: the old Palais of Benedict XII on the rock of Doms, and the new Palais of Clement VI, the most extravagant of the Avignon popes.The final combination the largest Gothic building of the Middle Ages, and one of the best examples of the International Gothic architectural style.
Since 1995 lo Palais dei Papas has been classified, along with the historic center of Avignon, as a UNESCO World Heritage Site. |
||||||||
 |
Château de Potelle (or Château de Potelles) Potelle, Nord, Nord-Pas-De-Calais, FRANCE.
The Château de Potelles was built around 1290 by Willes (Gilles) de Mortagne, seigneur de Potelles (the chapel retains a fragment of his tomb). The châtelet (entry gate) on the left in the photograph dates from the fourteenth century
Le château and its chapel (outside the moat) were incrit as monuments historiques in1944. |
||||||||
 |
Château de Meillant Meillant, Cher, Centre, FRANCE
Château de Meillant is a Renaissance Château with elements dating from the thirteenth century.
It was Inscrit in 1926, and classé as a monument historique 1963 |
||||||||
 |
The Potala Palace Lhasa
The Potala Palace was the chief residence of the Dalai Lama until the 14th Dalai Lama fled to India during the 1959 Tibetan uprising.
It is now a museum and UNESCO World Heritage Site. |
||||||||
 |
Château de Bannes Beaumont-du-Périgord, Dordogne, Aquitaine, FRANCE.
Built between 1498 and 1519. |
||||||||
 |
Château d'Illasi Via Strada Nuova, 37031 Illasi, Verona, ITALY.
The Château d'Illasi is situated between the valleys of Illasi and Tramigna. Of the original structure only the gateway, a small tower, the remains of a chapel, two cisterns, the keep and 30meter high square tower remain.
The keep was transformed into a country house by the descendants of Malachino. It was inhabited up until 1737 when Giunio III Pompei built a large villa at Illasi, which now surrounds the castle ruins.
The site is now the property of the Sagramoso-Pompei Family and is not open to the public. |
||||||||
 |
Château de Caussade Trélissac, Périgueux, Dordogne, Aquitaine, FRANCE.
The Château de Caussade is a small polygonal fortress surrounded by a dry moat, located in the vallée de l’Isle, in the forêt de Lanmary.
It held great strategic importance in the twelfth century. From the Twelfth to the Fourteenth century it was the property of VIigier family, a daughter of the family became the wife of the famous troubadour, Bertran de Born. |
||||||||
 |
Langley Castle Langley, Northumberland, ENGLAND.
Langley Castle is a restored medieval tower house, situated in the valley of the River South Tyne south of Haydon Bridge,
The south west tower boasts 12 garderobes, four to each floor.
It is a Grade I listed building. |
||||||||
 |
|||||||||
 |
Blair Castle, Blair Atholl, Perthshire, SCOTLAND
Blair Castle is the ancestral home of the Clan Murray, and was historically the seat of their chief, the Duke of Atholl,
The castle stands in Glen Garry, and commands a strategic position on the main route through the central Scottish Highlands.
The oldest part of the castle is the six-storey Cummings or Comyn's Tower, which retains some13th-century fabric, though it was largely built in the 15th century.
The castle is a category A listed building, and the grounds are included in the Inventory of Gardens and Designed Landscapes in Scotland. |
||||||||
 |
Château de la Madeleine Chevreuse, département of Yvelines, Île de France, FRANCE.
The construction of the Château de la Madeleine began between 1020 and 1090, under Guy I, Lord of Chevreuse. From this period, only the keep remains.
Originally, the keep was surrounded by a wooden palisade, replaced by stone curtain walls during the 12th century. A century later, probably under the reign of Anseau de Chevreuse, the castle was modified, notably with the construction of the machicolations. The gatehouse was protected by a moat.
The castle changed hands in 1356. Ingerger le Grand, Lord of Chevreuse and Amboise, was taken prisoner by the English during the Hundred Years' War. He was obliged to sell his domain to pay his ransom; the castle was bought by the future Pierre de Chevreuse.
The existing fortifications were improved under the reigns of Charles V and Charles VI; who financed the outworks with royal taxes. Modifications were completed under Louis XI (1461 – 1483).
The village was also fortified: a crenelated rampart, 3.5 m high (11.5 feet) with turrets, was built. The defence was completed by a 15 m large ditch (50 feet). |
||||||||
 |
The Château de Mauvezin Mauvezin, Hautes-Pyrénées, FRANCE.
The site, occupied since the Dark Ages, was transformed into a castrum in the Middle Ages. The castle was built by Gaston Phoebus around 1380.
Following the merging of Bigorre into the Kingdom of France in 1607, the castle fell into disuse and was dismantled, its stones used for other buildings.
Today, the castle is being restored and is listed as a monument historique by the French Ministry of Culture. |
||||||||
 |
Château de Menthon Saint-Bernard |
||||||||
 |
Château de la Motte Acqueville, l’Orne, Normandie, FRANCE |
||||||||
 |
Schloss Augustusburg, Brühl, North Rhine-Westphalia, GERMANY.
UNESCO world heritage site. |
||||||||
 |
Château Saint-Hilaire, Sud de Louviers, Eure, Haute-Normandie, FRANCE |
||||||||
 |
Citadelle de Corté Corte en Haute-Corse, Corsica, FRANCE
The Citadelle de Corte also known as the Nid d'aigle (Eagle's Nest) is an eighteenth century citadelle, build around a fifteenth century core, and now housing a museum of Corsica.
It has been classée as a monument historique in 1977. |
||||||||
 |
Coca Castle Coca, Segovia, Castile-Leon, SPAIN
The castle was built on the site of ancient Cauca, the birthplace of the Roman emperor Theodosius. This area was populated by the Arevaca in the 2nd century BC.
Begun in 1448 by Don Alonso de Fonseca (1418–1473), Bishop of Avila and Archbishop of Seville, the castle wast still unfinished at the end of the 15th century.
Coca is an example of the Mudéjar style, combining elements drawn from Islamic traditions with Flamboyant Gothic. |
||||||||
 |
Sigiriya near the town of Dambulla, central Matale District, Central Province
Sigiriya (Lion Rock) is an ancient palace which you can just make out at the top left of the rock. |
||||||||
 |
La Torre Monreal Tudela, Navarra, SPAIN
A tower of Arab origin |
||||||||
 |
Sandcastle |
||||||||
 |
Castillo de Cullera Cullera, Valencia, SPAIN |
||||||||
 |
Castell de Mur Lleida, Catalonia, SPAIN |
||||||||
 |
Atalaya Castle (Castillo de la Atalaya or Castillo de Villena) Villena, province of Alicante, southern SPAIN.
It commands the former frontier between Castile and Kingdom of Aragon. |
||||||||
 |
Parador de Cardona or Castell de Cardona Cardona, Barcelona, Catalonia |
||||||||
 |
Château de Caussade 24 Trélissac, Dordogne, Périgord, FRANCE |
||||||||
 |
Château d'Harcourt, Harcourt, Eure, FRANCE
The Château d'Harcourt is the cradle of the Harcourt family. The first stone castle here was built by Robert II d'Harcourt, a crusader companion of Richard Lionheart.
Harcourts appear later among the most important barons of Normandy. Jean II d'Harcourt was a Maréchal de France.
The castle is one of the best preserved castles in the country and contains the oldest arboretum in France. |
||||||||
 |
Château d'Harcourt Harcourt, Eure, FRANCE
The Château d'Harcourt is the cradle of the Harcourt family. The first stone castle here was built by Robert II d'Harcourt, a crusader companion of Richard Lionheart.
Harcourts appear later among the most important barons of Normandy. Jean II d'Harcourt was a Maréchal de France.
The castle is one of the best preserved castles in the country and contains the oldest arboretum in France. |
||||||||
|
|
|||||||||
 |
Schloss Seehof Domplatz 8, Memmelsdorf, 96049 Bamberg, Bavaria, GERMANY
The Seehof Palace was built from 1686 as a summer residence for the Prince-Bishops of Bamberg
|
||||||||
 |
Château de Lassay Lassay-les-Châteaux, Mayenne, FRANCE.
The original castrum or castellum here, built in the early years of the twelfth century, was probably a motte and bailey castle.
The present Château de Lassay was classified as a monument historique in 1862 and is still a private residence. |
||||||||
 |
Château de la Rochepot La Rochepot, Côte d'Or département, Burgundy, FRANCE.
The Château de la Rochepot is a 13th-century castle, later converted into a château, on the N6 to the south west of the town of Beaune.
The castle was built in the 13th century on an outcrop of limestone to the north of the village of La Rochepot. As with many castles, it fell into ruin after the medieval period and was restored in the 19th century. It is open to visitors. |
||||||||
 |
Château de la Roche-Jagu Ploëzal, Côtes-d'Armor, Bretagne, FRANCE. |
||||||||
 |
Château de Puilaurens Lapradelle-Puilaurens, Aude département, Laguedoc-Roussillon, FRANCE
The Château de Puilaurens (also Puylaurens; in Occitan: lo Castèl de Puèg-Laurenç) is one of the so-called Cathar castles in what is now the South of France.
The castle stands on a spur of rock above the Boulzane Valley and the villages of Lapradelle and Puilaurens. |
||||||||
 |
Château-Gaillard commune of Les Andelys overlooking the River Seine, in the Eure département of historical Normandy, now Upper Normandy, FRANCE.
Château Gaillard is a ruined medieval castle. Construction began in 1196 under the auspices of Richard the Lionheart, King of ENGLAND and Duke of Normandy. The castle was built in just two years, at the same time the town of Petit Andely
Château Gaillard has a complex and advanced design - it was possibly designed by Richard himself. It uses principles of concentric fortification It was also one of the earliest European castles to use machicolations - an idea that Richard might well have brought back from the Holy Land. The castle consists of three enclosures separated by dry moats, with a keep in the inner enclosure.
Château Gaillard was captured in 1204 by the French king Philip II, after a lengthy siege. In the mid-14th century, the castle became the residence of the exiled David II of Scotland.
The castle changed hands several times in the Hundred Years' War, but in 1449 the French captured Château Gaillard from the English for the last time, and from then on it remained in French ownership. Henry IV of France ordered the demolition of Château Gaillard in 1599; The castle ruins are listed as a monument historique by the French Ministry of Culture. |
||||||||
 |
Château de Azay-le-Rideau Azay-le-Rideau, Chinon, Indre-et-Loire, Centre, FRANCE |
||||||||
 |
Kitchen, The Château de Biron, Biron, Dordogne, FRANCE
The Château de Biron is a large castle in the valley of the Lède. It was the castle from which the Gontaut-Biron took their name. It was their seat from the twelfth century. Biron was seized by Simon IV de Montfort in 1212 from forces sypathetic to the Cathars.
The Plantagenets held it at times during the 14th and 15th centuries. Biron was erected as a duché-pairie in 1598, for Charles de Gontaut, created duc de Biron.
The present château bears additions over the centuries: notably a twelfth-century keep and sixteenth-century living quarters and vaulted kitchens.
Since 1928, it has been listed as a monument historique by the French Ministry of Culture. The local commune purchased the Château de Biron in 1978, with a view to restoring it as a tourist attraction. |
||||||||
 |
Châteaux de Lastours Lastours, département of l'Aude, FRANCE
The Châteaux de Lastours (in Occitan Lastors) are three Cathar castles (and a later French one).
The four castles are on a rocky spur above the village of Lastours, isolated by the deep valleys of the Orbeil and Grésilhou rivers.
They were built at an altitude of 300 m along a rock wall just 1300 feet (~400 m) long by 165 feet (~50 m) wide.
Cabaret, Surdespine and la Tour Régine [the French one] stand in line, while Quertinheux is built on a separate pinnacle close by.
The site has been classified monument historique (historic monument) by the French Ministry of Culture since 1905. Archaeological digs are still in progress. |
||||||||
 |
Caldicot Castle (Welsh: Castell Cil-y-coed) Caldicot, Monmouthshire, southeast WALES.
Caldicot Castle is an extensive stone medieval castle in the built near the site of Harold Godwinson's former Saxon castle by the Norman earls of Hereford from about 1100
The castle became a Grade I listed building in 1953. |
||||||||
 |
Killyleagh Castle Killyleagh, County Down, Northern Ireland.
Killyleagh Castle dominates the small village of Killyleagh
It is believed to be the oldest inhabited castle in the country, parts dating back to 1180.
Killyleagh Castle follows the architectural style of a Loire Valley château, having been redesigned by architect Sir Charles Lanyon in the mid-19th century.
It has been owned by the Hamilton family since the early 17th century. |
||||||||
 |
Château de Combourg Combourg, Ille-et-Vilaine, Brittany, FRANCE.
The castle stands on a small hill next to Lac Tranquille (Lake Tranquil) in the town.
Privately owned, the Château de Combourg is listed as a monument historique by the French Ministry of Culture. |
||||||||
|
|
|||||||||
 |
Schloss Berlepsch Witzenhausen, GERMANY
Berlepsch Castle was built in 1298 by Arnold of Berlepsch, on behalf of the landgrave of Hesse to protect this part of Hesse against encrouchments of the Duke of Brunswick.
The castle was rebuilt and extended in the 19th. century.
It still belongs still to the Berlepsch family. |
||||||||
 |
Schönbrunn Palace Vienna
Schönbrunn Palace (or Schloss Schönbrunn) is a former imperial 1,441-room Rococo summer residence.
One of the most important cultural monuments in the country, it is one of the major tourist attractions in Vienna.
The palace and gardens reflect the tastes, interests, and aspirations of successive Habsburg monarchs. |
||||||||
 |
Schloss Wernigerod (Wernigerode Castle) Harz mountains, Saxony-Anhalt, GERMANY.
Wernigerode Castle is a castle located above the town of Wernigerode. The present-day building, finished in the late 19th century, is similar in style to Neuschwanstein Castle, though its foundations are much older. |
||||||||
 |
Château du Sailhant Andelat, Cantal, FRANCE |
||||||||
 |
Castle Bolkow Bolków, Jawor County, Lower Silesian Voivodeship, south-western POLAND.
The ruins of Bolków Castle, built in the 13th century, stand above the town of Bolków.
Devastated in the Thirty Years' War it became a property of Grüssau Abbey in 1703, though restoration efforts did not begin until 1905. |
||||||||
|
|
|||||||||
 |
Kasteel de Haar (Castle De Haar) near Haarzuilens, Province of Utrecht, NETHERLANDS |
||||||||
 |
Château de Chenonceau Chenonceau, Indre-et-Loire, FRANCE
The estate of Chenonceau is first mentioned in writing in the 11th century. The current château was built in 1514–1522 on the foundations of an old mill and was later extended to span the river.
The bridge over the river was built (1556-1559) to designs by the French Renaissance architect Philibert de l'Orme, and the gallery on the bridge (1570–1576) to designs by Jean Bullant
The château has been classified as a Monument historique since 1840 by the French Ministry of Culture. It is one of the most famous Loire Valley châteaux. |
||||||||
 |
Château Solvay, also called the Château de La Hulpe La Hulpe, Walloon Brabant, BELGIUM.
The château was built by the Marquis de Béthune in the French style in 1842.
In the late 19th century, the house and estate were acquired by Ernest Solvay, and have since been known as the Domaine Solvay.
Today the property is owned by the regional government of Wallonia, and is classified as an "Exceptional Heritage Site in Wallonia." The grounds are open to the public. |
||||||||
 |
Château de Blandy-les-Tours Blandy-les-Tours, Seine-et-Marne, FRANCE
(photo shows just one tour)
The Château de Blandy-les-Tours was mentioned in a text in 1216. It belonged to Adam II de Chailly, Viscount of Melun. It consisted of a simple manor and chapel, the only construction made of stone. The site was previously a Merovingian necropolis.
In the 14th century, the castle was modified with new fortifications and structures of defence. A moat was dug and a new gate-tower with a drawbridge was included in the enclosing wall. |
||||||||
 |
Matsumoto Castle, ("Crow Castle")
Matsumoto Castle is one of Japan's premier historic castles. The keep (tenshukaku), was completed in the late sixteenth century, It is listed as a National Treasure of Japan.
Matsumoto Castle is a flatland castle (hirajiro) built on a plain. Its defences would have included an extensive system of inter-connecting walls, moats, and gatehouses. |
||||||||
 |
Dover Castle Dover, Kent, ENGLAND.
Dover Castle was founded in the 12th century and has been described as the "Key to ENGLAND" due to its defensive significance. It is the largest castle in ENGLAND.
During the reign of Henry II t the castle began to take recognisable shape. The inner and outer baileys and the great keep belong to this time. Maurice the Engineer was responsible for building the keep, one of the last rectangular keeps ever built.
Dover Castle is a Scheduled Monument and a Grade I listed building. The castle, its secret tunnels, and surrounding land are owned by English Heritage and the site is a major tourist attraction.
Dover has always been a chief member of the Cinque Ports since their foundation in 1050. The Lord Warden of the Cinque Ports is officially head of the castle, in his conjoint position of Constable of Dover Castle. The Deputy Constable has his residence in Constable's Gate. |
||||||||
 |
Leeds Castle, Kent, ENGLAND
Leeds Castle is in Kent, ENGLAND, 5 miles (8 km) southeast of Maidstone. A castle has been on the site since 1119. In the 13th century it came into the hands of King Edward I, for whom it became a favourite residence; in the 16th century, Henry VIII used it as a residence for his first wife, Catherine of Aragon.
The castle was a location for the 1949 film Kind Hearts and Coronets where it stood in for "Chalfont", the ancestral home of the d'Ascoyne family. The castle also appeared in Moonraker (1958) and Waltz of the Toreadors (1962). It was the set for the Doctor Who episode The Androids of Tara.
The castle today dates mostly from the 19th century and is built on islands in a lake formed by the River Len to the east of the village of Leeds. It has been open to the public since 1976 |
||||||||
 |
Schloss Hohenzollern (Hohenzollern Castle), 72379 Burg Hohenzollern, GERMANY
Schloss Hohenzollern (Hohenzollern Castle) 72379 Burg Hohenzollern, GERMANY
Hohenzollern Castle is the ancestral seat of the Hohenzollern family, who became German Emperors
A castle was first constructed here in the early 11th century. The present castle was constructed for King Frederick William IV of Prussia between 1846 and 1867. The design was based on English Gothic Revival architecture and the Châteaux of the Loire Valley.
In 1945 it became home to the former Crown Prince Wilhelm of GERMANY, son of the last Hohenzollern monarch, Kaiser Wilhelm II, who is buried there with his wife, Crown Princess Cecilie |
||||||||
 |
Château de Vitré Vitré, Ille-et-Vilaine, FRANCE.
The first stone castle was built by the baron Robert I of Vitré at the end of the 11th century. The defensive site chosen, a rocky promontory, dominated the valley of the Vilaine. A Romanesque style doorway still survives from this building. During the first half of the 13th century, baron André III, rebuilt it in its present triangular form, following the contours of the rocks, surrounded with dry moats.
The castle was bought by the town in the 1820 for 8500 francs. In 1872, it was one of the first castles in France to be classified as a monument historique (historic monument) and restored from 1875. |
||||||||
 |
Château de la Goujeonnerie Vendee, FRANCE |
||||||||
 |
Chateau des Plantais Le Donjon, Allier, Auvergne, FRANCE
|
||||||||
 |
Dairsie Castle, Dairsie, north-east Fife, SCOTLAND.
Dairsie Castle is a a restored tower house overlooking the River Eden. A Scottish parliament was held at the castle in early 1335.
The first castle built here was the property of the bishops of St Andrews, and was probably constructed by William de Lamberton, Bishop of St Andrews from 1298 to 1328. |
||||||||
 |
Château d'Amboise Amboise, Indre-et-Loire département, FRANCE
The royal Château at Amboise is a fortress in the Loire Valley. Confiscated by the monarchy in the 15th century, it became a favoured royal residence and was extensively rebuilt. King Charles VIII died at the château in 1498 after hitting his head on a door lintel.
The château fell into decline from the second half of the 16th century and the majority of the interior buildings were later demolished. Some survived and have been restored, along with the outer defensive circuit of towers and walls.
It has been recognised as a monument historique by the French Ministry of Culture since 1840. |
||||||||
 |
Château Fort de Guédelon Treigny, Yonne, Burgundy, FRANCE 2013
Château Fort de Guédelon (Guédelon Castle) is a medieval construction project. The object of which is to build a castle using only the techniques and materials used in the Middle Ages.
Building materials, including wood and stone, are obtained locally. Jacques Moulin, the chief architect for the project, designed the castle according to the architectural model developed during the 12th and 13th centuries by Philip II of France.
Construction started in 1997 under Michel Guyot, owner of Saint-Fargeau castle. The site was chosen in the light of the availability of a stone quarry, in a large forest, with a pond close by.
The project has created 55 jobs and is now a tourist destination, with more than 300 000 visits each year
When completed in the 2020s, it should be an authentic recreation of a 13th-century medieval castle. |
||||||||
 |
Château de Chenonceau Chenonceau, Indre-et-Loire, FRANCE
The estate of Chenonceau is first mentioned in writing in the 11th century. The current château was built in 1514–1522 on the foundations of an old mill and was later extended to span the river.
The bridge over the river was built (1556-1559) to designs by the French Renaissance architect Philibert de l'Orme, and the gallery on the bridge (1570–1576) to designs by Jean Bullant
The château has been classified as a Monument historique since 1840 by the French Ministry of Culture. It is one of the most famous Loire Valley châteaux. |
||||||||
 |
Castle of Carmona Carmona, Seville, SPAIN |
||||||||
 |
Gatehouse Stokesay Castle Shropshire, ENGLAND
Stokesay Castle is a fortified manor house built in the late 13th century by Laurence of Ludlow, then the leading wool merchant in England. Laurence's descendants continued to own the castle until the 16th century. By the time of the outbreak of the English Civil War in 1641, Stokesay was owned by William Craven, the first Earl of Craven and a supporter of King Charles I. After the Royalist war effort collapsed in 1645, Parliamentary forces besieged the castle in June and quickly forced its garrison to surrender. Parliament ordered the property to be slighted, but only minor damage was done to the walls, allowing Stokesay to continue to be used as a house by the Baldwyn family until the end of the 17th century.
Architecturally, Stokesay Castle is one of the best-preserved medieval fortified manor houses in England. The castle comprises a walled, moated enclosure, with an entrance way through a 17th-century timber and plaster gatehouse. Inside, the courtyard faces a stone hall and solar block, protected by two stone towers. The hall features a 13th-century wooden-beamed ceiling, and 17th-century carved figures ornament the gatehouse and the solar. The castle was never intended to be a serious military fortification, but its style was intended to echo the much larger castles being built by Edward I in North Wales. Originally designed as a prestigious home, the castle has changed very little since the 13th century, and is a rare example of a near complete set of medieval buildings. |
||||||||
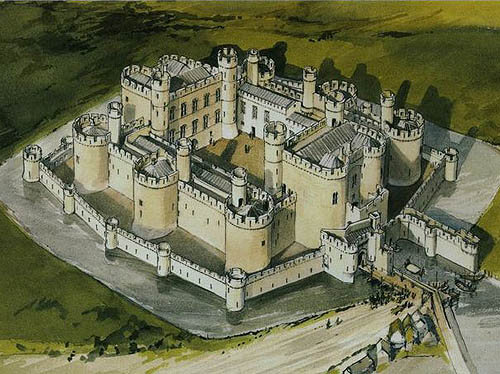 |
Beaumaris Castle Beaumaris Isle of Anglesey, WALES.
Concentric castle built by Edward I - as it might have looked if completed. |
||||||||
 |
Het Loo Palace Apeldoorn, NETHERLANDS |
||||||||
 |
Thyme Walk Highgrove House Doughton, Gloucestershire, ENGLAND
Highgrove House is the country home of Prince Charles, situated southwest of Tetbury. Highgrove House was purchased in 1980 by the Duchy of Cornwall which manages the house and the estate surrounding the house.. |
||||||||
 |
Schloss Nordkirchen Nordkirchen, Coesfeld administrative district, North Rhine Westphalia, GERMANY.
Schloss Nordkirchen is a palace, largely built between 1703 and 1734. It is known as the "Versailles of Westphalia" since it is the largest of the fully or partly moated Wasserschlösser in the region.
It was originally one of the residences of the Prince-Bishopric of Münster. |
||||||||
 |
Castillo de San Marcos St. Augustine, Florida, USA
The Castillo de San Marcos is the oldest masonry fort in the continental United States. Located on the shore of Matanzas Bay, construction began in 1672, 107 years after the city's founding by Spanish Admiral and conquistador Pedro Menéndez de Avilés, when Florida was part of the Spanish Empire.
After Britain gained control of Florida in 1763, St. Augustine became the capital of British East Florida, and the fort was renamed Fort St. Mark until the Peace of Paris (1783) when Florida was transferred back to Spain. In 1819 Spain signed the Adams–Onís Treaty which ceded Florida to the United States in 1821 and the fort became a United States Army base which was renamed Fort Marion. In 1942 the original name, Castillo de San Marcos, was restored by an Act of Congress. The fort was declared a National Monument in 1924 and after 251 years of continuous military possession, the fort was deactivated in 1933 and the site was turned over to the United States National Park Service. |
||||||||
 |
Citadel of Aleppo Aleppo
The Citadel of Aleppo is a large medieval fortified palace in the centre of the old city. It one of the oldest and largest castles in the world. Usage of the Citadel hill dates back at least to the middle of the 3rd millennium BC. Subsequently occupied by many civilizations including the Greeks, Byzantines, Ayyubids and Mamluks, the majority of the construction as it stands today is thought to originate from the Ayyubid period. Extensive conservation work has taken place in the 2000s by the Aga Khan Trust for Culture in collaboration with Aleppo Archeological Society.
Dominating the city, the Citadel is part of the Ancient City of Aleppo, a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 1986. The Citadel received significant damage in the Syrian Civil War from 2013. |
||||||||
 |
Cité de Carcassonne, Languedoc, FRANCE.
The Castrum of Raymond Roger Trencavel, Viscount of Carcassonne, Béziers, Albi and the Razès. He died in his own prison here in 1209, aged 24, after being taken prisoner while under a safe-conduct from the Cistercian Abbot Arnaud Amaury the papal legate and military leader of the Albigensian Crusade who was besieging Carcassonne (and who then appointed Simon de Montfort as military leader of the crusade).
Castrum = Cité + château Comtal
UNESCO World Heritage Site |
||||||||
 |
Wasserschloss Haus Bodelschwingh, Mengede, Dortmund, GERMANY
Wasserschloss Haus Bodelschwingh (Bodelschwingh Castle) is a moated castle. It was built in the 13th century by the family of Bodelschwinghstraße and is still owned by the family
Bodelschwingh castle is located near to the water tower house Dellwig and the moated castle Haus Rodenberg the largest and most important water castle in Dortmund.
Near the castle developed a settlement, Bodelschwinghstraße, which kept its independence until 1928. Today, the district of Bodelschwinghstraße belongs to the municipality of Mengede.
The castle is registered as a historic landmark in the list of monuments of the city of Dortmund. |
||||||||
 |
Vianden Castle Vianden
Vianden Castle (French: Château de Vianden, German: Burg Vianden Luxembourgish: Buerg Veianen), is located in Vianden, in the north of Luxembourg.
Vianden is one of the largest fortified castles west of the Rhine. Its origins date to the 10th century. The castle was built in the Romanesque style between the 11th and 14th centuries. Gothic aspects were added at the end of this period.
A Renaissance mansion was added in the 17th century. After the seventeenth century the castle was allowed to fall into ruin, and has recently been restored.
It is now open to visitors. |
||||||||
 |
La Torre del Oro, Seville, SPAIN |
||||||||
 |
Château de Germolles Mellecey, Burgundy, FRANCE.
The Château de Germolles is the best preserved of the residences of the Dukes of Burgundy. Built during the second part of the 14th century, it is important for the history of the region and a rare example of a well-preserved surviving 14th Century French castle.
It has been listed as a Historic monument since 1989. |
||||||||
 |
Parterre The Château de Villandry Villandry Indre-et-Loire |
||||||||
 |
Divinity School, Oxford |
||||||||
 |
Castello a San Leo Novafeltria, Emilia-Romagna, provincia di Rimini, ITALY |
||||||||
 |
Waldeck Castle Dorweiler, Dommershausen, Rhein-Hunsrück-Kreis, Rhineland-Palatinate. GERMANY.
William I of Heinzenberg built the fortress in 1150 establishing the house of "Boos-Waldeck". This was the main seat of the Hunsrück Family Boos.
The mediaeval castle saw several wars, and was partially destroyed by the French (1689) in the course of the Nine Years' War. The castle was in use until 1833 when the family of Boos von Waldeck sold its holdings in the Rhineland. |
||||||||
 |
Château de La Ferté-Imbault Salbris, Romorantin-Lanthenay, Loir-et-Cher, Centre, FRANCE
|
||||||||
 |
Château du Rivau 37120 Lémeré, Indre-et-Loire, Touraine, FRANCE.
In 1429, towards the end of the Hundred Years' War, before the siege of Orleans, Joan of Arc and her followers came to fetch horses from Le Rivau, renowned for the quality of the war horses that were raised there.
In Rabelais' Gargantua, it was given to captain Tolmere as a reward for his victories in the Picrocholean Wars.
|
||||||||
 |
Castillo de Almodóvar del Río Almodóvar del Río, Province of Córdoba, SPAIN.
It is situated 15 miles (24 km) from Córdoba, on the left bank of the Guadalquivir.
The Moors built a castle here on the site of a Roman fort. The current structure has Berber origins, and dates from the year 760. During the Middle Ages, the castle underwent several periods of reconstruction. |
||||||||
 |
Château of Vizille 38220 Vizille, Isere, Region Rhone-Alpes, FRANCE.
The Château de Vizille, near Grenoble, is one of the most prestigious and important castles of the Dauphiné. |
||||||||
 |
Kasteel Dussen (Dussen Castle) Dussen, Noord-Brabant, NETHERLANDS.
Dating to 1331 |
||||||||
 |
Leeds Castle, Kent, ENGLAND
Leeds Castle is in Kent, ENGLAND, 5 miles (8 km) southeast of Maidstone. A castle has been on the site since 1119. In the 13th century it came into the hands of King Edward I, for whom it became a favourite residence; in the 16th century, Henry VIII used it as a residence for his first wife, Catherine of Aragon.
The castle was a location for the 1949 film Kind Hearts and Coronets where it stood in for "Chalfont", the ancestral home of the d'Ascoyne family. The castle also appeared in Moonraker (1958) and Waltz of the Toreadors (1962). It was the set for the Doctor Who episode The Androids of Tara.
The castle today dates mostly from the 19th century and is built on islands in a lake formed by the River Len to the east of the village of Leeds. It has been open to the public since 1976 |
||||||||
 |
Little Moreton Hall 4 miles (6.4 km) southwest of Congleton, Cheshire, ENGLAND
Little Moreton Hall, also known as Old Moreton Hall, is a moated half-timbered manor house. The earliest parts of the house were built for the prosperous Cheshire landowner William Moreton in about 1504–08, and the remainder was constructed in stages by successive generations of the family until about 1610.
The building is highly irregular, with three asymmetrical ranges forming a small, rectangular cobbled courtyard. The weight of the third-storey glazed gallery, possibly added at a late stage of construction, has caused the lower floors to bow and warp.
The house remained in the possession of the Moreton family for almost 450 years, until ownership was transferred to the National Trust in 1938. Little Moreton Hall and its sandstone bridge across the moat are recorded in the National Heritage List for ENGLAND as a designated Grade I listed building, and the ground on which Little Moreton Hall stands is protected as a Scheduled Monument. The gardens lay abandoned until their 20th-century re-creation. |
||||||||
 |
Oravský Hrad located above the Orava river in the village of Oravský Podzámok, SLOVAKIA.
In Eglish it is called Orava Castle, in German Arwaburg and in Hungarian: Árva vára)
Orava Castle stands on the site of an old wooden fortification, built after the Mongol invasion of Hungary of 1241.The later design was in Romanesque and Gothic style. Later still it was reconstructed as a Renaissance and Neo-Gothic structure,.
Many scenes of the 1922 film Nosferatu were filmed here. After a period of dilapidation the castle became a national monument after World War II,. |
||||||||
 |
|||||||||
 |
Ávila Town walls Ávila, Castile and León, SPAIN.
Ávila is sometimes called the Town of Stones and Saints. It is notable for having complete and prominent medieval town walls, built in the Romanesque style.
The town is also known as Ávila de los Caballeros, Ávila del Rey and Ávila de los Leales (Ávila of the Knights, the King and the Loyalists). It is "perhaps the most 16th-century town in Spain". It was declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1985. |
||||||||
 |
Château de Chenonceau Chenonceau, Indre-et-Loire, FRANCE
The estate of Chenonceau is first mentioned in writing in the 11th century. The current château was built in 1514–1522 on the foundations of an old mill and was later extended to span the river.
The bridge over the river was built (1556-1559) to designs by the French Renaissance architect Philibert de l'Orme, and the gallery on the bridge (1570–1576) to designs by Jean Bullant
The château has been classified as a Monument historique since 1840 by the French Ministry of Culture. It is one of the most famous Loire Valley châteaux. |
||||||||
 |
Schloss Hof (Hof Palace) Engelhartstetten (east of Vienna), Lower AUSTRIA.
Schloss Hof is located near the border of Slovakia. It once belonged to Prince Eugene of Savoy who purchased it in 1726. He had it enlarged in the Baroque style in 1729, and used it as an elaborate hunting lodge. He left it to a niece in his will, and it was later purchased by Empress Maria Theresa of Austria and became part of the imperial estates. |
||||||||
 |
Château de Bridoire Dordogne, Aquitane, FRANCE.
A castle was built here before the 12th century. North, south and west sides are protected by steep rock. To the east, a gap between the castle and the plateau was crossed by a drawbridge. In the 16th century, the drawbridge was replaced by a stone arched bridge. |
||||||||
 |
Corvin Castle aka Corvins' Castle, Hunyad Castle or Hunedoara Castle, Hunedoara, Transylvania
[Castelul Huniazilor or Castelul Corvinilor (Romanian)] [Vajdahunyad vára (Hungarian)] |
||||||||
 |
Castle design for King Henry VIII for a castle to defend the South Coast of ENGLAND.
Design for a “Device Fort” or “Henrician Castle”. |
||||||||
|
|
|||||||||
 |
main hall and staircase (1729-1733) The Palazzina di caccia of Stupinigi (Stupinigi Palace), Stupinigi, Nichelino, Nr Turin, ITALY
Stupinigi Palace is one of the Residences of the Royal House of Savoy in northern Italy, built as a royal hunting lodge in the early 18th century.
It is part of a UNESCO World Heritage Site. |
||||||||
 |
Castel Sant' Angelo (The Mausoleum of Hadrian) Parco Adriano, Rome, ITALY
Castel Sant' Angelo is where popes traditionally carried out the executions of their enemies, with a large mallet, or by hanging drawing and quartering. |
||||||||
 |
Eilean Donan (Eilean Donnain) Dornie, Kyle of Lochalsh IV40 8DX, SCOTLAND
Eilean Donan is a castle and small tidal island where three lochs meet, Loch Duich, Loch Long and Loch Alsh, in the western Highlands of Scotland.
The castle was founded in the thirteenth century, and became a stronghold of the Clan Mackenzie and their allies the Clan Macrae.
Between 1919 and 1932 the castle was rebuilt by Lt. Col. John MacRae-Gilstrap. The restoration included the construction of an arched bridge to give easier access to the island. |
||||||||
 |
Château de Suscinio (or de Susinio) Sarzeau, Morbihan, Brittany, FRANCE
Built in the late Middle Ages as the residence of the Dukes of Brittany.
The Château de Suscinio dates from the beginning of the 13th century. It was enlarged at the end of 14th century, when the heirs of the duchy were fighting to keep their possessions (Brittany was not annexed by France until 1514).
From 1471 to 1483, the castle was home to Jasper Tudor, Henry Tudor (later King Henry VII of ENGLAND), and the core of their group of exiled Lancastrians, numbering about 500 by 1483. Duke Francis II supported this group of exiles against Plantagenet demands for their surrender. |
||||||||
 |
Old Keiss Castle north of Keiss, Caithness, Highland, SCOTLAND.
Keiss Castle is a partially ruined castle on sheer cliffs, overlooking Sinclairs' Bay. The old castle, a Scheduled Monument, was built possibly on the site of an earlier fort in the late 16th or early 17th century by George 5th Earl of Caithness (1582-1643). |
||||||||
 |
Wartburg overlooking the town of Eisenach, Thuringia, GERMANY
The Wartburg is a castle originally built in the Middle Ages, situated on precipice. It was the home of St. Elisabeth of Hungary, the place where Martin Luther translated the New Testament of the Bible into German
It was an inspiration for Ludwig II when he decided to build Neuschwanstein Castle. Although the castle today still contains substantial original structures from the 12th through 15th centuries, much of the interior dates to the 19th-century period of Romanticism.
In 1999, UNESCO added Wartburg Castle to the World Heritage List |
||||||||
 |
Frederiksborg Castle Hillerød
Frederiksborg Palace or Frederiksborg Castle (in Danish, Frederiksborg Slot) was built as a royal residence for King Christian IV and is now a museum of national history.
The current edifice replaced a previous castle erected by Frederick II and is the largest Renaissance palace in Scandinavia. The palace is located on three small islands in the middle of Palace Lake (Slotsøen) and is adjoined by a large formal garden in the Baroque style. |
||||||||
 |
Örebro (Oerebro) Castle Örebro, Närke
The castle lies on an island in the river Svartån.
For over 700 years occupants of Örebro Castle monitored the bridge over the River Svartån. The oldest part of the castle, a defence tower, was erected in the latter half of the 13th century. This tower was added to in the 14th century to make a larger stronghold, and towards the end of the 16th century most of the castle we see today was built. It was expanded during the reign of the royal House of Vasa and rebuilt about 1900. |
||||||||
 |
Burg Gudenau Wachtberg, Rhein-Sieg, North Rhine-Westphalia, GERMANY.
Castle Gudenau is a Wasserschloß - or moated castle. |
||||||||
 |
Matsumoto Castle, ("Crow Castle") Matsumoto, Nagano Prefecture near Tokyo, JAPAN
Matsumoto Castle is one of Japan's premier historic castles. The keep (tenshukaku), was completed in the late sixteenth century, It is listed as a National Treasure of Japan.
Matsumoto Castle is a flatland castle (hirajiro) built on a plain. Its defences would have included an extensive system of inter-connecting walls, moats, and gatehouses. |
||||||||
 |
Fagaras Castle Fagaras, Brazov County
In 1696, following penetration of the Austrian army in Transylvania, Fagaras Castle (or Fagaras Fortress) became Crown property of the Habsburgs. |
||||||||
 |
The Château de Ternay Loire Valley, Poitou-Charentes, FRANCE.
The Château de Ternay was built by the Aviau de Ternay family. The present château, on twelfth-century foundations, is the result of building campaigns from the fifteenth to the seventeenth centuries.
It has been listed as a Monument historique since 1996. It is still the seat of the comte de Ternay. Today the château is open for tours and overnight guests. |
||||||||
 |
Château de Cheverny Cheverny, Loir-et-Cher, FRANCE.
Hergé used Cheverny, one of the châteaux of the Loire valley, as a model for his "Château de Moulinsart" (Marlinspike Hall in English) in his Tintin books. |
||||||||
 |
Dover Castle Dover, Kent, ENGLAND.
Dover Castle was founded in the 12th century and has been described as the "Key to ENGLAND" due to its defensive significance. It is the largest castle in ENGLAND.
During the reign of Henry II t the castle began to take recognisable shape. The inner and outer baileys and the great keep belong to this time. Maurice the Engineer was responsible for building the keep, one of the last rectangular keeps ever built.
Dover Castle is a Scheduled Monument and a Grade I listed building. The castle, its secret tunnels, and surrounding land are owned by English Heritage and the site is a major tourist attraction.
From the Cinque Ports foundation in 1050, Dover has always been a chief member. The Lord Warden of the Cinque Ports is officially head of the castle, in his conjoint position of Constable of Dover Castle, and the Deputy Constable has his residence in Constable's Gate. |
||||||||
 |
Where is this ? |
||||||||
![The Punakha Dzong or Pungtang Dechen Photrang Dzong [the palace of bliss], Punakha, Bhutan - www.castlesandmanorhouses.com The Punakha Dzong or Pungtang Dechen Photrang Dzong [the palace of bliss], Punakha, Bhutan - www.castlesandmanorhouses.com](photos/punakha_04.jpg) |
The Punakha Dzong or Pungtang Dechen Photrang Dzong [the Palace of Bliss] Punakha, Bhutan |
||||||||
 |
Château de Najac Najac, Aveyron, FRANCE.
The the royal fortress of Najac was built in 1253 on the orders of Alphonse de Poitiers, brother of Saint Louis, on the site of a square tower built in 1100 by Bertrand of St Gilles, son of Raymond IV, Count of Toulouse before the area was annexed by FRANCE.
The castle is built at the summit of a hill formed by a loop of the river.
The castle holds a world record for its 6.80 metre high archères (arrow loops), designed to allow use by three archers at the same time. A secret corridor, hidden within the walls, links the Romanesque tower to the chapel of the keep.
Najac has been near major events including, the Albigensian Crusade, the Hundred Years' War, the imprisonment of the Knights Templar, the peasants' revolts, and the French Revolution.
The castle has been listed as a monument historique by the French Ministry of Culture since 1925. |
||||||||
 |
Krak des Chevaliers (or Crac Des Chevaliers)
Krak des Chevaliers is one of the most important preserved medieval castles in the world. The site was settled in the 11th century by Kurds; as a result it was known as Hisn al Akrad, meaning the "Castle of the Kurds". In 1142 it was given by Raymond II, Count of Tripoli, to the Knights Hospitaller. It remained in their possession until it fell in 1271. It was known as Crac de l'Ospital (the name Krak des Chevaliers was coined only in the 19th century.) |
||||||||
 |
Castle of Santiago Sanlúcar de Barrameda, Cádiz province, Andalucía, SPAIN.
The Castle of Santiago was constructed by the Second Duke of Medina-Sidonia (Enrique Perez de Guzman y Meneses) between 1477 and 1478. The style is late Gothic. The castle is rectangular with towers around a central courtyard. |
||||||||
 |
Castillos de Monzón y Loarre Loarre, Huesca. SPAIN.
The Loarre castle complex was built largely during the 11th and 12th centuries, when its position on the frontier between Christian and Muslim lands gave it strategic importance.
The first of the two major building programs began ca. 1020, when Sancho el Mayor (r. 1063–94) reconquered the surrounding lands from the Muslims. At least three towers, two of which survive, the Homage tower (Torre del Homenaje) and the "Tower of the Queen" (Torre de la Reina), are attributed to this campaign.
The Homage tower was built in an isolated position in front of the fortifications, to which it was connected by a wooden bridge. The Torre de la Reinahas both Lombard and Mozarabic architectural forms. |
||||||||
 |
Saint Catalina's Castle (Castillo de Santa Catalina) Cerro de Santa Catalina, overlooking the city of Jaén, Andalusia, SPAIN
The castle began as an 8th Century Moorish fortress last improved by the Nasrid King Abdallah ibn al-Ahmar (who also built Alhambra). Earlier there was a tower known as Hannibal's Tower, of which traces remain. After King Ferdinand III of Castile captured the city in 1246 following the Siege of Jaén, he commenced a transformation of the castle, including construction of what became known as the New Castle on the eastern extreme of the hill.
The construction in 1965 of a parador resulted in the destruction of many of the elements of the Old Castle. The few remnants of the original fortress occupy the western extreme of the hill. |
||||||||
 |
Ribat of Monastir
Ribat of Monastir on the Mediterranean coast is the oldest and largest Maghreb Ribat. Built in 796 by the Abbasid general and governor of Ifriqiya, Harthimâ Ibn A’yûn, the complex that can be seen today is the result of a long evolution of successive additions and changes. The original nucleus of the building presents a regular plan with massive façades with cylindrical towers at the corners and a watchtower located to the southeast. The courtyard is lined with galleries which open on several stories. |
||||||||
 |
Craigievar Castle south of Alford, Aberdeenshire, SCOTLAND.
Craigievar Castle was the seat of Clan Sempill and the Forbes family who resided here for 350 years until 1963, when the property was given to the National Trust for Scotland.
An example of the original Scottish Baronial architecture, the seven-storey castle was completed in 1626 by the Aberdonian merchant William Forbes. Forbes purchased the partially completed structure from the Mortimer family in the year 1610. Designed in the L plan, Craigievar is noted for its exceptionally crafted plasterwork ceilings. The ceilings feature plaster figures of the Nine Worthies and other family emblems. |
||||||||
 |
Bled Castle above the city of Bled, Slovenia.
Bled Castle (Slovene: Blejski grad, German: Burg Veldes) is a medieval castle built on a precipice overlooking Lake Bled. It was first mentioned in a 1011 deed of donation issued by Emperor Henry II in favour of the Bishops of Brixen. It passed to the Austrian House of Habsburg in 1278.
The oldest part of the castle is the Romanesque tower. In the Middle Ages more towers were built and the fortifications were improved. Other buildings were constructed in the Renaissance style. The buildings are arranged around two courtyards connected by a staircase. The castle also has a drawbridge over a moat. |
||||||||
 |
Schloss Vetschau Vetschau, Oberspreewald-Lausitzt, Brandenburg, GERMANY.
The Vetschau Castle is a castle built in the Renaissance style in the Spreewald Standing on a small rise, the three-storey buildings are grouped around a small rectangular courtyard. The present appearance of the castle, built from 1538, is due to alterations in the years 1860-1870. The tower is provided with a lantern crowned by a dome. |
||||||||
 |
Valencia de Don Juan León, Castile and León, SPAIN.
Originally called Valencia de Campos, it was renamed after its First Lord, Infante John of Portugal. |
||||||||
 |
Citadel of Raymond de Saint-Gilles (Qala'at Sanjil) Tripoli
The citadel takes its name from Raymond IV, Raymond de Saint-Gilles, the Count of Toulouse and Crusader commander. He started its construction on a hilltop outside Tripoli in 1103 in order to lay siege to the city during the First Crusade. Later, Raymond enlarged the fortress, which he named Mont Peregrinus ("Mount Pilgrim").
Iit is not be confused with the Citadel of Tripoli, built by the Arabs in 636 and subsequently enlarged and modified by the Fatamids of Egypt and, later, by the Crusaders and Ottomans). |
||||||||
 |
Laarne Castle Laarne, East Flanders, BELGIUM.
Laarne Castle (Kasteel van Laarne) is a moated castle, established in the 11th or 12th century to guard the approaches to Ghent from the sea, it was comprehensively renovated in the 17th century.
Since 1953 the castle has belonged to the Koninklijke Vereniging der Historische Woonsteden en Tuinen van België ("The Royal Association of Historical Houses and Gardens in Belgium"), to whom it was given by the last private owner, the Comte de Ribaucourt. It is a protected national monument and is now used as a museum. |
||||||||
 |
Eggenberg (Schloss Eggenberg) Graz,
Eggenberg Palace is the most significant Baroque palace complex in Styria. In 2010, Schloss Eggenberg was recognized for its significance to cultural history in an expansion to the listing of the Graz Historic Old Town among UNESCO World Cultural Heritage Sites. |
||||||||
 |
Anholt Castle District of Borken, North Rhine Westphalia, GERMANY
The Lordship of Anholt was a state of the Holy Roman Empire. It was an imperial estate and a member of the Lower Rhenish-Westphalian Circle. The Lordship bordered three larger states: the Duchy of Guelders, the Bishopric of Münster, and the Duchy of Cleves. |
||||||||
 |
Alarcon Castle Cuenca, Castile-La Mancha, SPAIN.
In 1177 Ferren Martínez de Ceballos led the Christian forces which captured Alarcón - then an important fortress - from the Almohads. . |
||||||||
 |
Tarasp Castle Lower Engadin, Graubünden, SWITZERLAND
Chastè da Tarasp (Tarasp Castle or in German, Schloss Tarasp) sits on a hill top near Tarasp. Located in the Romansh speaking area of Switerland, it is a Swiss heritage site of national significance. |
||||||||
 |
Château de Rambures Rambures, Somme
The château was constructed in the the 15th century in the style of a late medieval military fortress. It was one of the first castles in Europe to be constructed almost exclusively in bricks.
The castle is set in a park, the Parc et Roseraie du Château de Rambures containing a rose garden and ancient trees.
It has been classified as a monument historique by the French Ministry of Culture since 1927. |
||||||||
 |
The Entrance Hall Blair Castle, Blair Atholl, Perthshire, SCOTLAND
Blair Castle is the ancestral home of the Clan Murray, and was historically the seat of their chief, the Duke of Atholl,
The castle stands in Glen Garry, and commands a strategic position on the main route through the central Scottish Highlands.
The oldest part of the castle is the six-storey Cummings or Comyn's Tower, which retains some13th-century fabric, though it was largely built in the 15th century.
The castle is a category A listed building, and the grounds are included in the Inventory of Gardens and Designed Landscapes in Scotland. |
||||||||
 |
Orford Castle, Orford, Suffolk, ENGLAND
Orford Castle was built between 1165 and 1173 by King Henry II of ENGLAND to consolidate royal power in the region. The well-preserved keep, "one of the most remarkable keeps in ENGLAND", is of a unique design and probably based on Byzantine architecture (brought back by crusaders). |
||||||||
 |
Laolongtou or “The Old Dragon’s Head” part of the Shanhai Pass (also known as Shanhaiguan) of the Great Wall of CHINA |
||||||||
 |
Umaid Bhawan Palace Jodhpur, Rajasthan
Umaid Bhawan Palace is one of the world's largest private residences. Named after Maharaja Umaid Singh, grandfather of the present owners of the palace, this monument has 347 rooms and serves as the principal residence of the Jodhpur royal family.
The present owner of the Palace is Maharaja of Jodhpur Gaj Singh. The Palace is divided into three functional parts - the residence of the royal family, the Taj Palace Hotel and a Museum focusing on the 20th century history of the Royal Family. |
||||||||
 |
Above average Sand Castles |
||||||||
 |
San Lorenzo de El Escorial northwest of Madrid, SPAIN.
El Escorial is a historical residence of the King of Spain, It functions as a monastery, royal palace, museum, and school. Originally a property of the Hieronymite monks, the monastery monastery now belongs to the Order of Saint Augustine. Philip II of Spain, engaged the Spanish architect, Juan Bautista de Toledo, to be his collaborator in the design of El Escorial. Philip appointed him architect-royal in 1559, and together they designed El Escorial as a monument to Spain's role as a center of the Christian world. On 2 November 1984, UNESCO declared The Royal Seat of San Lorenzo of El Escorial a World Heritage Site. |
||||||||
 |
Castelo de Évoramonte Evoramonte (officially Évora Monte), Estremoz, Alentejo Central, PORTUGAL.
Founded in 1160. |
||||||||
 |
The Roman walls of Barcelona. Barcelona is now the capital city of the autonomous community of Catalonia in SPAIN
The founding of Barcelona is the subject of two different legends. The first attributes the founding of the city to Hercules. The second to the Carthaginian Hamilcar Barca, (father of Hannibal) who named the city Barcino after his family in the 3rd century BC.
About 15 BC, the Romans created a castrum here centred on the "Mons Taber". The colony bore the name of Faventia, in full, Colonia Faventia Julia Augusta Pia Barcino, or Colonia Julia Augusta Faventia Paterna Barcino.. The Roman city minted its own coins. The typically Roman grid plan is still visible today in the layout of the historical centre. Some fragments of the Roman walls have been incorporated into the cathedral.
The city was subsequently conquered by the Visigoths in the early 5th century. After being conquered by the Arabs in the early 8th century, it was conquered in 801 by Charlemagne's son Louis, who made Barcelona the seat of the Carolingian "Hispanic March" (Marca Hispanica), a buffer zone ruled by the Count of Barcelona. |
||||||||
 |
Ávila Town walls Ávila, Castile and León, SPAIN.
Ávila is sometimes called the Town of Stones and Saints. It is notable for having complete and prominent medieval town walls, built in the Romanesque style.
The town is also known as Ávila de los Caballeros, Ávila del Rey and Ávila de los Leales (Ávila of the Knights, the King and the Loyalists). It is "perhaps the most 16th-century town in Spain". It was declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1985. |
||||||||
 |
Corvin Castle aka Corvins' Castle, Hunyad Castle or Hunedoara Castle [Castelul Huniazilor or Castelul Corvinilor (Romanian)] [Vajdahunyad vára (Hungarian)] Hunedoara, Transylvania |
||||||||
 |
Eilean Donan (Eilean Donnain) Dornie, Kyle of Lochalsh IV40 8DX, SCOTLAND
Eilean Donan is a castle and small tidal island where three lochs meet, Loch Duich, Loch Long and Loch Alsh, in the western Highlands of Scotland.
The castle was founded in the thirteenth century, and became a stronghold of the Clan Mackenzie and their allies the Clan Macrae.
Between 1919 and 1932 the castle was rebuilt by Lt. Col. John MacRae-Gilstrap. The restoration included the construction of an arched bridge to give easier access to the island. |
||||||||
 |
Burg Hochosterwitz near Sankt Georgen am Längsee, east of the town of Sankt Veit an der Glan in the state of Carinthia
Hochosterwitz Castle is considered to be one of Austria's most impressive medieval castles.
There are 14 defensive gates, each equipped with different methods of guarding the path. Local legend maintains that the castle has never been conquered and that none of the attacks managed to get beyond the fourth gate. |
||||||||
 |
Harlaxton Manor Harlaxton, Lincolnshire, ENGLAND
Harlaxton Manor, built in 1837, is a manor house which combines elements of Jacobean and Elizabethan styles with symmetrical Baroque massing.
The manor is a popular location for filming. Exterior and interior shots have been featured in the films The Ruling Class, The Last Days of Patton, The Lady and the Highwayman, The Haunting, and The Young Visiters.
It is now part of the University of Evansville's British campus. |
||||||||
 |
La porte Notre Dame Le château de Fougères Ille-et-Vilaine, Brittany
The Château de Fougères is a castle was built on a naturally protected site, a rock emerging from a swamp surrounded by a loop of the Nançon river acting as a natural moat.
It had three rings of defense. In all it has 13 towers.
The first wooden fort was built by the House of Amboise in the eleventh century. It was destroyed in 1166 after it was besieged and taken by King Henry II of ENGLAND. It was immediately rebuilt by Raoul II Baron de Fougères.
Today the castle belongs to the municipality of Fougères and is one of Europe's largest medieval fortresses. |
||||||||
 |
Po Shanu Cham Towers Phan Thiet
West of Mui Ne, the Po Shanu Cham towers, remnants of the once flourishing Cham empire, occupy a hill near Phan Thiet, with sweeping views of the town.
Dating from the 9th century, this complex consists of the ruins of three towers, none of which is in very good shape, largely due to destructive restoration efforts. |
||||||||
|
|
|||||||||
 |
Palmanova Friuli-Venezia Giulia, ITALY.
The town of Palmanova is an example of star fort of the Late Renaissance. It was built by the Venetians in 1593. |
||||||||
 |
Palmanova Friuli-Venezia Giulia, ITALY.
The town of Palmanova is an example of star fort of the Late Renaissance. It was built by the Venetians in 1593.
You can just make out the star shaped defences outside the town at the top of the photograph. |
||||||||
 |
Palmanova Friuli-Venezia Giulia, ITALY.
The town of Palmanova is an example of star fort of the Late Renaissance. It was built by the Venetians in 1593. . |
||||||||
 |
Château d'Apremont Apremont-sur-Allier, Cher, Centre
Château d'Apremont overlooks the River Allier. It lies on the limits of Berry. Not much remains of the great Anglo-Burgundian fortress with its 14 towers dating from the fifteenth century.
The Château was classified as as a monument historique in 1989. |
||||||||
 |
Schloss Celle Celle, Lower Saxony, GERMANY
Also known as das Celler Schloss and as Celle Palace, this quadrangular building was one of the residences of the House of Brunswick-Lüneburg.
The castle has rooms and halls datig back to different periods. The court chapel was converted after the Reformation and has been preserved almost unchanged with its Renaissance architecture. The baroque-style state rooms have also been preserved. In the Gothic Hall there are constantly changing exhibitions and in the East Wing is a section of Celle's Bomann Museum, dedicated to the history of the Kingdom of Hanover. The historic castle rooms and the castle chapel, restored between 1978 and 1981, may be visited as part of a guided tour. |
||||||||
 |
Garsington Manor Garsington, near Oxford, ENGLAND
Garsington Manor is a Tudor building, built on land once owned by the son of the poet Geoffrey Chaucer. At one time it was called “Chaucers”.
Lady Ottoline and her husband, Philip Morrell, bought the manor house in 1914.They restored the house and Garsington became a haven for the Morrells’ friends, including D. H. Lawrence, Siegfried Sassoon, Lytton Strachey, Aldous Huxley, Mark Gertler, and Bertrand Russell. |
||||||||
 |
Blenheim Palace, Woodstock, Oxfordshire, ENGLAND
Blenheim Palace is a monumental country house and the principal residence of the dukes of Marlborough. The palace, one of ENGLAND's largest houses, was built between 1705 and circa 1722. as a reward to John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough, from a grateful nation for the duke's military triumphs against the French and Bavarians during the War of the Spanish Succession, culminating in the 1704 Battle of Blenheim.
Following the palace's completion, it became the home of the Churchill, later Spencer-Churchill, family for the next 300 years. The palace is s the birthplace and ancestral home of Sir Winston Churchill.
It is the only non-royal non-episcopal building in ENGLAND to hold the title of palace. It was designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1987. |
||||||||
 |
King John's Castle (Irish: Caisleán Luimnigh), King's Island, Limerick, Ireland.
King John's Castle is a 13th-century castle located next to the River Shannon. Although the site dates back to 922 when the Vikings lived on the Island, the castle itself was built on the orders of King John in 1200. One of the best preserved Norman castles in Europe, the walls, towers and fortifications remain today and are visitor attractions. |
||||||||
|
|
|||||||||
 |
Château d'Ainay-le-Vieil Ainay-le-Vieil, Cher
Built in the 14th century, the castle has been listed as a Monument historique since 1968 by the French Ministry of Culture. |
||||||||
 |
The Château de Fougères Fougères, Ille-et-Vilaine, Brittany
Château de Fougères is Fougères' most famous monument and attraction. It is a medieval stronghold built on a granite ledge. It played an imporant part in the Duchy of Brittany's ultimately unsuccessful defence against French annexation in 1532. |
||||||||
 |
Château de Chenonceau Chenonceau, Indre-et-Loire
The estate of Chenonceau is first mentioned in writing in the 11th century. The current château was built in 1514–1522 on the foundations of an old mill and was later extended to span the river.
The bridge over the river was built (1556-1559) to designs by the French Renaissance architect Philibert de l'Orme, and the gallery on the bridge (1570–1576) to designs by Jean Bullant
The château has been classified as a Monument historique since 1840 by the French Ministry of Culture. It is one of the most famous Loire Valley châteaux. |
||||||||
 |
The Château de Fougères-sur-Bièvre, Fougères-sur-Bièvre, Loir-et-Cher
Originally an 11th-century structure, the castle was rebuilt at the end of the 15th century, only the large square keep being preserved. The first changes retained military features(ditches, cannon-holes, wall walk) but more Renaissance refinements were added later, such as a gallery, mullioned windows and steep-sloped roofs. The castle was purchased and restored by the state in the 1930s. It has been listed since 1912 as a monument historique by the French Ministry of Culture. |
||||||||
 |
Bruce Castle (Lordship House) Lordship Lane, Tottenham, London
Bruce Castle (formerly the Lordship House) is a Grade I listed 16th-century manor house.. It is named after the House of Bruce who formerly owned the land on which it is built. The current house is one of the oldest surviving English brick houses. It was remodelled in the 17th, 18th and 19th centuries.
The building also houses the archives of the London Borough of Haringey. Since 1892 the grounds have been a public park. |
||||||||
 |
Château d'Ussé Rigny-Ussé, Indre-et-Loire
This stronghold at the edge of the Chinon forest overlooking the Indre Valley was first fortified in the eleventh century by the Norman seigneur of Ussé, Gueldin de Saumur, who surrounded the fort with a palisade on a high terrace. The site passed to the Comte de Blois, who rebuilt in stone.
It was completed in 1612. The flamboyant Gothic style is mixed with new Renaissance motifs, and began the process of rebuilding the fifteenth-century château that resulted in the sixteenth-seventeenth century aspect of the structure to be seen today.
It is classified as a monument historique since 1931 by the French Ministry of Culture. |
||||||||
 |
The Château de Fougères-sur-Bièvre Fougères-sur-Bièvre, Loir-et-Cher
Originally an 11th-century structure, the castle was rebuilt at the end of the 15th century, only the large square keep being preserved. The first changes retained military features(ditches, cannon-holes, wall walk) but more Renaissance refinements were added later, such as a gallery, mullioned windows and steep-sloped roofs. The castle was purchased and restored by the state in the 1930s. It has been listed since 1912 as a monument historique by the French Ministry of Culture. |
||||||||
 |
Bojnice Castle Bojnice, SLOVAKIA
Bojnice Castle, dating from the 12th century, is today a Romantic castle with Gothic and Renaissance elements
Bojnice Castle is one of the most visited castles in Slovakia. |
||||||||
 |
Château de Biron Biron, Dordogne
The Château de Biron is a large castle in the valley of the Lède. It was the castle from which the Gontaut-Biron took their name. It was their seat from the twelfth century. Biron was seized by Simon IV de Montfort in 1212 from forces sypathetic to the Cathars.
The Plantagenets held it at times during the 14th and 15th centuries. Biron was erected as a duché-pairie in 1598, for Charles de Gontaut, created duc de Biron.
The present château bears additions over the centuries: notably a twelfth-century keep and sixteenth-century living quarters and vaulted kitchens.
Since 1928, it has been listed as a monument historique by the French Ministry of Culture. The local commune purchased the Château de Biron in 1978, with a view to restoring it as a tourist attraction. |
||||||||
 |
Edinburgh Castle, Castle Rock, Edinburgh, SCOTLAND
Edinburgh Castle is a historic fortress diminating the skyline of the city of Edinburgh. There has been a royal castle on the rock since at least the reign of David I in the 12th century.
As one of the most important strongholds in the Kingdom of Scotland, Edinburgh Castle was involved in many historical conflicts from the Wars of Scottish Independence in the 14th century to the Jacobite Rising of 1745.
The castle houses the Scottish regalia, known as the Honours of Scotland and is the site of the Scottish National War Memorial and the National War Museum of Scotland. The British Army is still responsible for some parts of the castle.
The castle is in the care of Historic Scotland and is Scotland's most-visited paid tourist attraction. As the backdrop to the Edinburgh Military Tattoo during the annual Edinburgh International Festival the castle has become a recognisable symbol of Edinburgh and of Scotland. |
||||||||
 |
Highclere Castle Hampshire, ENGLAND,
Highclere Castle is a country house in the Jacobethan style, with a park designed by Capability Brown. It is the country seat of the Earl of Carnarvon, head of a branch of the Anglo-Welsh Herbert family.
Highclere Castle is the main filming location for the British television period drama Downton Abbey.
The Castle and gardens are open to the public during July and August and at times during the rest of the year. |
||||||||
 |
Walmer Castle, Walmer, Kent, ENGLAND.
Walmer Castle was built by Henry VIII in 1539–1540 as an artillery fortress to counter the threat of invasion from Catholic France and Spain. It was part of his programme to create a chain of coastal defences along ENGLAND's coast known as the Device Forts or as Henrician Castles.
It was one of three forts constructed to defend the Downs, an area of safe anchorage protected by the Goodwin Sands. The other forts were at Deal and Sandown. The castle is now owned and managed by English Heritage. |
||||||||
 |
The Château de Lichtenberg Lichtenberg, northern Vosges, Bas-Rhin department, Alsace, FRANCE.
The Château de Lichtenberg is a castle built on a singular prominence, built in the 13th century by the Hanau-Lichtenberg family. It was in the center of a constantly shifting territory, which traded hands many times until the Franco-Prussian War in 1870, when it was partly destroyed by artillery fire and the resulting fires.
It was left to deteriorate for 120 years. In the 1990s, a massive consolidation project was undertaken on the ruins, with an investment of 52 million francs. |
||||||||
 |
Caernarfon Castle (Welsh: Castell Caernarfon) Caernarfon, Gwynedd, north-west WALES
There was a motte-and-bailey castle in the town of Caernarfon from the late 11th century until 1283 when King Edward I of ENGLAND began replacing it with the current stone structure. The Edwardian town and castle acted as the administrative centre of north Wales and as a result the defences were built on a grand scale. There was a deliberate link with Caernarfon's Roman past – nearby is the Roman fort of Segontium – and the castle's walls are reminiscent of the Walls of Constantinople.
While the castle was under construction, town walls were built around Caernarfon. The work cost between £20,000 and £25,000 from the start until the end of work in 1330. Despite Caernarfon Castle's external appearance of being mostly complete, the interior buildings no longer survive and many of the building plans were never finished. The town and castle were sacked in 1294 when Madog ap Llywelyn led a rebellion against the English. Caernarfon was recaptured the following year. During the Glyndwr Rising of 1400–1415, the castle was besieged. When the Tudor dynasty ascended to the English throne in 1485, tensions between the Welsh and English began to diminish and castles were considered less important. As a result, Caernarfon Castle was allowed to fall into a state of disrepair.
During the English Civil War Caernarfon Castle was held by Royalists, and was besieged three times by Parliamentarian forces. Caernarfon Castle was neglected until the 19th century when the state funded repairs. In 1911, Caernarfon Castle was used for the investiture of the Prince of Wales, and again in 1969. It is part of the World Heritage Site "Castles and Town Walls of King Edward in Gwynedd" |
||||||||
 |
Tamworth Castle Tamworth, Staffordshire, ENGLAND.
Overlooking the River Tame, the site has been fortified since Anglo-Saxon times, when Ethelfleda, the Mercian Queen, built a burh to defend against Danes in 913. It served as a residence of the Mercian kings. Rebuilt and enlarged by the Normans, it is today one of the best preserved Norman motte-and-bailey castles in ENGLAND.
Today it is a monument of local council philistinism, surrounded by ugly modern housing.
The present castle was constructed by the Norman invaders in the 1080s, occupying the south western part of the earlier burh. It dates primarily from the 11th and 12th century and was constructed in the typical Norman motte and bailey fashion. Following the Norman Invasion of 1066, Tamworth was granted to Robert Despenser, steward to William the Conqueror. Robert died childless and so the castle passed to a daughter of his brother Urse d'Abetot's, Matilida, who married Robert de Marmion. The Marmion family, from Fontenay-le-Marmion, Normandy, held the castle for 6 generations from c.1100 - 1294. The Marmion family were hereditary champions to the Dukes of Normandy and then of the new Kings of ENGLAND. This role required them to offer a ceremonial challenge to those who would oppose the King.
Tamworth Castle is a Grade I listed building. |
||||||||
 |
Château du Gué-Péan Monthou-sur-Cher, Loir-et-Cher, Centre
Monument historique |
||||||||
 |
Belvoir Castle Leicestershire, ENGLAND
Belvoir Castle is a stately home, the traditional seat of the Dukes of Rutland, overlooking the Vale of Belvoir. It is a Grade I listed building.
A corner of the castle is still used as the family home of the Manners family and remains the seat of the Dukes of Rutland, most of whom are buried in the grounds of the mausoleum there. |
||||||||
 |
Château de Azay-le-Rideau Azay-le-Rideau, Chinon, Indre-et-Loire, Centre |
||||||||
.jpg) |
Windsor Castle, Windsor, Berkshire, ENGLAND
Windsor Castle is a royal residence notable for its long association with the English and later British royal family and also for its architecture. The original castle was built in the 11th century after the Norman invasion by William the Conqueror. Since the time of Henry I, it has been used by succeeding monarchs and is the longest-occupied palace in Europe. More than five hundred people live and work in Windsor Castle.
Originally designed to protect Norman dominance around the outskirts of London, and to oversee a strategically important part of the River Thames, Windsor Castle was built as a motte and bailey, with three wards surrounding a central mound. Gradually replaced with stone fortifications, the castle withstood a prolonged siege during the First Barons' War at the start of the 13th century. Henry III built a luxurious royal palace within the castle during the middle of the century, and Edward III went further, rebuilding the palace to produce an even grander set of buildings. Edward's core design lasted through the Tudor period, during which Henry VIII and Elizabeth I made increasing use of the castle as a royal court and centre for diplomatic entertainment. |
||||||||
 |
Arundel Castle Arundel, West Sussex, ENGLAND.
Arundel Castle is a restored medieval castle. It was established by Roger de Montgomery on Christmas Day 1067. Roger became the first to hold the earldom of Arundel under William the Conqueror.
The castle was damaged in the English Civil War and then restored in the 18th and 19th centuries.
From the 11th century onward, the castle has served as a hereditary stately home and has been in the family of the Duke of Norfolk for over 400 years. The castle was damaged in the English Civil War and then restored in the 18th and 19th centuries. It is still the principal seat of the Norfolk family. It is a Grade I listed building |
||||||||
 |
Château de Menthon Saint-Bernard above the lac d'Annecy, Haute-Savoie |
||||||||
 |
Ljubljana Castle (Slovene: Ljubljanski Grad) Ljubljana, Slovenia.
Ljubljana Castle is located on Castle Hill (Grajski gric) overlooking the old town of Ljubljana. The area has been settled continuously since 1200 BC. The hill probably became a Roman army stronghold after fortifications were built in Illyrian and Celtic times.
In 1335 it became property of the House of Habsburg. In the 15th century it was almost completely demolished and rebuilt with a complete wall and towers at the entrance.
In the 17th and 18th centuries, the castle became an arsenal and a military hospital. It was damaged during the Napoleonic period and, once back in the Austrian Empire, became a prison, which it remained until 1905, resuming that function during World War II. |
||||||||
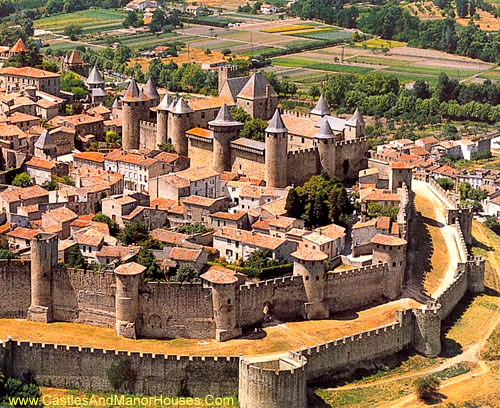 |
Château Comtal Carcassonne, Languedoc
The Castle of Raymond Roger Trencavel, Viscount of Carcassonne, Béziers, Albi and the Razès. He died in his own prison here in 1209, aged 24, after being taken prisoner while under a safe-conduct from the Cistercian Abbot Arnaud Amaury the papal legate and military leader of the Albigensian Crusade who was besieging Carcassonne (and who then appointed Simon de Montfort as military leader of the crusade). |
||||||||
 |
The White Tower, Tower of London Borough of Tower Hamlets, London, ENGLAND
Her Majesty's Royal Palace and Fortress, known as the Tower of London, is a historic castle located on the north bank of the River Thames in central London. It is separated from the eastern edge of the square mile of the City of London by Tower Hill. It was founded towards the end of 1066 as part of the Norman Conquest of ENGLAND.
The castle was used as a prison from 1100 (Ranulf Flambard) until 1952 (Kray twins), although that was not its primary purpose. It served as a royal residence. As a whole, the Tower is a complex of several buildings set within two concentric rings of defensive walls and a moat. There were several phases of expansion, mainly under Kings Richard the Lionheart, Henry III, and Edward I in the 12th and 13th centuries. The general layout established by the late 13th century remains despite later activity on the site.
The Tower of London has played a prominent role in English history. It was besieged several times and controlling it has been important to controlling the country. The Tower has served variously as an armoury, a treasury, a menagerie, the home of the Royal Mint, a public records office, and the home of the Crown Jewels of the United Kingdom.
it is cared for by the charity Historic Royal Palaces and is protected as a World Heritage Site. |
||||||||
 |
Ceramic poppies at the Tower of London, 2014.
Installation “Blood Swept Lands and Seas of Red”, marking the centenary of the outbreak of the First World War. Created by ceramic artist Paul Cummins, with setting by stage designer Tom Piper, 888,246 ceramic poppies progressively fill the Tower’s moat, each poppy representing a British fatality during the First World War. |
||||||||
 |
Garsington Manor Garsington, near Oxford, ENGLAND.
Garsington Manor is a Tudor building, built on land once owned by the son of the poet Geoffrey Chaucer. At one time it was called "Chaucers". Lady Ottoline and her husband, Philip Morrell, bought the manor house in 1914.They restored the house and Garsington became a haven for the Morrells’ friends, including D. H. Lawrence, Siegfried Sassoon, Lytton Strachey, Aldous Huxley, Mark Gertler, and Bertrand Russell. |
||||||||
 |
Classiebawn Castle Mullaghmore peninsula near Cliffoney, County Sligo, Republic of Ireland.
Classiebawn Castle is a country house built for Viscount Palmerston on what was formerly a 10,000 acre estate. The current castle was largely built in the nineteenth century and is seen here against the Benbulbin. It was designed in the Baronial style by J. Rawson Carrol, and is constructed from a yellow-brown sandstone from County Donegal. It comprises a gabled range with a central tower topped by a conical roofed turret. |
||||||||
 |
Château St-Ferriol Saint-Ferriol, Aude, Languedoc-Roussillon
The Château St-Ferriol, is a late-medieval / early Renaissance castle in the heart of Cathar Country, built by a family (de Planh in Occitan or de Plaigne in French) at least three members of which were besieged at Montsegur in 1244.
The photo shows the Château in the early morning mist. |
||||||||
 |
Castle of Santiago Sanlúcar de Barrameda, Cádiz province, Andalucía, SPAIN.
The Castle of Santiago was constructed by the Second Duke of Medina-Sidonia (Enrique Perez de Guzman y Meneses) between 1477 and 1478. The style is late Gothic. The castle is rectangular with towers around a central courtyard. |
||||||||
 |
Le château de la Ferté La Ferté-Saint-Aubin, Loiret, Centre
One of the famous châteaux de la Loire. |
||||||||
 |
Burg Gudenau Wachtberg, Rhein-Sieg district, North Rhine-Westphalia, GERMANY.
Castle Gudenau is a Wasserschloß - or moated castle. |
||||||||
 |
|||||||||
 |
Design for a 'Device Fort' or 'Henrician Castle'.
Castle design for King Henry VIII for a castle to defend the South Coast of ENGLAND.
|
||||||||
 |
Deal Castle, Deal, Kent, ENGLAND.
One of the most impressive of the Device Forts or Henrician Castles built by Henry VIII between 1539 and 1540 as an artillery fortress to counter the threat of invasion, brought about by the alliance between Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor and King Francis I of France in 1538. |
||||||||
 |
Schloss Hof (Hof Palace) Engelhartstetten (east of Vienna) Lower AUSTRIA.
Schloss Hof near the border of Slovakia. It once belonged to Prince Eugene of Savoy who purchased it in 1726, He had it enlarged in the Baroque style in 1729, and used it as an elaborate hunting lodge. He left it to a niece in his will, and it was later purchased by Empress Maria Theresa of Austria and became part of the imperial estates. |
||||||||
 |
Château de Puilaurens Lapradelle-Puilaurens, Aude département, Laguedoc-Roussillon
The Château de Puilaurens (also Puylaurens; in Occitan: lo Castèl de Puèg-Laurenç) is one of the so-called Cathar castles in what is now the South of France.
The castle stands on a spur of rock above the Boulzane Valley and the villages of Lapradelle and Puilaurens.
from an unusual angle |
||||||||
 |
Bolsover Castle Bolsover, Derbyshire, ENGLAND
.Bolsover Castle was founded in the 12th century by the Peverel family, who also owned Peveril Castle in Derbyshire. The site is now in the care of English Heritage and is a Grade I listed building and a Scheduled Ancient Monument. |
||||||||
 |
Ceramic poppies at the Tower of London, 2014.
Installation “Blood Swept Lands and Seas of Red”, marking the centenary of the outbreak of the First World War. Created by ceramic artist Paul Cummins, with setting by stage designer Tom Piper, 888,246 ceramic poppies progressively fill the Tower’s moat, each poppy representing a British fatality during the First World War. |
||||||||
 |
|||||||||
 |
Kimbolton Castle Kimbolton, Huntingdonshire district of Cambridgeshire, Engtland
Kimbolton Castle is best known as the final home of King Henry VIII's first queen, Catherine of Aragon. Catherine was sent here in April 1534 for refusing to give up her status or deny the validity of her marriage. The fenland climate damaged her health, and she died here in January 1536. Her body was taken and buried in Peterborough Abbey (now Peterborough Cathedral).
Originally a medieval castle it was converted into a stately palace, it was the family seat of the Dukes of Manchester from 1615 until 1950. It now houses Kimbolton School. |
||||||||
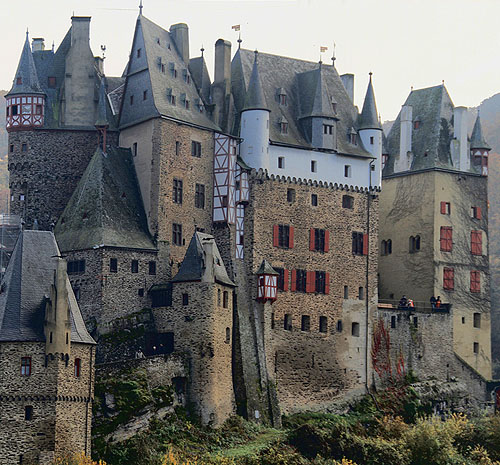 |
Eltz Castle (Burg Eltz) a medieval castle in the hills above the Moselle River between Koblenz and Trier, GERMANY.
The Eltz family lived there in the 12th century, 33 generations ago, and still does. About 100 members of the owners’ families lived in the over 100 rooms of the castle. It is a Ganerbenburg, or castle belonging to a community of joint heirs. It is divided into several parts, which belong to different branches of a family. In the case of Eltz, the family comprised three branches and the existing castle comprises three separate complexes of buildings The Rübenach and Rodendorf families’ homes in the castle are now open to the public, while the Kempenich branch of the family uses the other third of the castle. The main part of the castle consists of the family portions with up to eight stories and with eight towers reaching heights of between 30 and 40 meters.
This is as close as reality gets to Mervyn Peake’s Gormenghast |
||||||||
 |
Castle Bürresheim (Schloss Bürresheim),
The castle consists of buildings constructed between the twelfth and the seventeenth century. Almost all of it is original, including the twelfth century keep, which is the oldest part. The castle was never taken or raised or slighted (unlike almost all other Rhine castles).
It featured in the film Indiana Jones and the Last Crusade, in which it was called Brunwald Castle |
||||||||
 |
Niederfalkenstein (Falkenstein Castle) Pfaffenberg 19, 9821 Obervellach, Carinthia,
Niederfalkenstein is a castle complex near on the southern slope of the Hohe Tauern mountain range.
The fortification was first mentioned as Valchenstain Castle in a deed of 1164. The former fortification of Oberfalkenstein is a ruin, while the lower barbican of Niederfalkenstein is preserved. Niederfalkenstein is situated at an altitude of 843 meters.. |
||||||||
 |
Alcazar Segovia, SPAIN.
The Alcázar of Segovia (literally, The Castle of Segovia) is a stone fortification, rising out on a rocky crag above the confluence of the rivers Eresma and Clamores near the Guadarrama mountains.
It is one of the most distinctive castle-palaces in Spain, shaped like the bow of a ship. (The photo shows only part of it)
The Alcázar of Segovia, like many fortifications in Spain, started off as an Arab fort, which itself was built on a Roman fort but little of that structure remains. It has served as a royal palace, a state prison, a Royal Artillery College and a military academy since Moorish times. |
||||||||
 |
The Château de Mauvezin Mauvezin, Gers, Hautes-Pyrénées
The site, occupied since prehistory, was transformed into a castrum in the Middle Ages and later into a castle with a square plan. The present castle was built around 1380, by the great Gaston Phoebus, Count of Foix and Viscount of Béarn,.
Foix along with Bigorre were absorbed into the Kingdom of France in 1607, after which the Count's castle fell into disuse. It was dismantled its stones being used for other buildings.
Today, the castle is being restored. It is listed as a monument historique by the French Ministry of Culture. |
||||||||
 |
The Hall Christ Church College Oxford, ENGLAND.
The Hall is a vestige of the main room in castles and other great medieval buildings (such as Westminster Hall). All traditional Oxford and Cambridge Colleges have them - the colleges have retained the tradition of everyone eating together, as have the Inns of Court and many public (ie private) schools. Such halls are often now called Great Halls or Dining Halls since the idea of a hall has changed to no more than an entrance or vestibule. ("Refectories" are for monasteries and aspirational modern institutions)
The tables here have individual seats rather than the traditional benches. Until recently, before Health and Safety moved in, it was normal practice for undergraduates to walk over the tables to get to their benches on the other side of the table. You can just see the High Table at the far end.
Christ Church College is usually called just Christ Church, or for those in the know "The House". It was originally called Cardinal's College after its founder Cardinal Wolsey. It still bears his arms. It has a certain prestige - it was re-founded by Henry VIII, it has produced 13 British Prime Ministers and its chapel is a cathedral.
The hall here was used as a model for the hall at Hogwarts in the Harry Potter films. The college is the setting for parts of Evelyn Waugh's Brideshead Revisited, as well as part of Lewis Carroll's Alice's Adventures in Wonderland, and also the film adaptation of Philip Pullman's novel Northern Lights. |
||||||||
 |
The Veste Coburg, or Coburg Fortress, on a hill above the city of Coburg, Bavaria, GERMANY.
Veste Coburg (also called the "Franconian Crown" )is one of GERMANY's largest castles. It dominates the town of Coburg on Bavaria's border with Thuringia. The Veste Coburg was the historical seat of the independent duchy of Coburg in Franconia, now part of the German state of Bavaria. Martin Luther lived in the Veste for a number of months during the Diet of Augsburg in 1530.
In the twentieth century, the castle was the residence of Charles Edward, Duke of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha, a grandson of Queen Victoria, who was also (until 1919) the 2nd Duke of Albany in the United Kingdom. |
||||||||
 |
Inchdrewer Castle Banff, Aberdeenshire, SCOTLAND.
Inchdrewer Castle is a 16th-century tower house in the northeast of Scotland. Originally owned by the Currour family, it was purchased by the Ogilvies of Dunlugas in 1557 and became their main family seat. It became uninhabited after 1836 and the structure deteriorated. It is a category A listed building. The former model Olga Roh bought it in 2014 intending to restore it. |
||||||||
 |
The Evenburg Loga (or Leer), Lower Saxony, GERMANY.
The Evenburg is a water castle not far from the River Leda. In 1861/62, the building was rebuilt in the Neo-Gothic style.
After recent extensive renovation work the Evenburg is now home to various institutions including the Education Academy of East Frisia and a college for grammar school teachers. |
||||||||
 |
Château des Allymes Les Allymes, Ambérieu-en-Bugey, Ain, Rhône-Alpes
The Château des Allymes is a thirteenth-century castle, rebuilt in the sixteenth century and restored in the nineteenth. It was built around 1310, overlooking the plain of Ain from a height of some 800 m, It is a typical medieval stone castle — a large stronghold, built with a commanding the plain below. The quadrangular enclosure of the castle is flanked by a large cylindrical donjon of the Roman type and by a round tower, the two connected by four curtain walls. The exterior features a large wall 90 metres long terminating in a lookout tower that once protected an adjoining town.
The Château des Allymes became French by the Treaty of Lyon in 1601 when King Henri IV attached Bugey to the Kingdom of France. At the time it was in a strategic military position as it was near the border with Savoy, then an independent state.
In 1960 the Château des Allymes was classed a monument historique. The roof and frame of the round tower were restored in 1977, the four curtain walls in 1984 and the barbican at the main entrance in 1991. |
||||||||
 |
Châteaux de La Roche-Guyon La Roche-Guyon, Val-d'Oise, Île-de-France
The original château fort was built on the hill here in the 12th century, controlling a crossing of the Seine, and a route to Normandy. The donjon (keep) can still be seen at the top of the photo. In the mid-13th century, a fortified manor house (the château-bas) was added below.
The lord here, Guy de La Roche fell at the Battle of Agincourt, and his widow was ousted from the Roche, after six months of siege.
The Château-bas was largely extended in the 18th century. During the Second World War, it was used as German Field Marshal Erwin Rommel's headquarters. |
||||||||
 |
The Castle of Cardona, Cardona, Catalonia, SPAIN.
The Castle of Cardona (Catalan: Castell de Cardona) is a medieval fortress situated on a hill overlooking the valley of the Cardener river. A fortress was constructed here by Wilfred the Hairy in 886. The 11th century torre de la minyona is a tower measuring 15 metres in height and 10 in diameter. A Romanesque Church dedicated to Sant Vicenç de Cardona stands adjacent to the castle.
Today the castle is used as a parador, a state-run hotel. Because of its history, it has become significant to the Catalonian independence movement |
||||||||
 |
Château de Sully-sur-Loire Sully-sur-Loire, Loiret
The Château de Sully-sur-Loire is a a château-fort, a true castle, built to control one of the few sites where the Loire can be forded. It has been converted to a palatial seigneurial residence.
The Château was the seat of the ducs de Sully. In 1716 and again in 1719 the château offered refuge to Voltaire after he had been exiled from Paris for affronting the Régent, Philippe, duc d'Orléans.
The Château remained in the possession of the Sully family until 1962 when it became the property of the Département du Loiret. The Château de Sully-sur-Loire is listed as a monument historique by the French Ministry of Culture. |
||||||||
 |
Bouzov Castle between Hvozdek and Bouzov, Moravia, CZECH REPUBLIC.
Bouzov Castle (Czech: Hrad Bouzov) built on a hill is an early 14th-century fortress first mentioned in 1317. In 1558 the castle burned down. In 1696 the barony was bought by the Grand Master of the Teutonic Order. The Grand Master from 1799 to 1839, Archduke Eugen Habsburg, decided to rebuild it in a Romantic, Neo-Gothic style.
Today an eight-storey watchtower dominates the complex. The buildings are grouped around it in the form of a horseshoe. Two bridges, ending with a short drawbridge, span the deep dry moat around the castle. Since 1999 the castle has been a national monument. |
||||||||
 |
Le Château d'Ô Mortrée, Orne, Normandie
An eleventh century fortress stood here. A later castle was constructed by Robert VII d'Ô (who was killed at Agincourt in 1415), and refurbished over the subsequent centuries.
The château is built on an island in the centre of a lake. The site, rectangular in shape with two towers, contains a courtyard with an upper gallery. It was classified as a monument historique in stages between 1964 and 1973 |
||||||||
 |
The dining room set for a Regency-era dinner. Attingham Park near Atcham, Shropshire, ENGLAND.
Attingham Park is a Neoclassical country house and estate, finished in 1785. The Attingham Estate, comprising the mansion and some 650 acres, was gifted to the National Trust in 1947. The house is a Grade I listed building. Attingham Park is now the regional headquarters of the National Trust. |
||||||||
 |
Château de Chissay Place Paul Boncour, 41400 Chissay-en-Touraine, Loir-et-Cher
Situated between Montrichard and Chenonceaux, this former fortified castle was built under Charles the 7th for Pierre Bérard, chancellor of France. In 1543 Bérard sold the estate to the king's treasurer and superintendent of finance, for £16 690. The castle remained in the family, then passed into the hands of Duke of Choiseul until the eve of the revolution. Today it is an hotel. |
||||||||
 |
Longleat Warminster, Wiltshire BA12 7NW, ENGLAND.
Longleat is an English stately home and the seat of the Marquesses of Bath. It is noted for its Elizabethan country house, maze, landscaped parkland and safari park. The house is set in parkland landscaped by Capability Brown.
Longleat is occupied by Alexander Thynn, 7th Marquess of Bath. |
||||||||
 |
Longleat, Warminster, Wiltshire BA12 7NW, ENGLAND.
Longleat is an English stately home and the seat of the Marquesses of Bath. It is noted for its Elizabethan country house, maze, landscaped parkland and safari park. The house is set in parkland landscaped by Capability Brown.
Longleat is occupied by Alexander Thynn, 7th Marquess of Bath. |
||||||||
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|||||||||
 |
state room Windsor Castle, Windsor, Berkshire, ENGLAND
Windsor Castle is a royal residence notable for its long association with the English and later British royal family and also for its architecture. The original castle was built in the 11th century after the Norman invasion by William the Conqueror. Since the time of Henry I, it has been used by succeeding monarchs and is the longest-occupied palace in Europe. More than five hundred people live and work in Windsor Castle.
Originally designed to protect Norman dominance around the outskirts of London, and to oversee a strategically important part of the River Thames, Windsor Castle was built as a motte and bailey, with three wards surrounding a central mound. Gradually replaced with stone fortifications, the castle withstood a prolonged siege during the First Barons' War at the start of the 13th century. Henry III built a luxurious royal palace within the castle during the middle of the century, and Edward III went further, rebuilding the palace to produce an even grander set of buildings. Edward's core design lasted through the Tudor period, during which Henry VIII and Elizabeth I made increasing use of the castle as a royal court and centre for diplomatic entertainment. |
||||||||
 |
Lutsk High Castle, also known as Lubart's Castle Lutsk, Lutsk Raion, Volyn Oblastnorth western UKRAINE.
Lubart's Castle began its life in the mid-14th century as the fortified seat of Gediminas' son Liubartas (Lubart), the last ruler of united Galicia-Volhynia. It is the most prominent landmark of Lutsk, Ukraine and appears on the 200 hryvnia bill.
The current castle, towering over the Styr River, was built mostly in the 1340s, although some parts of the earlier walls were used. It repelled sieges by numerous potentates, Three main towers, named after Lubart, Švitrigaila and the Bishop, were built in the course of the 16th and 17th centuries.
The walls of the castle formerly enclosed St. John's Cathedral, the residence of the Grand Duke of Lithuania, and an episcopal palace. Of these buildings, only the Neoclassical palace of the bishops still stands. 1,160 Jews were murdered within the walls of the castle on July 2, 1941. |
||||||||
 |
Medieval Kitchen Gainsborough Old Hall Gainsborough, Lincolnshire, ENGLAND.
The hall was built by Sir Thomas Burgh in 1460. In 1484 Sir Thomas entertained King Richard III in his hall. King Henry VIII visited Gainsborough twice; once in 1509 and again in 1541 with the doomed Queen Catherine Howard. The Queen was accused of indiscretions both at Gainsborough and nearby Lincoln, for which she was executed.
The Old Hall has changed very little over the years. It is principally a timber framed building, giving it its characteristic 'striped' or 'black and white' appearance. On the north east corner is a brick tower. The Hall with its elaborate timber roof survives as well as the kitchen—possibly the most complete medieval kitchen in England. The kitchen still contains many original features, including two open fireplaces, each large enough to roast an ox, and two bread ovens served by a third chimney.
Unfortunately some philistine has built an ugly council estate right next to the Hall. The Hall is now owned by English Heritage and is open to the public as a museum. It is listed as Grade I for Heritage Protection. |
||||||||
 |
Kilchurn Castle Loch Awe, Argyll and Bute, SCOTLAND.
Kilchurn Castle is a ruined 15th and 17th century structure on a rocky peninsula at the northeastern end of Loch Awe Access to the Castle is sometimes restricted by higher-than-usual levels of water in the Loch, at which times the site becomes a temporary island.
It was the ancestral home of the Campbells of Glen Orchy, later Earls of Breadalbane - the Breadalbane family branch, of the Clan Campbell. |
||||||||
 |
Inveraray Castle near Inveraray, Argyll, western SCOTLAND.
Inveraray Castle is a country house on the shore of Loch Fyne, Scotland’s longest sea loch. It has been the seat of the Duke of Argyll, chief of Clan Campbell since the 17th century.
The house is a mostly mid-18th-century neo-Gothic design.
The 13th Duke and his family live in private apartments occupying two floors and set between two of the castle's crenellated circular towers.
Inveraray Castle is a Category A listed building. It is surrounded by a 16-acre garden and estate of 60,000 acres.
In 2012, part of the Christmas episode of Downton Abbey was filmed here; the castle stood in for the fictional "Duneagle Castle." |
||||||||
 |
Glamis Castle, situated beside the village of Glamis, in Angus, SCOTLAND.
It is the home of the Earl and Countess of Strathmore and Kinghorne, and is open to the public. It has been the home of the Lyon family since the 14th century, though the present building dates largely from the 17th century. Glamis was the childhood home of Queen Elizabeth The Queen Mother, wife of King George VI. Their second daughter, Princess Margaret, Countess of Snowdon, was born there.
The castle is protected as a category A listed building, and the grounds are included on the Inventory of Gardens and Designed Landscapes in Scotland, the national listing of significant gardens. |
||||||||
 |
Eilean Donan (Eilean Donnain) Dornie, Kyle of Lochalsh IV40 8DX, SCOTLAND
Eilean Donan is a castle and small tidal island where three lochs meet, Loch Duich, Loch Long and Loch Alsh, in the western Highlands of Scotland.
The castle was founded in the thirteenth century, and became a stronghold of the Clan Mackenzie and their allies the Clan Macrae.
Between 1919 and 1932 the castle was rebuilt by Lt. Col. John MacRae-Gilstrap. The restoration included the construction of an arched bridge to give easier access to the island.
|
||||||||
 |
Eilean Donan (Eilean Donnain) Dornie, Kyle of Lochalsh IV40 8DX, SCOTLAND
Eilean Donan is a castle and small tidal island where three lochs meet, Loch Duich, Loch Long and Loch Alsh, in the western Highlands of Scotland.
The castle was founded in the thirteenth century, and became a stronghold of the Clan Mackenzie and their allies the Clan Macrae.
Between 1919 and 1932 the castle was rebuilt by Lt. Col. John MacRae-Gilstrap. The restoration included the construction of an arched bridge to give easier access to the island.
|
||||||||
 |
Eilean Donan (Eilean Donnain) Dornie, Kyle of Lochalsh IV40 8DX, SCOTLAND
Eilean Donan is a castle and small tidal island where three lochs meet, Loch Duich, Loch Long and Loch Alsh, in the western Highlands of Scotland.
The castle was founded in the thirteenth century, and became a stronghold of the Clan Mackenzie and their allies the Clan Macrae.
Between 1919 and 1932 the castle was rebuilt by Lt. Col. John MacRae-Gilstrap. The restoration included the construction of an arched bridge to give easier access to the island.
|
||||||||
 |
Eilean Donan (Eilean Donnain) Dornie, Kyle of Lochalsh IV40 8DX, SCOTLAND
Eilean Donan is a castle and small tidal island where three lochs meet, Loch Duich, Loch Long and Loch Alsh, in the western Highlands of Scotland.
The castle was founded in the thirteenth century, and became a stronghold of the Clan Mackenzie and their allies the Clan Macrae.
Between 1919 and 1932 the castle was rebuilt by Lt. Col. John MacRae-Gilstrap. The restoration included the construction of an arched bridge to give easier access to the island. |
||||||||
 |
Eilean Donan (Eilean Donnain) Dornie, Kyle of Lochalsh IV40 8DX, SCOTLAND
Eilean Donan is a castle and small tidal island where three lochs meet, Loch Duich, Loch Long and Loch Alsh, in the western Highlands of Scotland.
The castle was founded in the thirteenth century, and became a stronghold of the Clan Mackenzie and their allies the Clan Macrae.
Between 1919 and 1932 the castle was rebuilt by Lt. Col. John MacRae-Gilstrap. The restoration included the construction of an arched bridge to give easier access to the island.
|
||||||||
 |
Dunrobin Castle north of Golspie, Highland area, SCOTLAND
Dunrobin Castle is a stately homeand the family seat of the Earl of Sutherland and the Clan Sutherlan, overlooking the Dornoch Firth .
During the Rising of 1745, Jacobites under Charles Edward Stuart stormed Dunrobin Castle without warning, because the Clan Sutherland supported the British government. The 17th Earl of Sutherland, who had changed his surname from Gordon to Sutherland, narrowly escaped them, leaving through a back door. He sailed for Aberdeen where he joined the Duke of Cumberland's army.
Dunrobin's origins lie in the Middle Ages, but most of the present building and the gardens was added by Sir Charles Barry between 1835 and 1850. Some of the original building is visible in the interior courtyard, despite a number of expansions and alterations. There are 189 rooms within the castle, making it the largest in the northern Highlands
It is now open to the public. Falconry displays are held in the castle's gardens by a resident Falconer. |
||||||||
 |
Burleigh Castle Perth and Kinross, SCOTLAND
The remains of Burleigh Castle are located just outside the village of Milnathort, 1.5 miles north of Kinross, and now sits beside the A911 road.
The castle dates from the 15th and 16th centuries. The remains of the castle comprise the western part of what was once a square courtyard or barmkin. In the north-west corner, the original tower house survives largely intact (though one of the first floor windows has been greatly enlarged) to three storeys and a garret in height. The 5-foot-thick (1.5 m) walls rise to corbels which once supported a parapet walk. The roof and internal floors are now gone, although the vaulted basement remains. The turnpike stair in the north-east corner originally led up to a caphouse giving access to the parapet walk.
To the south-west is a 16th-century corner tower, two storeys high above a basement, which retains its roof. The tower is round at the base, and corbelled out to a square upper storey, and is a particularly fine and picturesque example of Scottish baronial architecture of the period. The two surviving towers are connected by a section of curtain wall pierced by an arched gate. Though now only a 'skin' of masonry, this wall once fronted a two-storey gatehouse. With its string-course, hood-mould over the gateway and moulded surround formerly containing a heraldic panel, this wall is an excellent example of small-scale but refined architectural sophistication of its period in Scotland.
|
||||||||
 |
Kasteel van Wijnendale Wijnendale, Torhout, West Flanders, BELGIUM.
The present castle is largely a 19th-century reconstruction, but a part of the north wing is still 15th century.
One wing is inhabited by the present owners. Another wing is a museum, open to the public. |
||||||||
 |
Bamburgh Castle Bamburgh, Northumberland, ENGLAND.
Built on a dolerite outcrop, on the coast, the location was previously the site of a fort of the native Britons known as Din Guarie and may have been the capital of the local British kingdom from the realm's foundation in c.420 until 547. In that year the citadel was captured by the Anglo-Saxon ruler Ida of Bernicia (Beornice) and became Ida's seat. It was briefly retaken by the Britons from his son Hussa during the war of 590 before being relieved later the same year.
The Normans built a new castle on the site, which forms the core of the present one. William II unsuccessfully besieged it in 1095 during a revolt supported by its owner, Robert de Mowbray, Earl of Northumbria. After Robert was captured, his wife continued the defence until forced to surrender by the king's threat to blind her husband. Bamburgh then became the property of the reigning English monarch.
The castle now belongs to the Armstrong family, and is opened to the public. It has been used as a film location since the 1920s, featuring in films such as Ivanhoe (1952), El Cid (1961), Mary, Queen of Scots (1971), and Elizabeth (1998).It is a Grade I listed building. |
||||||||
 |
Stokesay Castle Shropshire, ENGLAND
Stokesay Castle is a fortified manor house built in the late 13th century by Laurence of Ludlow, then the leading wool merchant in England. Laurence's descendants continued to own the castle until the 16th century. By the time of the outbreak of the English Civil War in 1641, Stokesay was owned by William Craven, the first Earl of Craven and a supporter of King Charles I. After the Royalist war effort collapsed in 1645, Parliamentary forces besieged the castle in June and quickly forced its garrison to surrender. Parliament ordered the property to be slighted, but only minor damage was done to the walls, allowing Stokesay to continue to be used as a house by the Baldwyn family until the end of the 17th century.
Architecturally, Stokesay Castle is one of the best-preserved medieval fortified manor houses in England. The castle comprises a walled, moated enclosure, with an entrance way through a 17th-century timber and plaster gatehouse. Inside, the courtyard faces a stone hall and solar block, protected by two stone towers. The hall features a 13th-century wooden-beamed ceiling, and 17th-century carved figures ornament the gatehouse and the solar. The castle was never intended to be a serious military fortification, but its style was intended to echo the much larger castles being built by Edward I in North Wales. Originally designed as a prestigious home, the castle has changed very little since the 13th century, and is a rare example of a near complete set of medieval buildings. |
||||||||
 |
Château de Castanet Pourcharesses, Lozère
The territory of Castanet has its origin in the name (chestnut) in Occitan. It is the most common tree in the territory. The castle is next to the lake of Villefort, an artificial lake created behind a dam. |
||||||||
 |
Castell Conwy (Conway Castle), Conway, WALES
Conway Castle is a medieval fortification on the north coast of Wales. It was built by Edward I, during his conquest of Wales, between 1283 and 1289. Over the next few centuries, the castle played an important part in several wars. It withstood the siege of Madog ap Llywelyn in the winter of 1294–95, acted as a temporary haven for Richard II in 1399 and was held for several months by forces loyal to Owain Glyndwr in 1401.
Following the outbreak of the English Civil War in 1642, the castle was held by forces loyal to Charles I, holding out until 1646 when it surrendered to the Parliamentary armies. In the aftermath the castle was partially slighted by Parliament to prevent it being used in any further revolt, and was finally completely ruined in 1665 when its remaining iron and lead was stripped and sold off.
UNESCO considers Conwy to be one of "the finest examples of late 13th century and early 14th century military architecture in Europe", and it is classed as a World Heritage site.
The castle has the earliest surviving stone machicolations in Britain Like Edwardian castles in North Wales, the architecture of Conwy has close links to that found in the kingdom of Savoy during the same period, an influence probably derived from the Savoy origins of the main architect, James of Saint George. |
||||||||
 |
The Château de Biron Biron, Dordogne
The Château de Biron is a large castle in the valley of the Lède. This photograph shows just one small tower.
It was the castle from which the Gontaut-Biron took their name. It was their seat from the twelfth century. Biron was seized by Simon IV de Montfort in 1212 from forces sypathetic to the Cathars.
The Plantagenets held it at times during the 14th and 15th centuries. Biron was erected as a duché-pairie in 1598, for Charles de Gontaut, created duc de Biron.
The present château bears additions over the centuries: notably a twelfth-century keep and sixteenth-century living quarters and vaulted kitchens.
Since 1928, it has been listed as a monument historique by the French Ministry of Culture. The local commune purchased the Château de Biron in 1978, with a view to restoring it as a tourist attraction. |
||||||||
 |
The Angel Roof at Westminster Hall (looking East) |
||||||||
 |
Khiva City Walls Xorazm Province |
||||||||
 |
Highclere Castle Hampshire, ENGLAND,
Highclere Castle is a country house in the Jacobethan style, with a park designed by Capability Brown. It is the country seat of the Earl of Carnarvon, head of a branch of the Anglo-Welsh Herbert family.
Highclere Castle is the main filming location for the British television period drama Downton Abbey.
The Castle and gardens are open to the public during July and August and at times during the rest of the year. |
||||||||
 |
Saint-Nazaire-sur-Charente Charente-Maritime |
||||||||
 |
Ashdown House Oxford, ENGLAND |
||||||||
 |
Castel Nuovo, aka Maschio Angioino Naples, ITALY |
||||||||
 |
Dairsie Castle Dairsie, north-east Fife, SCOTLAND.
Dairsie Castle is a a restored tower house overlooking the River Eden. A Scottish parliament was held at the castle in early 1335.
The first castle built here was the property of the bishops of St Andrews, and was probably constructed by William de Lamberton, Bishop of St Andrews from 1298 to 1328. |
||||||||
|
|
|||||||||
 |
Preparations, state banquet in honor of Elizabeth II, 1957 Ajuda Palace, Ajuda, Lisbon.
Palácio Nacional da Ajuda (The Ajuda National Palace) is a neoclassical palace, built on the site of a temporory.wooden building constructed after the famous 1755 Lisbon earthquake. |
||||||||
 |
Neuschwanstein Castle Above the village of Hohenschwangau, Bavaria, Germany.
Neuschwanstein Castle (Schloss Neuschwanstein), is a nineteenth-century Romanesque Revival palace. It was commissioned by King Ludwig II of Bavaria as a retreat and as an homage to Richard Wagner. The palace was intended as a personal refuge but it was opened to the paying public immediately after his suspicious death in 1886. Since then more than 61 million people have visited Neuschwanstein Castle. The palace has appeared prominently in several movies and was the main inspiration for Disney’s Sleeping Beauty Castle. |
||||||||
 |
Fasanenschlösschen Schloßallee, 01468 Moritzburg, Saxony, GERMANY
The small château of Faisanderie (Fasanenschlößchen) is a pavillon in the parc of Schloss Moritzburg (Castle Moritzburg).
Moritzburg Castle is a Baroque palace in Moritzburg, in the German state of Saxony, about 13 kilometres (8.1 mi) Northwest of Dresden. |
||||||||
 |
Burg Hohenwerfen (Hohenwerfen Castle) above the town of Werfen, Salzach Valley
The castle is surrounded by the Berchtesgaden Alps. The fortification is a "sister" of Hohensalzburg Castle, both dating from the 11th century. A fortification was built here between 1075 and 1078 (during the Imperial Investiture Controversy) by Archbishop Gebhard of Salzburg as a strategic bulwark. He had three major castles extended to secure his archbishopric against the forces of King Henry IV. Gebhard was expelled in 1077 and could not return to Salzburg until 1086, only to die at Hohenwerfen two years later. In the following centuries Hohenwerfen served Salzburg's rulers, the prince-archbishops, as a military base, residence and hunting retreat. The fortress was extended in the 12th century and again in the 16th century during the German Peasants' War. Later it was used as a state prison and like many ecclesiastical prisons developed a particularly sinister reputation.
Hohenwerfen Castle served as the backdrop for the song "Do-Re-Mi" in the film The Sound of Music and as 'Schloss Adler' in the 1968 film Where Eagles Dare. Among the attractions offered by the fortress today are guided tours showing its weapons collection, a falconry museum and a fortress tavern. |
||||||||
 |
Château de Puymartin Marquay, Dordogne
The castle was built during the 13th century.
It is listed as a monument historique by the French Ministry of Culture. |
||||||||
 |
Stokesay Castle Shropshire, ENGLAND
Stokesay Castle is a fortified manor house built in the late 13th century by Laurence of Ludlow, then the leading wool merchant in England. Laurence's descendants continued to own the castle until the 16th century. By the time of the outbreak of the English Civil War in 1641, Stokesay was owned by William Craven, the first Earl of Craven and a supporter of King Charles I. After the Royalist war effort collapsed in 1645, Parliamentary forces besieged the castle in June and quickly forced its garrison to surrender. Parliament ordered the property to be slighted, but only minor damage was done to the walls, allowing Stokesay to continue to be used as a house by the Baldwyn family until the end of the 17th century.
Architecturally, Stokesay Castle is one of the best-preserved medieval fortified manor houses in England. The castle comprises a walled, moated enclosure, with an entrance way through a 17th-century timber and plaster gatehouse. Inside, the courtyard faces a stone hall and solar block, protected by two stone towers. The hall features a 13th-century wooden-beamed ceiling, and 17th-century carved figures ornament the gatehouse and the solar. The castle was never intended to be a serious military fortification, but its style was intended to echo the much larger castles being built by Edward I in North Wales. Originally designed as a prestigious home, the castle has changed very little since the 13th century, and is a rare example of a near complete set of medieval buildings. |
||||||||
 |
Gatehouse Stokesay Castle Shropshire, ENGLAND
Stokesay Castle is a fortified manor house built in the late 13th century by Laurence of Ludlow, then the leading wool merchant in England. Laurence's descendants continued to own the castle until the 16th century. By the time of the outbreak of the English Civil War in 1641, Stokesay was owned by William Craven, the first Earl of Craven and a supporter of King Charles I. After the Royalist war effort collapsed in 1645, Parliamentary forces besieged the castle in June and quickly forced its garrison to surrender. Parliament ordered the property to be slighted, but only minor damage was done to the walls, allowing Stokesay to continue to be used as a house by the Baldwyn family until the end of the 17th century.
Architecturally, Stokesay Castle is one of the best-preserved medieval fortified manor houses in England. The castle comprises a walled, moated enclosure, with an entrance way through a 17th-century timber and plaster gatehouse. Inside, the courtyard faces a stone hall and solar block, protected by two stone towers. The hall features a 13th-century wooden-beamed ceiling, and 17th-century carved figures ornament the gatehouse and the solar. The castle was never intended to be a serious military fortification, but its style was intended to echo the much larger castles being built by Edward I in North Wales. Originally designed as a prestigious home, the castle has changed very little since the 13th century, and is a rare example of a near complete set of medieval buildings. |
||||||||
 |
Tudor Bedroom Hever Castle Hever, Edenbridge, Kent TN8 7NG, ENGLAND.
Hever Castle began as a country house, built in the 13th century. From 1462 to 1539 it was the seat of the Bullen (later Boleyn family.
Anne Boleyn, the second queen consort of King Henry VIII , spent her early youth there, after her father, Thomas Boleyn had inherited it in 1505.
It later came into the possession of King Henry's fourth wife, Anne of Cleves.
The castle is now a major tourist attraction. |
||||||||
 |
Grand Palace Bangkok
The Grand Palace is a complex of buildings at the heart of Bangkok. The palace has been the official residence of the Kings of Siam (and later Thailand) since 1782. The king, his court and his royal government were based on the grounds of the palace until 1925. The present monarch, King Bhumibol Adulyadej (Rama IX), resides at Chitralada Palace, but the Grand Palace is still used for official events. |
||||||||
 |
Château de Vitré Vitré, Ille-et-Vilaine |
||||||||
 |
Château Boisset-les-Prévanches Boisset-les-Prévanches, Eure, Haute-Normandie |
||||||||
 |
Cervená Lhota 20 km north-west of Jindrichuv Hradec, south Bohemia, CZECH REPUBLIC
Cervená Lhota is a water castle. It stands in the middle of a lake on a rocky island. The four-winged two-storey château, with a small coutyard in the center, occupies the whole rock and juts into the lake. A stone bridge, built in 1622, links the castle with the banks of the pond, replacing the original drawbridge. |
||||||||
 |
Interior view of the dome Emam (Shah abbasi) Mosque Isfahan
The mosque was built during the Safavid period, ordered by the first Shah Abbas of Persia. It is regarded as an excellent example of Islamic era architecture of Iran. It is registered, along with the Naghsh-e Jahan Square, as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Its construction began in 1611, and its splendor is mainly due to the beauty of its seven-colour mosaic tiles and calligraphic inscriptions. |
||||||||
 |
Lismore Castle Lismore, County Waterford, Ireland
Lismore Castle is a stately home belonging to the Dukes of Devonshire. It was largely re-built in the Gothic style during the mid-nineteenth century by William Cavendish, 6th Duke of Devonshire.
The castle site was originally occupied by Lismore Abbey, established in the early 7th century. Henry II, King of England stayed here in 1171. After 1185 his son King John built a 'castellum' here, which served as the residence of the local bishop. In 1589, Lismore was leased to and later acquired by Sir Walter Raleigh. Raleigh sold the property during his imprisonment for High Treason in 1602 to another colonial adventurer, Richard Boyle, later 1st Earl of Cork. After purchasing Lismore Boyle made it his principal seat. It was here in 1627 that Robert Boyle The Father of Modern Chemistry, the fourteenth of the Earl's fifteen children, was born.
Lismore featured in the Cromwellian wars when, in 1645, a force of Catholic confederacy commanded by Lord Castlehaven sacked the town and Castle. Some restoration was carried out by Richard Boyle, 2nd Earl of Cork (1612-1698) to make it habitable again but neither he nor his successors lived at Lismore. The castle (along with other Boyle properties was acquired by the Cavendish family in 1753.
Lismore Castle was used as Northanger Abbey in the 2007 ITV dramatisation of that name during its Jane Austen season. |
||||||||
 |
Burg Hohenwerfen (Hohenwerfen Castle) above the town of Werfen, Salzach Valley
The castle is surrounded by the Berchtesgaden Alps. The fortification is a "sister" of Hohensalzburg Castle, both dating from the 11th century. A fortification was built here between 1075 and 1078 (during the Imperial Investiture Controversy) by Archbishop Gebhard of Salzburg as a strategic bulwark. He had three major castles extended to secure his archbishopric against the forces of King Henry IV. Gebhard was expelled in 1077 and could not return to Salzburg until 1086, only to die at Hohenwerfen two years later. In the following centuries Hohenwerfen served Salzburg's rulers, the prince-archbishops, as a military base, residence and hunting retreat. The fortress was extended in the 12th century and again in the 16th century during the German Peasants' War. Later it was used as a state prison and like many ecclesiastical prisons developed a particularly sinister reputation.
Hohenwerfen Castle served as the backdrop for the song "Do-Re-Mi" in the film The Sound of Music and as 'Schloss Adler' in the 1968 film Where Eagles Dare. Among the attractions offered by the fortress today are guided tours showing its weapons collection, a falconry museum and a fortress tavern. |
||||||||
 |
Tower ceiling Canterbury Cathedral, Canterbury, Kent, ENGLAND
Canterbury Cathedral is one of the oldest and most famous Christian structures in England and forms part of a World Heritage Site. It is the cathedral of the Archbishop of Canterbury, leader of the Church of England and symbolic leader of the worldwide Anglican Communion. |
||||||||
 |
Château fort de Couzan 15240 Vebret, Antignac, Cantal, Auvergne
15th Century. Privately owned. Inscrit on the inventaire supplémentaire des Monuments Historiques since 1994. |
||||||||
 |
The Hospices de Beaune or Hôtel-Dieu de Beaune Beaune, Burgundy
The Hôtel-Dieu de Beaune is a former charitable almshouse founded in 1443 by Nicolas Rolin, chancellor of Burgundy, as a hospital for the poor. The original hospital building, one of the finest surviving examples of Burgundian fifteenth-century architecture, is now a museum. |
||||||||
 |
Windsor Castle, Windsor, Berkshire, ENGLAND
Windsor Castle is a royal residence notable for its long association with the English and later British royal family and also for its architecture. The original castle was built in the 11th century after the Norman invasion by William the Conqueror. Since the time of Henry I, it has been used by succeeding monarchs and is the longest-occupied palace in Europe. More than five hundred people live and work in Windsor Castle.
Originally designed to protect Norman dominance around the outskirts of London, and to oversee a strategically important part of the River Thames, Windsor Castle was built as a motte and bailey, with three wards surrounding a central mound. Gradually replaced with stone fortifications, the castle withstood a prolonged siege during the First Barons' War at the start of the 13th century. Henry III built a luxurious royal palace within the castle during the middle of the century, and Edward III went further, rebuilding the palace to produce an even grander set of buildings. Edward's core design lasted through the Tudor period, during which Henry VIII and Elizabeth I made increasing use of the castle as a royal court and centre for diplomatic entertainment. |
||||||||
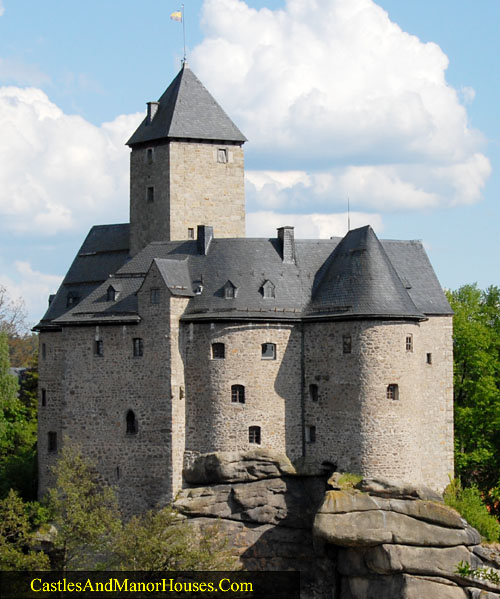 |
Falkenberg Castle (Burg Falkenberg) Falkenberg (district of Tirschenreuth), Upper Palatinate, Bavaria, Germany.
The castle walls have foundations dating back to the eleventh century. It was mentioned for the first time in 1154.
In 1803 it was acquired by the Crown of Bavaria. |
||||||||
 |
Château d'Ainay-le-Vieil Ainay-le-Vieil, Cher
Built in the 14th century, this moated castle has been listed as a Monument historique since 1968 by the French Ministry of Culture. |
||||||||
 |
The Red Castle (Castell Coch) situated on a hillside above the village of Tongwynlais, to the north of Cardiff, WALES
Castell Coch is a 19th-century Gothic Revival castle built on the remains of a 13th-century fortification. It is a Grade I listed building
Designed by William Burges, it has a superficially medieval appearance, working portcullis and drawbridge. Its sumptuous interiors rival those of nearby Cardiff Castle |
||||||||
 |
Peyrepertuse is a ruined fortress and one of the Cathar castles of the Languedoc located in the French Pyrénées in the commune of Duilhac-sous-Peyrepertuse, in the Aude département.
The castle ruins are impressive, set high on a defensive crag. From the approach road it is difficult to see where the rock stops and the castle starts. The castle was built in the 11th century on a site dominating the Corbières and the sea. The main part, resembles the prow of a ship, running along the top of an 800m (2,600 ft) high crag. It houses the church of Sainte-Marie and the governor’s residence.
The castle was associated with the Counts of Barcelona, later kings of Aragon. The name Peyrepetuse is derived from Pèirapertusa, Occitan, meaning Pierced Rock. The lower part of the castle was built on a strategic location by the kings of Aragon in the 11th Century and the higher part by the French King Louis IX later on, after the area was annexed to France. The two castles are linked together by a staircase. The castle lost importance as a strategic castle when the border between France and Spain was moved in 1659, causing the castle to be abandoned.
It was never subjected to attack during the Crusade against the Cathars. Nevertheless, it was surrendered to the French Crusaders 22nd of May 1217, reclaimed again as the balance of power changed. Guilhem de Peyrepertuse, was excommunicated in 1224 because of his refusal to submit to the Catholic Crusaders. He surrendered after the siege of Carcassonne (the Viscount of Carcassonne, Guilhem’s suzerain, having failed to retake Carcassonne from the French invaders in 1240). Peyrepertuse became a French possession the same year. In 1258, the Treaty of Corbeil defined the border between France and Aragon for four centuries : Peyrepertuse became a royal French fortress at the southern border of the French kingdom. At the end of the 13th century, it was a powerful stronghold with strong defences. |
||||||||
 |
Montségur is a castle in the foothills of the Pyrenees, not far from Lavelanet, due South from Mirepoix in the Ariege, FRANCE
Some 225 Cathars were burned alive at the Château de Montsegur in 1244 for the crime of not being Catholic. A Garrison of around 200 had defended them for 10 months against a French Crusader army of 5,000 - 10,000 before they surrendered. A monument on the site reads
EN CE LIEU LE 16 MARS 1244
IN THIS PLACE ON 16th MARCH 1244
There were so many victims that a special wooden pen had to be constructed, filled with heaps of brushwood, to burn them. A clerical chronicler preened that they passed directly from the flames of this world to the flames on the next. |
||||||||
 |
Fontfroide Abbey 15 kilometers south-west of Narbonne, Aude
Fontfroide Abbey or l’Abbaye Sainte-Marie de Fontfroide is a former Cistercian monastery founded in 1093 by the Viscount of Narbonne. It remained poor and obscure until 1144 when it affiliated itself to the Cistercian reform movement. Shortly afterwards the Count of Barcelona gave it the land in Spain that was to form the great Catalan monastery of Poblet, of which Fontfroide was the mother house. In 1157 the Viscountess Ermengard of Narbonne granted it a great stretches of land locally, securing its wealth and status.
This abbey was the Cistercian centre of operations during the Albigensian Crusade - the 13th Century war against the Cathars of the Languedoc. It was dissolved in 1791 in the course of the French Revolution. |
||||||||
 |
Cité Carcassonne, Languedoc
The largest surviving medieval walled city in Europe. Inside is the Château Comtal, the Castle of Raymond Roger Trencavel, Viscount of Carcassonne, Béziers, Albi and the Razès. He died in his own prison here in 1209, aged 24, after being taken prisoner while under a safe-conduct from the Cistercian Abbot Arnaud Amaury the papal legate and military leader of the Albigensian Crusade who was besieging Carcassonne (and who then appointed Simon de Montfort as military leader of the crusade). |
||||||||
 |
Quéribus Cucugnan, Aude, Languedoc
The castle of Quéribus is high and isolated. It stands on top of the highest peak for miles around. From a distance it can be seen on the horizon, sticking up into the sky. Quéribus is sometimes regarded as the last Cathar stronghold. In a sense it was. After the fall of the Château of Montségur in 1244 surviving Cathars gathered together in the Corbières at this mountain-top stronghold on the border of Aragon (The present border between the Aude département and the Pyrénées-Orientales département). The Cathar deacon of the Razès, Benoît de Termes, took refuge here under Chabert de Barbaira, who was finally forced to surrender to Saint-Louis in 1255. The last stronghold to fall, eleven years after the fall of Montségur, Quéribus then became part of the French frontier defence system against Aragon.
This is one of the “Five Sons of Carcassonne”, along with Termes, Aguilar, Peyrepertuse and Puilaurens: five castles strategically placed to defend the new French border against the Spanish. It lost all strategic importance after the Treaty of the Pyrenees in 1659 when the border was moved even further south to its present position along the crest of the Pyrenees. |
||||||||
 |
The Aude Gate, Cité, Carcassonne, Languedoc
Just inside this gate was the thirteenth century house of the Dominican Inquisitors - there’s a plaque on the house. Outside the gate was the “Wall” the Inquisitors’ prison where people were imprisoned in dark, cold, damp conditions, chained up and without sanitation, living on stale bread and filthy water, often until they died.
Carcassonne is the largest surviving medieval walled city in Europe. Inside is the Château Comtal, the Castle of Raymond Roger Trencavel, Viscount of Carcassonne, Béziers, Albi and the Razès. He died in his own prison here in 1209, aged 24, after being taken prisoner while under a safe-conduct from the Cistercian Abbot Arnaud Amaury the papal legate and military leader of the Albigensian Crusade who was besieging Carcassonne (and who then appointed Simon de Montfort as military leader of the crusade). |
||||||||
|
|
|||||||||
 |
The Château de Foix Foix, Ariège
Built on an older 7th-century fortification, the castle is known from 987. In 1002, it was mentioned in the will of Roger I, Count of Carcassonne, who bequeathed it to his youngest child. The branch family ruling over the region, the Counts of Foix, lived here.
During the two following centuries, the castle was home to the Counts of Foix who were central to the Occitan resistance during the crusade against the Albigensians. The county became a refuge for persecuted Cathars. The castle was often besieged (notably by Simon de Montfort in 1211 and 1212).
It has been listed since 1840 as a monument historique by the French Ministry of Culture. |
||||||||
 |
Châteaux de Lastours Lastours, Aude, Languedoc
Lastours (Occitan: Las Tors = Les Tours = The towers) is an unusual arrangement of three castle towers (now four). The original castles belonged to the Lords of Cabaret, who held them in fief from the Trencavels. They received troubadours here, including Raymond de Miraval and Peire Vidal, who dedicated verses to the Cathar Ladies of the place.
During the Cathar Crusade this was one of the most ardent centres of resistance to the French Crusaders, |
||||||||
 |
Quéribus Cucugnan, Aude, Languedoc
The castle of Quéribus is high and isolated. It stands on top of the highest peak for miles around. From a distance it can be seen on the horizon, sticking up into the sky. Quéribus is sometimes regarded as the last Cathar stronghold. In a sense it was. After the fall of the Château of Montségur in 1244 surviving Cathars gathered together in the Corbières at this mountain-top stronghold on the border of Aragon (The present border between the Aude département and the Pyrénées-Orientales département). The Cathar deacon of the Razès, Benoît de Termes, took refuge here under Chabert de Barbaira, who was finally forced to surrender to Saint-Louis in 1255. The last stronghold to fall, eleven years after the fall of Montségur, Quéribus then became part of the French frontier defence system against Aragon.
This is one of the “Five Sons of Carcassonne”, along with Termes, Aguilar, Peyrepertuse and Puilaurens: five castles strategically placed to defend the new French border against the Spanish. It lost all strategic importance after the Treaty of the Pyrenees in 1659 when the border was moved even further south to its present position along the crest of the Pyrenees. |
||||||||
 |
Château de Saissac Saissac, Aude département, Languedoc
The Château de Saissac is a ruined Cathar Castle on a promontory at the southernmost tip of the commune of Saissac, north-west of Carcassonne. Saissac is mentioned in a legal document from the Abbey of Montolieu in 958, and again in a text of 960. The village is typical of the Black Mountains and is built between the ravines of the rivers Aiguebelle and Vernassonne, just above their confluence, overlooking the plain of Carcassonne at an important strategic position at the entry of the Black Mountains (Montagnes Noires). Vestiges of the fourteenth century city walls (enceinte) are still visible around the ancient village. |
||||||||
 |
Trencavel seal reproduced on the exterior wall of the Church of Saint Mary Magdalene, Béziers, Aude, Languedoc
In 1209, at the bidding of Pope Innocent III, a crusader army from France made its way down the Rhône Valley to the Languedoc. Its purpose was to exterminate a the Cathars. The Crusaders’ first major engagement, on 24 July 1209, was the siege of the town of Béziers, a county capital of Raymond Roger Trencavel, Viscount of Carcassonne and Béziers. The Crusader army was led by a papal legate, Arnaud Amaury, Abbot of Cîteaux. Arnaud was asked how the crusaders should distinguish Cathars from Catholics, in order to spare Catholics. He allegedly gave the reply “Kill them all. God will Know His Own”. According to a number of sources, all the citizens of Béziers, Cathars and Catholics alike, were then massacred by the crusader army.
Nothing remains of the Viscount’s castle here, nor the city walls, but the Cathedral and the Church of Saint Mary Magdalene still stand. Some 7000 people - men, women and children - were killed inside the church by Arnaud’s crusaders. |
||||||||
 |
|||||||||
 |
Château de Vendeuvre Vendeuvre, near to Lisieux in Normandy
The Château de Vendeuvre is a typical aristocratic Norman country house. It was built between 1750 and 1752. The château is famous for its eighteenth-century interiors. Formal gardens have been created by the present Count of Vendeuvre with a strictly symmetrical classical lay-out. The gardens contain two mazes, known as the ‘regular maze’ and the ‘field maze’.
An Ice House here was built as a pyramid, to store winter ice for use in the summer. It has a north-facing door to better help preserve the low temperature within. The Château de Vendeuvre is classed as an Historic Monument both for its exterior and interior. It was opened to the public in 1983. |
||||||||
 |
Schloss Hohenzollern (Hohenzollern Castle) 72379 Burg Hohenzollern, GERMANY
Hohenzollern Castle is the ancestral seat of the Hohenzollern family, who became German Emperors
A castle was first constructed here in the early 11th century. The present castle was constructed for King Frederick William IV of Prussia between 1846 and 1867. The design was based on English Gothic Revival architecture and the Châteaux of the Loire Valley.
In 1945 it became home to the former Crown Prince Wilhelm of GERMANY, son of the last Hohenzollern monarch, Kaiser Wilhelm II, who is buried there with his wife, Crown Princess Cecilie |
||||||||
 |
Château de Chenonceau Chenonceau, Indre-et-Loire
The estate of Chenonceau is first mentioned in writing in the 11th century. The current château was built in 1514–1522 on the foundations of an old mill and was later extended to span the river.
The bridge over the river was built (1556-1559) to designs by the French Renaissance architect Philibert de l'Orme, and the gallery on the bridge (1570–1576) to designs by Jean Bullant
The château has been classified as a Monument historique since 1840 by the French Ministry of Culture. It is one of the most famous Loire Valley châteaux. |
||||||||
 |
Château de Azay-le-Rideau Azay-le-Rideau, Chinon, Indre-et-Loire, Centre |
||||||||
 |
Le château Pichon Parempuyre, Gironde, Aquitaine
Le château Pichon was built in 1881 in a neo-rrenaissance style combining various elements of the châteaux de la Loire. It was inscribed in the list of monuments historiques in 2000. |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|||||||||
| :::: Link to us :::: Castle and Manor Houses Resources ::: © C&MH 2010-2014 ::: contact@castlesandmanorhouses.com ::: Advertising ::: |